Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction
- Begin by defining Fixed Dose Drug Combinations (FDCs) and their intended purpose in the field of pharmaceuticals.
Body
- Discuss the primary advantages of FDCs.
- Shift the discussion to the disadvantages associated with FDCs.
- Provide examples to reinforce each point.
Conclusion
- Conclude with an overview of the implications of FDCs on patient care and public health.
|
Introduction:
Fixed Dose Drug Combinations (FDCs) are pharmaceutical products that combine two or more active drugs in a single dosage form. They are designed to improve patient compliance and efficacy of treatment. In recent years, various government health agencies worldwide have advocated for their use to address public health issues such as HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria.
Body:
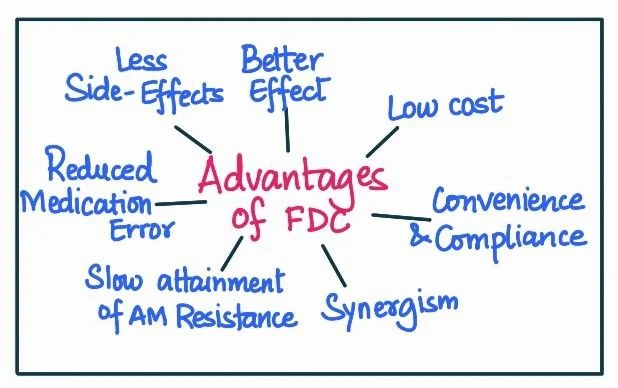
Merits of FDCs:
- Improved Compliance: FDCs simplify medication regimens, which can improve patient adherence to treatment schedules, especially in chronic illnesses.
- For example: HIV/AIDS treatments often use FDCs to enhance adherence.
- Synergistic Effects: Certain combinations can have synergistic effects, enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of the treatment.
- For instance, TB treatment often uses FDCs for this reason.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: FDCs can potentially lower costs by reducing the number of separate medications needed.
Demerits of FDCs:
- Risk of Side Effects: Combined drugs can increase the risk of adverse effects.
- For example, FDCs of painkillers and muscle relaxants can have side effects like gastric irritation and dizziness.
- Inappropriate Dosing: FDCs may result in inappropriate dosing as the dosage of individual drugs cannot be adjusted to individual patient needs.
- For example, FDCs for hypertension may not suit all patients equally.
- Resistance Development: In case of infectious diseases, incorrect use of FDCs can lead to drug resistance.
- For instance, Overuse of antibiotic FDCs has been linked to antibiotic resistance in India.
Conclusion:
While FDCs offer significant benefits, their use must be carefully managed to mitigate potential risks. Regulatory oversight is essential to ensure that FDCs are safe, effective, and necessary. In the Indian context, rational use of FDCs is important to tackle the dual burden of communicable and non-communicable diseases.
