Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction
- Brief about tropical cyclones.
Body
- Discuss the importance of geographic limitation.
Conclusion
- Conclude your answer with significant tropical cyclones.
|
Introduction:
Tropical cyclones, also known as hurricanes or typhoons, are severe weather events that can cause devastating damage to coastal communities. These storms are largely confined to specific regions of the world, including the South China Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Gulf of Mexico.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Body:
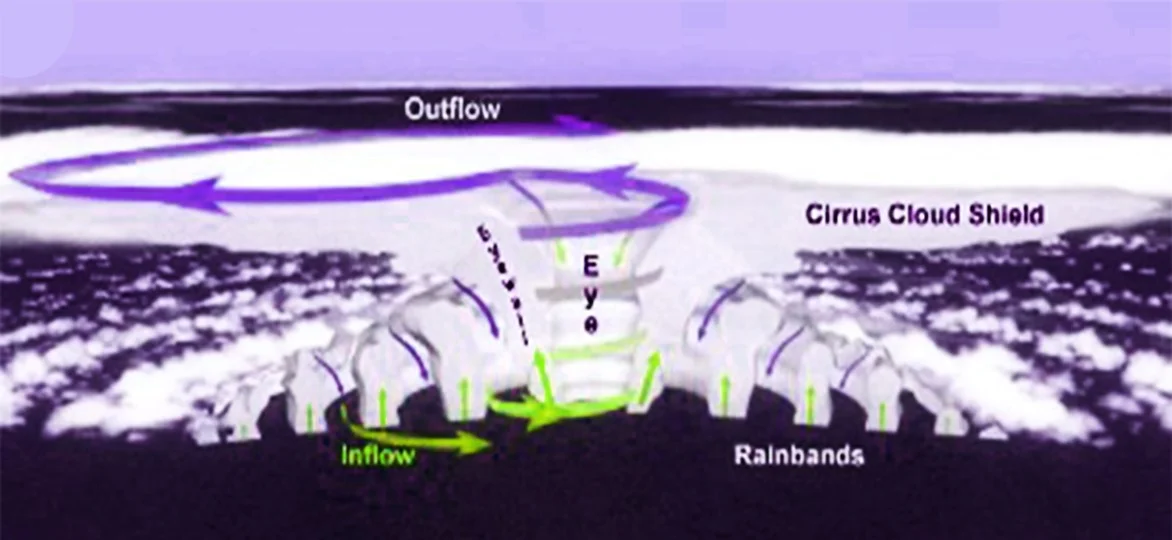
Important of geographic limitation:
- Warm sea surface temperature [SST]: Tropical cyclones require warm ocean waters of at least 26.5°C to develop and strengthen. The South China Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Gulf of Mexico have warm sea surface temperatures throughout the year, making them ideal regions for the formation and strengthening of tropical cyclones.
- Coriolis force: The Coriolis force is a result of the Earth’s rotation and causes the air to circulate around low-pressure systems, such as tropical cyclones. The Coriolis force is stronger near the poles and weaker near the equator. The circulation of air around a low-pressure system is weaker in the tropics, limiting the development of tropical cyclones.
- Low vertical wind shear: Vertical wind shear refers to the change in wind speed and direction with height. High vertical wind shear can inhibit the development of tropical cyclones. The South China Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Gulf of Mexico have relatively low vertical wind shear, which allows tropical cyclones to develop and strengthen.
- Monsoonal winds: The monsoon winds in the Bay of Bengal and the South China Sea are characterized by seasonal changes in direction and strength. These winds create favorable conditions for the formation and strengthening of tropical cyclones during the summer and fall seasons.
- Bathymetry: The shape and depth of the ocean floor can also influence the development of tropical cyclones. The Bay of Bengal and South China Sea have shallow coastal waters, which allow for greater mixing of the ocean water and a more favorable environment for tropical cyclone formation.
Conclusion:
The geographic confinement of tropical cyclones to the South China Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Gulf of Mexico is due to a combination of factors, including warm ocean temperatures, favorable atmospheric conditions, and the specific geography of these regions. While these storms can cause significant damage, continued research and preparedness measures can help to minimize the impact on coastal communities.
