The earth is the only planet which has life. The surface of the earth is a complex zone which has three main components of the environment viz. Lithosphere, Hydrosphere and Atmosphere. These 3 meet, overlap and interact and form a narrow zone called a Biosphere which sustains life. Along with land and water, air is a main part of this biosphere which plays a major role in regulating atmospheric activities. In this chapter, we will deal primarily with this composition of atmosphere and its major components.
In the Greek language, Lithos means Stone; Atmos means Vapour; Hudor means Water; and Bios means Life.
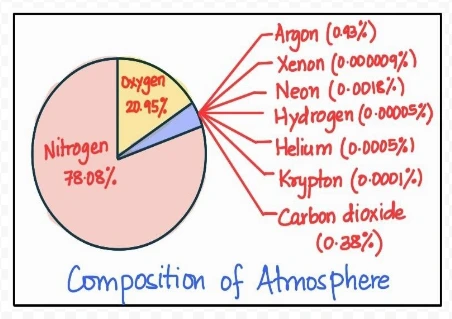
Composition of Atmosphere
Increased CO2 levels, from sources like factory emissions and car fumes, cause global warming by intensifying heat retention. This leads to the melting of polar ice, rising sea levels and causing coastal floods. Such drastic climate changes can lead to the extinction of certain plant and animal species over time.
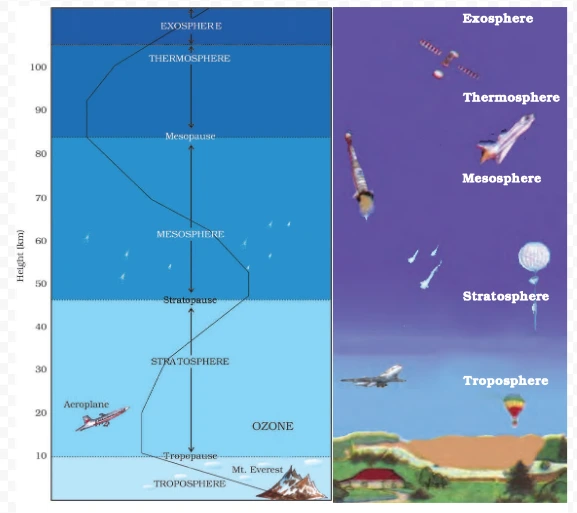
The Composition of Atmosphere is divided into distinct layers, each with its own characteristics .
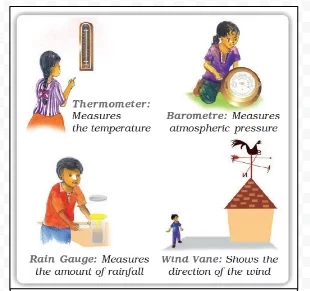
Weather Instruments
The standard unit of measuring temperature is degree Celsius. It was invented by Anders Celsius. On the Celsius scale the water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C.
When air is heated, it expands, becomes lighter and goes up. Cold air is denser and heavy. That is why it tends to sink down. When hot air rises, cold air from the surrounding area rushes there to fill in the gap. That is how air circulation takes place.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>