Economics is the study of how societies allocate their limited resources to meet their unlimited wants and needs. It delves into the mechanisms and patterns that govern the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
A central question in economics is understanding what generates economic wealth in a nation and why some countries are rich while others remain poor.
|
Adam Smith, a Scottish economist and philosopher, is considered one of the pioneers of economics. His most influential work, “An Enquiry into the Nature and Cause of the Wealth of Nations,” published in 1776, laid the foundation for modern economics. Smith explored several fundamental questions in this groundbreaking book that continue to shape economic thought and policy today. |
|---|
What Generates Economic Wealth? – Beyond Resources to Efficient Utilization
These are products used by producers as inputs in the production of other commodities.
Households spend their entire income on goods and services produced by domestic firms, and there are no taxes or imports.
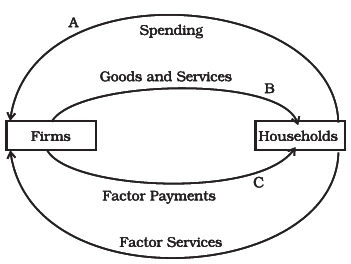
Circular flow of income in a Simple Economy
Income Loop: Household-Firm Exchange in Simple Economy
<div class="new-fform">
</div>