![]() 19 Feb 2024
19 Feb 2024
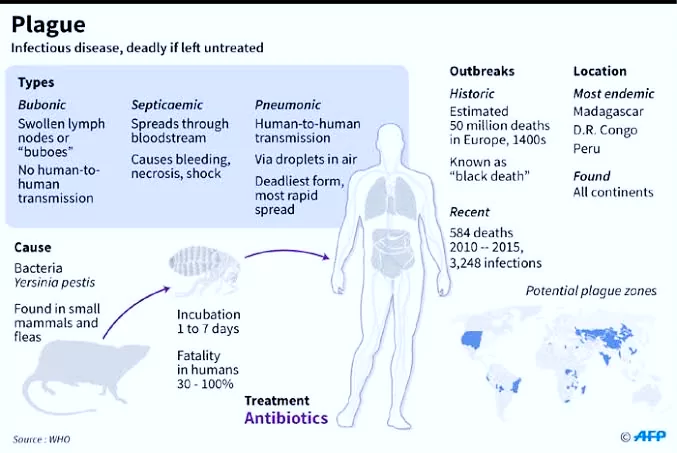
Recently, A confirmed case of Bubonic plague was reported in Oregon, USA.
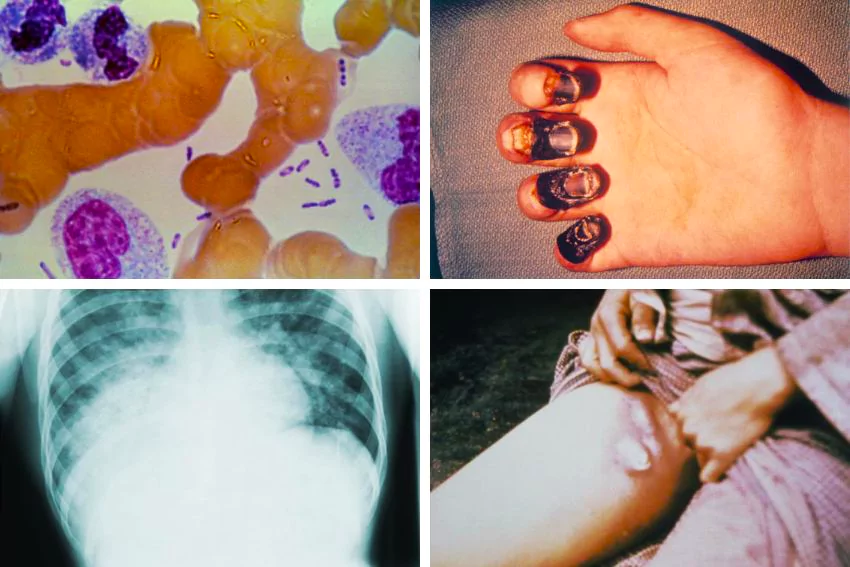 Symptoms:
Symptoms:
History of The Bubonic Plague in India
|
|---|
Also Read:
News Source: Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>