The Gupta Empire, flourishing from the 4th to 6th centuries AD, witnessed a golden era under the leadership of remarkable rulers. Starting from the humble origins of Sri Gupta, the dynasty saw the reigns of illustrious monarchs like Chandragupta I, Samudragupta, Chandragupta II, and others. Known for their military prowess, strategic alliances, and patronage of arts and sciences, the Gupta rulers left an indelible mark on Indian history.
Key Rulers and Achievements of the Gupta Empire
- Founder: The Gupta dynasty was founded by Sri Gupta (240–280 AD) who was succeeded by Ghatotkacha (280–319 AD). These two kings adopted the titles of ‘Maharajas’.
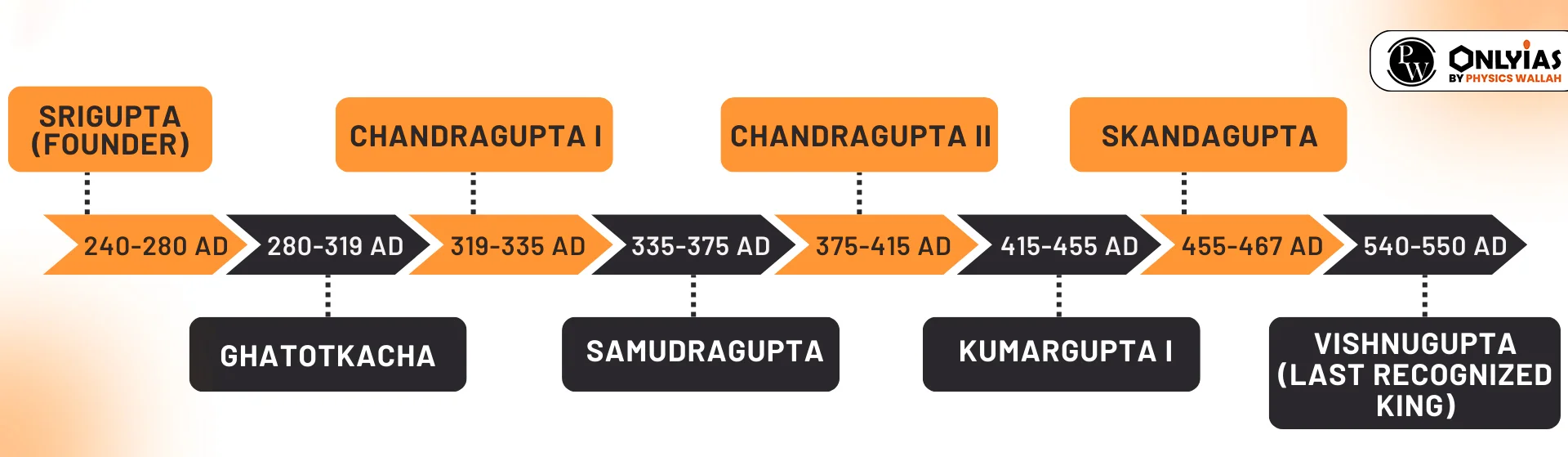
CHANDRAGUPTA I (319-335 AD)
- Pioneering the Gupta Era: He started the Gupta era in 319-20 AD and was the first to be called Maharajadhiraja (the great king of kings). This title indicates his extensive conquests.
- Strategic Marriages: Being a vaishya, he married the Kshatriya Princess of Licchavi from Nepal, Kumaradevi, to increase the prestige of the dynasty and spread his political power.
- Lichchavi was an established Gana-sangha lying between the Ganges and the Nepal Terai.
- No inscriptions or coins have survived from his reign.
SAMUDRAGUPTA (335-375 AD)
-
- Warrior King and Expansionist Policies: He was Chandragupta I’s son and successor. He followed the policy of conquest (opposite to Ashoka’s policy of peace).
- Allahabad Pillar Inscription: (same inscription on which Ashoka’s policy is engraved), composed by Harisena in Sanskrit, refers to his military campaigns
- Conquests: The place and countries conquered by him can be divided into five groups:
-
- Ganga-Yamuna doab.
- Himalayan and frontier states like Assam, Nepal, Bengal, Punjab, etc.
- Forest kingdom of the Vindhyan region (known as Atavika Rajya).
- Dakshinapatha Expedition against 12 rulers of eastern Deccan and South India. He reached up to Kanchi (Tamil Nadu), where Pallavas accepted his suzerainty.
- Against the Sakas and Kushans, some of which were ruling in Afghanistan.
- Subjugation and Hegemony: Nine Republics in Rajasthan, including the Malavas and Yaudheyas, were forced to accept Gupta’s suzerainty under his reign.
- Meghavarman (ruler of Sri Lanka) sent a missionary to Samudragupta for permission to build a Buddhist temple at Gaya.
- He is called ‘Napoleon of India’ by V.A. Smith, in the sense that he never knew any defeat.
- Sacred Rituals: He performed the Asvamedha sacrifice and issued gold and silver coins with the legend ‘restorer of the Asvamedha’.
- In spite of being an ardent follower of Vaishnavism, he was tolerant of other sects too.
- He was also the patron of the great Buddhist scholar ‘Vasubandhu’.
- Kaviraja: As a lover of poetry and music, he was given the title ‘Kaviraja’.
CHANDRAGUPTA II (375 – 415 AD)
- Inheriting the Throne: He was the son of Samudragupta and came to power after a succession struggle with his brother Ramagupta.
- Zenith of Power: His reign saw the highest watermark of the Gupta Empire and formed the peak of Gupta’s territorial expansion.
- Alliance and Conquest
- Extended his empire through marriage alliances and conquests
- He married Kuberanaga, a Naga princess of Central India.
- He gave his daughter Prabhavati in marriage to the Vakataka prince Rudrasena II, who occupied a strategic position in Deccan. This alliance served a useful purpose when Chandragupta-II undertook his campaign in western India against the Sakas.
- He defeated and killed the last ruler of Saka satrap and assumed the title ‘Sakari’ (meaning the destroyer of sakas). With this victory, the territories in the western Malwa and Kathiawar peninsula were annexed into the Gupta empire.
- As a result of the conquest of Western India, the empire gained access to Broach, Sopara, Cambay and other seaports, enabling the Gupta Empire to control trade with Western countries.
- After establishing himself in eastern and western India, Chandragupta II defeated northern rulers like the Huns, Kambojas and Kiratas.
- The Mehrauli Iron Pillar inscription mentions his extensive conquests.
- Vikramaditya: this title was adopted by Chandragupta II, which had been first used by a Ujjain ruler in 58 BC.
- His other names include Vikrama, Devagupta, Devaraja and Simhavikrama.
- Ujjain: seems to have been made the second capital by him.
- Silver Coins: He was the first Gupta ruler to issue silver coins.
- Fa Hein: The Chinese traveller Fa Hein visited the empire during his era.
Navaratnas: He is credited with maintaining in his court nine luminaries or great scholars.
Nine Luminaries Or ‘navaratnas’
| NAME |
WORK |
NAME |
WORK |
| 1.Dhanvantari |
Physician |
6.Varahamihira |
Panchasiddhantika |
| 2. Kalidasa |
Abhijnana Shakuntalam, Vikaramorvashiyam etc. |
7. Amarasimha |
Amarakosha (Sanskrit lexicography) |
| 3. Vararuchi |
Vyakarana |
8. Kshapanaka |
Jyotishya sastra (Astrology) |
| 4. Sanku |
Silpasastra (Architecture) |
9. Harisena |
Allahabad pillar inscription |
| 5. Vittal Bhat |
Mantra Shastra (Music) |
|
Fa Hein’s Visit (399-414 AD)
- He was a Chinese Pilgrim who visited India during the reign of Chandragupta II.
- He came to India by the land route through Khotan, Kashgar, Gandhara and Punjab and returned by the sea route, visiting Ceylon and Java.
- He visited Peshawar, Mathura, Kanauj, Sravasti, Kapilavastu, Kusinagara, Pataliputra, Kasi and Bodh Gaya, among other places.
- He described the people of Mathura as numerous and happy and the people of Pataliputra as rich and prosperous.
- The main purpose of his visit was to see the land of the Buddha and to collect Buddhist manuscripts from India.
- His accounts provided valuable information on the religious, social and economic condition of the Gupta empire.
- His primary interest was religion, and was not interested in political affairs.
|
KUMARAGUPTA I (415-455 AD)
- Sakraditya: He was also called Sakraditya and was the son of Chandragupta II.
- Era of Peace and Prosperity: His reign was marked by general peace and prosperity.
- He issued a number of coins and also performed the Asvamedha sacrifice.
- Nalanda University: He laid the foundation for the Nalanda university.
- Defense Against Invaders: During his reign, a branch of Huns from Central Asia made attempts to cross the Hindukush mountains and invade India.
SKANDAGUPTA (455-467 AD)
- Final Great Ruler: He was the son of Kumargupta and the last great king of the Gupta dynasty.
- Struggle Against Hun Invasions: He was able to repulse an attack by the Huns, but the recurrence of the Huns’ invasion strained his empire’s coffers.
- Bhitari Monolithic Pillar Inscription: gives an account of Skandagupta’s reign.
Conclusion
The Gupta Empire stands as a testament to the heights of Indian civilization during the classical period. From the pioneering reign of Chandragupta I to the scholarly achievements of Kumaragupta I and the resilient defense under Skandagupta, the Gupta rulers left a legacy of prosperity, cultural richness, and military prowess that continues to inspire generations.
![]() May 9, 2024
May 9, 2024
![]() 2806
2806
![]() 0
0
