Types of Forest in India: India, famous for its rich biodiversity and varied landscapes, is home to numerous forest areas. From the dense jungles of the Western Ghats to the Himalayan temperate forests.

The word Forest is derived from the Latin phrase ‘Forest’ meaning outdoor, the reference is to a village boundary or fence, and it consists of all uncultivated & uninhabited land. Forests are vast areas predominantly covered with trees, undergrowth, and various plants. They function as important habitats for flora and fauna, offer atmosphere services, and contribute notably to environmental balance. The importance of forests extends beyond ecological elements to encompass social, economic, and cultural components.
Here is the table below that describes the classification of forest In India;
Classification of Indian Forests |
|
Classification of Forests On Administration Basis(State Forest Departments have jurisdiction over forests notified under the Indian Forest (IF) Act, 1927) |
|
| Reserved Forests | These forests are under direct supervision of the government and no public entry is allowed for commercial purposes. |
| Protected Forests | are looked after by the government; local people are allowed to collect forest produce and graze cattle without damage. |
| Unprotected Forests | No restrictions on tree cutting or cattle grazing; they occupy 18% of the Total Forest Area (TFA) in the country. |
Classification of Forests As Per the Constitution |
|
| State Forests | Include important forest areas under full government control. |
| Commercial Forests | Owned and managed by local bodies such as municipal corporations and village panchayats. |
| Private Forests | It Is privately owned and covers slightly more than 1% of the TFA. |
Classification of Forests Based On Merchantability |
|
| Merchantable | Forests are accessible for commercial purposes. |
| Non Merchantable | Located in high mountainous peaks, non-accessible. |
Classification of Forests Based on Composition |
|
| Coniferous Forests | Found in the eastern Middle Himalayas and northeastern Indian states; they cover 6.50% of the TFA. |
| Broadleaf Forests | are found in plateaus, plains, and mountainous areas; they cover about 94% of the TFA. |
| Temperate Forests | Tropical and subtropical monsoon forests. |
Classification of Forests Based on Forest Cover Density(Forest Survey of India Classification) |
|
| Very Dense Forests | Dense canopy coverage( Cover Density > 70%) |
| Moderately Dense Forests | Moderately dense canopy coverage ( Cover Density 40%-70%) |
| Open Forests | Sparse canopy coverage ( Cover Density 40%-70%) |
India, famous for its rich biodiversity and varied landscapes, is home to numerous forest areas. From the dense jungles of the Western Ghats to the Himalayan temperate forests, India boasts an incredible array of ecosystems. Understanding the different forms of forests in India is important for appreciating their ecological significance and the essential role they play in sustaining existence.
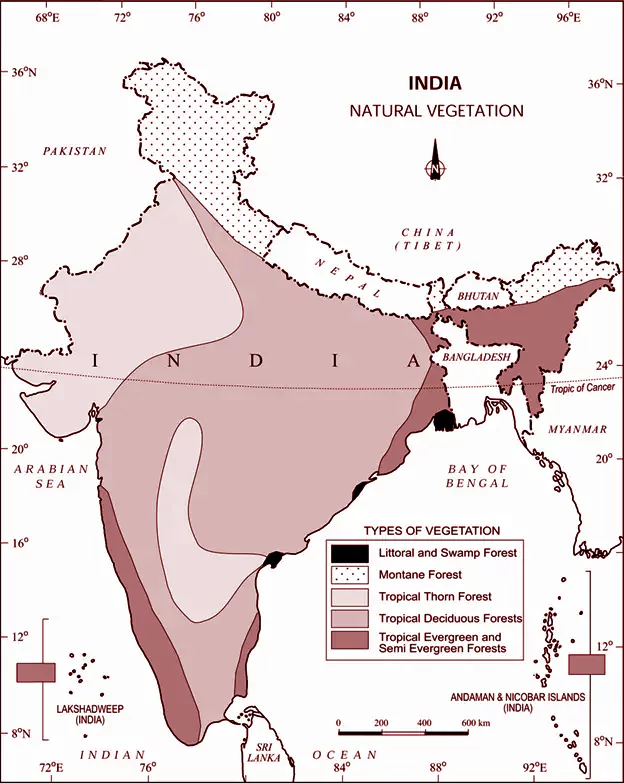





The State of Forests Report of India, compiled by the Forest Survey of India (FSI) and published by the Union Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change (MoEFCC), provides valuable insights into India’s Forest cover and biodiversity. The 2021 document, following the 2019 edition, offers a detailed analysis of Forest area types, distribution, trends, and conservation efforts.
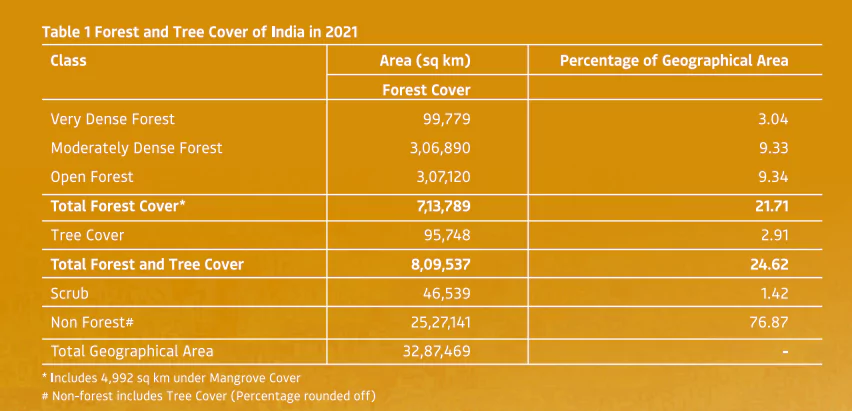
Classification based on Forest Cover Density: The Forest Survey of India (FSI) classifies forests based on canopy density:
| Forest Type | Cover Density Range | Characteristics |
| Very Dense Forests | > 70% | Dense canopy coverage |
| High biodiversity | ||
| Limited sunlight penetration | ||
| Moderately Dense Forests | 40% – 70% | Moderately dense canopy coverage |
| Moderate biodiversity | ||
| Some sunlight penetration | ||
| Open Forests | 10% – 40% | Sparse canopy coverage |
| Lower biodiversity compared to dense forests | ||
| Greater sunlight penetration, allowing understory growth |
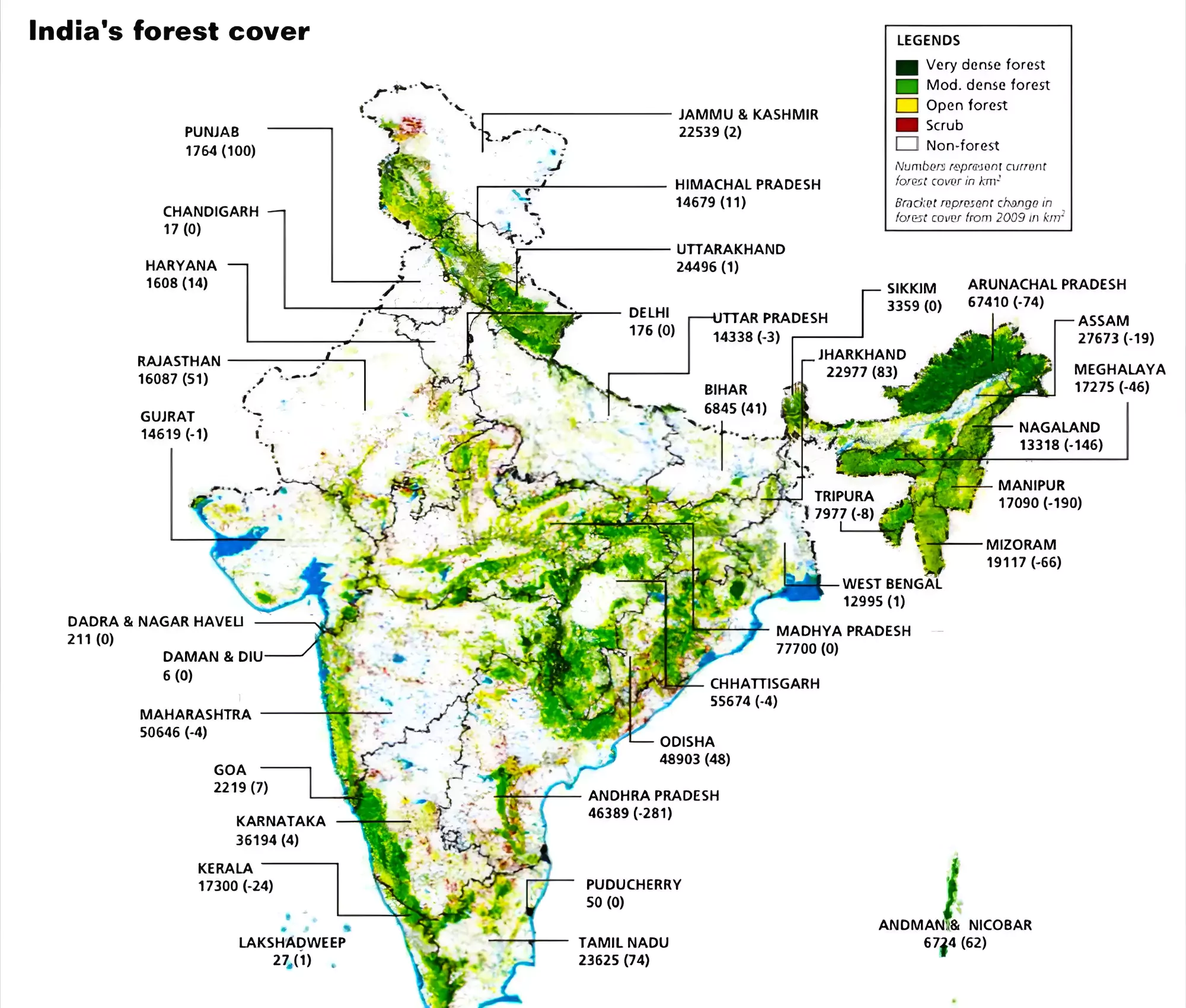
In terms of total area, the list of the top 5 states in terms of Largest Forest Areas in India is:
Considering the forest cover as a percentage of the total geographical area, the top 5 states in the India State of Forest Report are as follows:
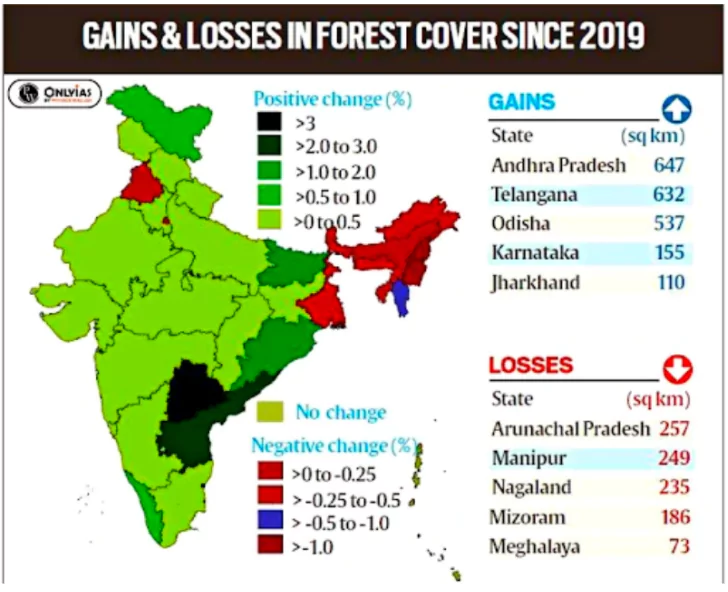
This record serves as a valuable tool for policymakers, conservationists, and stakeholders to formulate effective techniques for keeping India’s worthwhile Forest background.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |

<div class="new-fform">
</div>