![]() Madhavi Gaur
Madhavi Gaur
![]() September 05, 2023 06:34
September 05, 2023 06:34
![]() 34758
34758
![]() 1
1
Explore the complete list of 75 Ramsar Sites in India, showcasing the nation's dedication to preserving its precious wetland ecosystems. Discover the diverse ecological treasures and their significance in India's conservation efforts.
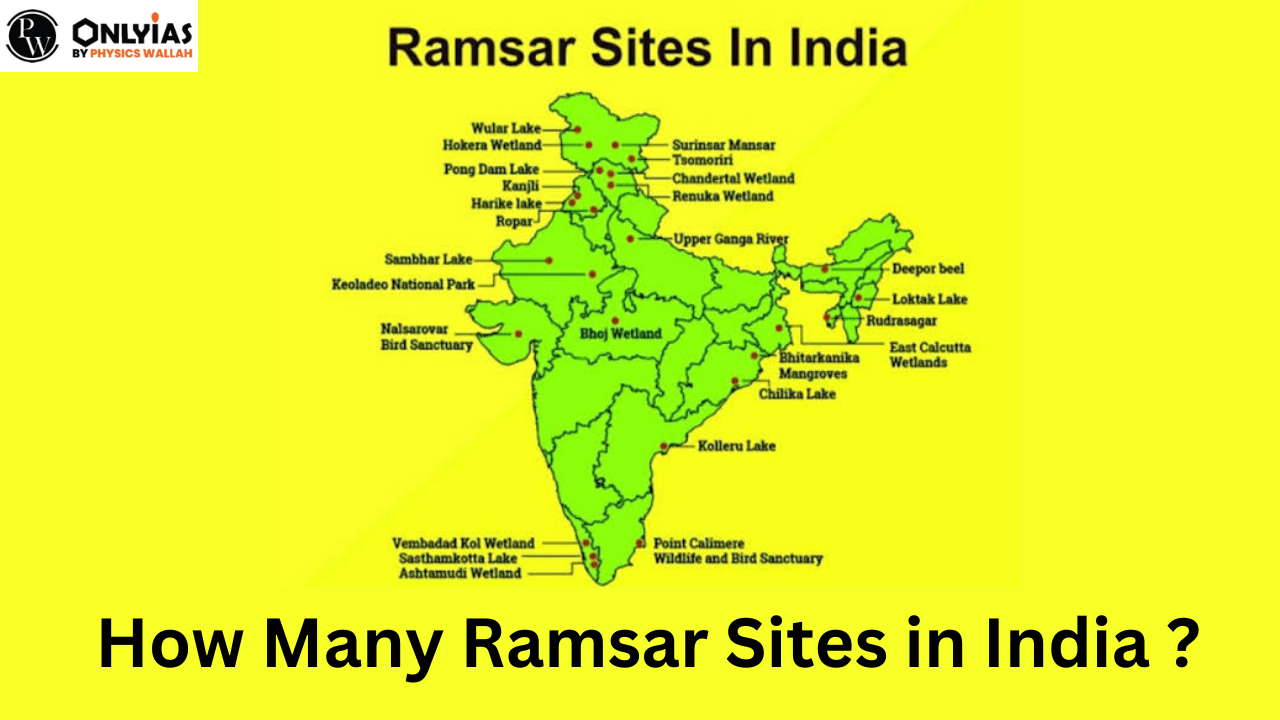
India’s Ramsar Sites, designated wetlands of global importance, have seen significant growth. The nation boasts a total of 75 Ramsar Sites, collectively covering an expansive 13,26,677 hectares. This expansion coincides with India’s 75th year of Independence, marking a crucial step in wetland conservation.
India became a signatory to the Ramsar Convention on February 1, 1982, following the convention’s initial establishment in Ramsar, Iran, in 1971. Over the years, the number of Ramsar Sites in India has steadily increased. From 1982 to 2013, 26 sites were designated. However, a notable surge occurred between 2014 and 2022 when an additional 49 wetlands earned Ramsar status. In 2022 alone, India added 28 new sites.
Among the Indian states, Tamil Nadu leads with 14 Ramsar Sites, followed closely by Uttar Pradesh with 10. This significant expansion underscores India’s commitment to preserving its wetlands, essential for biodiversity conservation and maintaining the health of ecosystems.
Ramsar Sites, also known as Wetlands of International Importance, are designated areas under the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands. The Ramsar Convention is an international treaty established in 1971 in Ramsar, Iran, with the aim of conserving and wisely using wetlands.
A wetland is defined by the Ramsar Convention as “areas of marsh, fen, peatland or water, whether natural or artificial, permanent or temporary, with water that is static or flowing, fresh, brackish, or salt, including areas of marine water, the depth of which at low tide does not exceed six meters.”
The primary goal of designating a site as a Ramsar Site is to promote the conservation and sustainable use of wetlands, recognizing their ecological importance. Wetlands provide numerous valuable ecosystem services, such as water purification, flood control, carbon storage, and habitat for a wide variety of plants and wildlife, including many threatened and endangered species.
Countries that are parties to the Ramsar Convention can nominate wetland sites within their territories for inclusion in the List of Wetlands of International Importance. To be designated as a Ramsar Site, a wetland must meet specific criteria related to its ecological, botanical, zoological, limnological, or hydrological features. Once a site is listed as a Ramsar Site, the respective country is expected to implement measures for its protection, management, and wise use.
There are 75 Ramsar sites in India. The table below contains the list that is about the Number of Ramsar Sites in India, as well as their names and Location:
| List of Ramsar sites in India | ||
|---|---|---|
| S.No. | Name of the Ramsar Sites in India | State – Location |
| 1 | Chilika Lake | Odisha |
| 2 | Keoladeo National Park | Bharatpur Rajasthan |
| 3 | Harike Wetland | Harike, Punjab |
| 4 | Loktak Lake | Bishnupur, Manipur |
| 5 | Sambhar Lake | Rajasthan |
| 6 | Wular Lake | Jammu and Kashmir |
| 7 | Kanjli Wetland | Kapurthala Punjab |
| 8 | Ropar Wetland | Ropar, Punjab |
| 9 | Ashtamudi Wetland | Kollam district, Kerala |
| 10 | Bhitarkanika Mangroves | Odisha India |
| 11 | Bhoj Wetland | Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh |
| 12 | Deepor Beel | Guwahati, Assam |
| 13 | East Kolkata Wetlands | Kolkata West Bengal |
| 14 | Kolleru Lake | Andhra Pradesh |
| 15 | Point Calimere Wildlife and Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 16 | Pong Dam Lake | Kangra, Himachal Pradesh |
| 17 | Sasthamkotta Lake | Kollam, Kerala |
| 18 | Tsomoriri | Ladakh |
| 19 | Vembanad-Kol Wetland | Kerala |
| 20 | Chandra Taal | Lahul, Himachal Pradesh |
| 21 | Hokera Wetland | Zainakote, Jammu and Kashmir |
| 22 | Renuka Lake | Simaur, Himachal Pradesh |
| 23 | Rudrasagar Lake | Melaghar, Tripura, India |
| 24 | Surinsar-Mansar Lakes | Jammu and Kashmir |
| 25 | Upper Ganga River (Brijghat to Narora Stretch) | Uttar Pradesh |
| 26 | Nalsarovar Bird Sanctuary | Ahmedabad, Gujarat |
| 27 | Sundarban Wetland | West Bengal |
| 28 | Nandur Madhameshwar | Nashik, Maharashtra |
| 29 | Nawabganj Bird Sanctuary | Unnao, Uttar Pradesh |
| 30 | Sarsai Nawar Jheel | Etawah, Uttar Pradesh |
| 31 | Beas Conservation Reserve | Harike Punjab |
| 32 | Keshopur-Miani Community Reserve | Punjab |
| 33 | Nangal Wildlife Sanctuary | Nangal, Punjab |
| 34 | Sandi Bird Sanctuary | Hardoi, Uttar Pradesh |
| 35 | Samaspur Bird Sanctuary | Uttar Pradesh |
| 36 | Parvati Aranga Bird Sanctuary | Gonda, Uttar Pradesh |
| 37 | Saman Bird Sanctuary | Mainpuri, Uttar Pradesh |
| 38 | Asan Barrage | Uttarakhand |
| 39 | Kanwar Taal or Kabar Taal Lake | Begusarai, Bihar |
| 40 | Sur Sarovar | Agra, Uttar Pradesh |
| 41 | Lonar Lake | Buldhana, Maharashtra |
| 42 | Tso Kar | Leh, Ladakh |
| 43 | Bhindawas Wildlife Sanctuary | Haryana |
| 44 | Sultanpur National Park | Haryana |
| 45 | Thol Lake Wildlife Sanctuary | Gujarat |
| 46 | Wadhvana Wetland | Gujarat |
| 47 | Haiderpur Wetland | Uttar Pradesh |
| 48 | Khijadiya wildlife sanctuary | Gujarat |
| 49 | Bakhira wildlife sanctuary | Uttar Pradesh |
| 50 | Pallikaranai Marsh Reserve Forest | Tamil Nadu |
| 51 | Kaikill Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 52 | Pichavaram Mangrove | Tamil Nadu |
| 53 | Pala wetland | Mizoram |
| 54 | Sakhya Sagar | Madhya Pradesh |
| 55 | Tampara Lake | Odisha |
| 56 | Hirakud Reservoir | Odisha |
| 57 | Ansupa Lake | Odisha |
| 58 | Yashwant Sagar | Madhya Pradesh |
| 59 | Chitrangudi Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 60 | Suchindram Theroor Wetland Complex | Tamil Nadu |
| 61 | Vaduvur Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 62 | Kanjirankulam Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 63 | Thane Creek | Maharashtra |
| 64 | Hygam Wetland Conservation Reserve | Jammu and Kashmir |
| 65 | Shallbugh Wetland Conservation Reserve | Jammu and Kashmir |
| 66 | Koonthankulam Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 67 | Udhayamarthandapuram Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 68 | Vedanthangal Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 69 | Vellode Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 70 | Vembannur Wetland Complex | Tamil Nadu |
| 71 | Gulf of Mannar Marine Biosphere Reserve | Tamil Nadu |
| 72 | Sirpur wetland | Madhya Pradesh |
| 73 | Ranganathituu BS | Karnataka |
| 74 | Nanda Lake | Goa |
| 75 | Satkosia Gorge | Odisha |
India had a rich biodiversity and was home to several ecologically significant wetlands that were designated as Ramsar sites. Ramsar sites are wetlands of international importance recognized under the Ramsar Convention, an intergovernmental treaty aimed at conserving and sustainably using these critical ecosystems. These sites play a crucial role in supporting various plant and animal species, maintaining water resources, and providing livelihoods to local communities.
Here are the newly designated Ramsar Sites in India:
1. Tampara Lake, located in Odisha.
2. Hirakud Reservoir, situated in Odisha.
3. Ansupa Lake, found in Odisha.
4. Yashwant Sagar, located in Odisha.
5. Chitrangudi Bird Sanctuary, situated in Madhya Pradesh.
6. Suchindram Theroor Wetland Complex, located in Tamil Nadu.
7. Vaduvur Bird Sanctuary, found in Tamil Nadu.
8. Kanjirankulam Bird Sanctuary, situated in Tamil Nadu.
9. Thane Creek, located in Maharashtra.
10. Hygam Wetland Conservation Reserve, found in Jammu and Kashmir.
11. Shallbugh Wetland Conservation Reserve, situated in Jammu and Kashmir.
India is a diverse country known for its rich natural heritage, and its commitment to environmental conservation is exemplified by the presence of numerous Ramsar sites across the nation. Ramsar sites are wetlands of international importance designated under the Ramsar Convention, an intergovernmental treaty aimed at conserving and sustaining wetland ecosystems.
The table below contains the Sate Wise List of Number of Ramsar Sites in India:
| State-wise List of Ramsar sites in India | |
|---|---|
| State | Number of Ramsar sites in India |
| Andhra Pradesh | 1 |
| Assam | 1 |
| Bihar | 1 |
| Goa | 1 |
| Gujarat | 4 |
| Haryana | 2 |
| Himachal Pradesh | 3 |
| Jammu and Kashmir | 5 |
| Karnataka | 1 |
| Kerala | 3 |
| Ladakh | 2 |
| Madhya Pradesh | 4 |
| Maharashtra | 3 |
| Manipur | 1 |
| Mizoram | 1 |
| Odisha | 6 |
| Punjab | 6 |
| Rajasthan | 2 |
| Tamil Nadu | 14 |
| Tripura | 1 |
| Uttar Pradesh | 10 |
| Uttarakhand | 1 |
| West Bengal | 2 |
| Total Wetlands in India | 75 |
India is a treasure trove of natural wonders, boasting a rich and diverse array of ecosystems that support an astonishing variety of flora and fauna. Among these ecological gems are the Ramsar sites, designated under the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands. These sites are recognized globally for their immense ecological importance and play a crucial role in conserving and safeguarding wetland ecosystems.
India takes pride in its commitment to the preservation of these invaluable habitats, with various states contributing to the cause through their own Ramsar sites. From the lush mangroves of the coastal regions to the serene lakes nestled in the mountains, each Ramsar site holds a unique significance, reflecting the country’s dedication to the conservation of its natural heritage. Let’s delve into the state-wise list of Ramsar sites in India and explore the wonders that make them so extraordinary.
The Following table contains the State wise list of Ramsar Sites in India:
| State-wise List of Ramsar sites in India | |
|---|---|
| State | List of Ramsar sites in India |
| Andhra Pradesh | Kolleru Lake |
| Assam | Deepor Beel |
| Bihar | Kanwar Lake |
| Goa | Nanda Lake |
| Gujarat | Khijadiya, Nalsarovar, Thol Lake, and Wadhvana Wetland |
| Haryana | Sultanpur National Park and Bhindawas Wildlife Sanctuary |
| Himachal Pradesh | Chandra Taal, Pong Dam Lake, and Renuka Lake |
| Jammu and Kashmir | Hokersar Wetland, Hygam Wetland Conservation Reserve, Shallbugh Wetland Conservation Reserve, Surinsar-Mansar Lakes, and Wular Lake |
| Karnataka | Ranganathittu Bird Sanctuary |
| Kerala | Ashtamudi Wetland, Sasthamkotta Lake, and Vembanad-Kol Wetland |
| Ladakh | Tso Kar, and Tsomoriri Lake |
| Madhya Pradesh | Bhoj Wetland, Sakhya Sagar, Sirpur Lake, and Yashwant Sagar |
| Maharashtra | Lonar Lake, Nandur Madhameshwar, and Thane Creek |
| Manipur | Loktak Lake |
| Mizoram | Pala Wetland |
| Odisha | Ansupa Lake, Bhitarkanika Mangroves, Chilika Lake, Hirakud Reservoir, Satkosia Gorge, and Tampara Lake |
| Punjab | Beas Conservation Reserve, Harike Wetland, Kanjli Wetland, Keshopur-Miani Community Reserve, Nangal Wildlife Sanctuary, and Ropar Wetland |
| Rajasthan | Keoladeo National Park, and Sambhar Lake |
| Tamil Nadu | Chitrangudi Bird Sanctuary, Gulf of Mannar Marine Biosphere Reserve, Kanjirankulam Bird Sanctuary, Karikili Bird Sanctuary, Koonthankulam Bird Sanctuary, Pallikarnai Marsh Reserve Forest, Pichavaram Mangrove, Point Calimere Wildlife and Bird Sanctuary, Suchindram Theroor Wetland Complex, Udhayamarthandapuram Bird Sanctuary, Vadavur Bird Sanctuary, Vedanthangal Bird Sanctuary, Vellode Bird Sanctuary, and Vembannur Wetland Complex |
| Tripura | Rudrasagar Lake |
| Uttar Pradesh | Bakhira Sanctuary, Haiderpur Wetland, Nawabganj Bird Sanctuary, Parvati Arga Bird Sanctuary, Saman Bird Sanctuary, Samaspur Bird Sanctuary, Sandi Bird Sanctuary, Sarsai Nawar Jheel, Sur Sarovar, and Upper Ganga River |
| Uttarakhand | Asan Barrage |
| West Bengal | East Kolkata Wetlands, and Sundarban Wetland |
Wetlands are diverse and unique ecosystems that form in various ways, typically through the interaction of water, soil, vegetation, and topography. The formation of wetlands can be influenced by both natural processes and human activities. Here are some common ways in which wetlands are formed:
India boasts a remarkable expanse of Ramsar Sites, numbering close to 27,000. Among these, approximately 23,000 are inland Ramsar Sites, while the remaining 4,000 are situated along the coastline. Wetlands, forming a substantial 18.4% of India’s land area, play a vital role in the nation’s ecological tapestry. Astonishingly, a significant portion, about 70%, serves as the cradle for the cultivation of paddy.
Distinguishing these wetlands further, we find that India is home to approximately 1.5 million hectares of natural Ramsar Sites, while an even more substantial 2.6 million hectares are a testament to human ingenuity, making the majority of India’s wetlands human-made.
Coastal wetlands, encompassing a sprawling 6,750 square kilometers, dominate the nation’s shoreline, primarily adorned with luxuriant mangrove vegetation. To categorize the diverse Ramsar Sites in India, distinctions are drawn based on geographical origin, nutrient status, vegetation types, and thermal characteristics.
Underpinning the importance of wetland conservation, the National Wetland Conservation & Management Programme (NWCMP) recognizes and safeguards around 100 identified wetlands across the nation, ensuring their continued ecological vitality.
Ramsar Sites in India exhibit a diverse range of features, reflecting the country’s rich ecological and geographical diversity. These features are instrumental in supporting biodiversity, water resources, and the overall well-being of the environment. Here are some of the prominent features of Ramsar Sites in India:
Wetlands, also known as Ramsar sites, play fundamental ecological roles and hold significant cultural, economic, scientific, and recreational value. The following information on India’s most ancient, extensive, and compact Ramsar sites.
Oldest Ramsar Sites in India:
Largest Ramsar Sites in India:
Smallest Ramsar Sites in India:
The Ramsar Sites in India hold significant importance for various reasons, encompassing ecological, cultural, economic, scientific, and recreational aspects. Here’s a breakdown of the significance of Ramsar Sites in India:
1. Ecological Importance:
2. Cultural Significance:
3. Economic Value:
4. Scientific Significance:
5. Recreational Value:
6. Conservation and Education:
7. Water Resources:
8. Climate Resilience:
For aspirants of the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) examinations, Ramsar Sites in India are an essential topic within the domain of environmental conservation and biodiversity. Ramsar Sites are designated wetlands of international importance, and India boasts a substantial number of them. These sites hold great significance as they play pivotal roles in biodiversity conservation, provide crucial ecosystem services, and contribute to various socio-economic aspects.
India’s Ramsar Sites encompass a diverse range of wetland ecosystems, including lakes, rivers, coastal areas, mangroves, marshes, and more. They serve as critical habitats for numerous plant and animal species, including migratory birds that follow the Central Asian Flyway. These sites also support traditional livelihoods, such as fishing and agriculture, thereby contributing to the socio-economic well-being of local communities.
Moreover, Ramsar Sites in India hold cultural importance as they are often associated with ancient traditions and religious practices. They also offer immense potential for scientific research, providing insights into wetland ecology, climate change impacts, and sustainable management practices. They have a role in mitigating climate change by sequestering carbon, especially in peatland ecosystems.
In the context of UPSC examinations, a thorough understanding of Ramsar Sites in India is essential as it reflects the nation’s commitment to environmental conservation and sustainable development. Candidates should be well-versed in the ecological, cultural, economic, and scientific significance of these sites, as well as their contribution to water resources and climate resilience.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments