Introduction
Tax evasion and tax avoidance might sound similar, but they’re worlds apart when it comes to the law. Tax evasion and tax avoidance are two distinct practices that undermine the integrity of a tax system and impact government revenue. Tax evasion involves illegal activities aimed at intentionally misrepresenting or concealing taxable income to evade paying taxes owed.
On the other hand, tax avoidance refers to legally exploiting loopholes or ambiguities in tax law to minimize tax liability. Both practices pose challenges for tax authorities, necessitating robust enforcement mechanisms and continual efforts to close loopholes and improve tax compliance.
Differences between tax evasion and tax avoidance
| Criteria |
Tax Evasion |
Tax Avoidance |
| Definition |
The illegal practice of not paying taxes that are legally due. |
Utilizing legal methods to minimize tax liability within the framework of Indian tax laws. |
| Legality |
Illegal and subject to legal penalties. |
Legal and complies with the law. |
| Methods |
Underreporting income, inflating expenses, concealing assets, or using false documents. |
Utilizing deductions, exemptions, and incentives provided under the Income Tax Act |
| Consequences |
Leads to penalties, fines, and possible imprisonment. |
No legal consequences, but might face ethical scrutiny if it involves aggressive tax planning. |
| Intent |
Deliberate intention to deceive tax authorities and reduce tax liability unlawfully. |
Using the tax system legally to reduce tax burden without deceit. |
| Example |
Not reporting cash transactions or income from property or business. |
Investing in tax-saving schemes like Public Provident Fund (PPF), National Pension System (NPS), or utilizing home loan interest deductions. |
| Government
Response |
Enforcement through audits, investigations, and legal action by the Income Tax Department. |
Periodic amendments to tax laws to close loopholes and discourage aggressive tax planning. |
| Perception |
Viewed as unethical and harmful to the country’s fiscal health. |
Generally seen as smart financial planning, but can be controversial if it involves very aggressive strategies. |
Government Measures on Tax Evasion vs. Tax Avoidance
Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA)
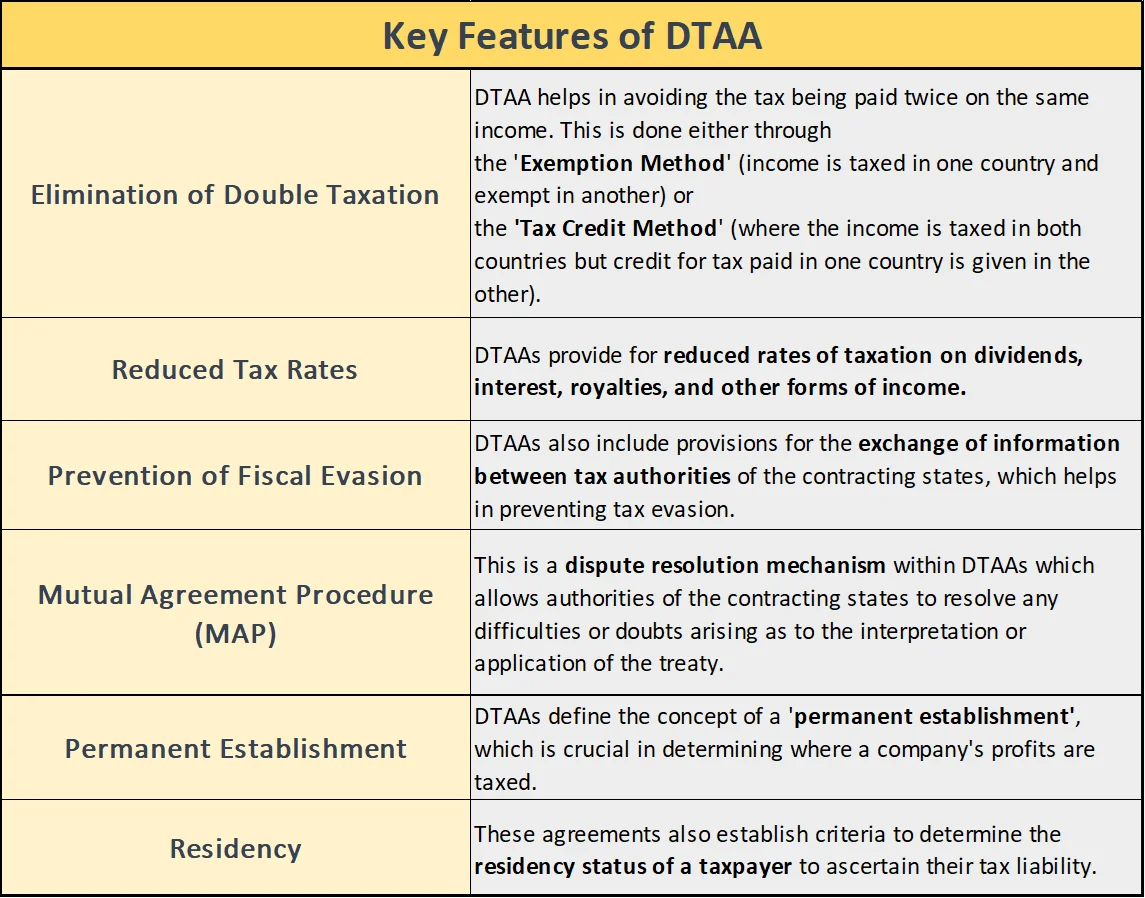
- Meaning: A Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) is a treaty signed between two or more countries to avoid a situation where the same income is taxed by two or more jurisdictions.
- Promoting Investment and Tax Relief: The main purpose of DTAA is to make a country an attractive investment destination by providing relief on dual taxation.
- Reliefs under DTAA: can be categorized as unilateral or bilateral tax reliefs under Section 90 of the Income Tax Act, 1961
- Bilateral Relief: Available with those countries with which India has entered into a DTAA treaty.
- Currently, India has a DTAA treaty with more than 80 countries where bilateral tax relief is available.
- Unilateral Tax Relief: It is granted when there is no Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) between India and the country where the income is generated.
- Mechanisms for Relief: This relief is provided by exempting income earned abroad from tax in the resident country or by providing credit to the extent taxes have already been paid abroad.
Base Erosion & Profit Shifting and OECD Framework
- Meaning: Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) refers to tax planning strategies used by multinational enterprises (MNEs) to exploit gaps and mismatches in tax rules across different jurisdictions.
- Purpose of BEPS: The goal of these strategies is to artificially shift profits from higher-tax jurisdictions to lower-tax jurisdictions or tax havens, where there is little or no economic activity by the company.
- Impact: This shifting results in eroding the tax base of the higher-tax jurisdictions and leads to minimal overall corporate tax being paid globally.
- OECD Framework: Working with the OECD/G20 Inclusive Framework on BEPS, more than 140 countries and regions are taking action on 15 different measures.
- These efforts aim to stop companies from avoiding taxes, make international tax rules more understandable, create a clearer tax system, and deal with tax issues related to the digital economy.

- BEPS and India:
- India is actively implementing the BEPS initiative, making amendments to its domestic laws to align with BEPS regulations.
- The Finance Act of 2016 includes several proposals influenced by BEPS recommendations. Some of these as below,
- Master File and CbC (Country-by-Country) Reporting
- Patent Box tax regime concerning royalty income
- Equalization levy.
- Transfer Pricing
- Definition: Transfer pricing in taxation refers to the rules and methods for pricing transactions between enterprises under common ownership or control.
- Types of Transactions: These transactions could involve the trade of goods, services, or intangible assets.
- Objectives of Transfer Pricing Rules: The primary goal of transfer pricing rules is to ensure that the transactions between related parties are conducted at arm’s length – that is, as if the transactions were between unrelated parties.
- Implications for Taxation
-
- MNCs can distribute earnings among their subsidiary and affiliate companies using transfer pricing.
- Transfer pricing allows companies to adjust their taxable income, potentially reducing their overall taxes.
- Some companies may misuse transfer pricing to shift tax liabilities to jurisdictions with lower tax rates.
- This practice enables companies to pay less in taxes by allocating profits to locations with more favorable tax laws.
- While transfer pricing is legal, its misuse can lead to tax avoidance and erosion of tax revenues in higher-tax jurisdictions.
- Transfer Pricing Regulations in India: These were introduced in the year 2001 under the Income-tax Act, 1961.
- It aims to ensure that any income and/or expense arising to a taxpayer in India, as a result of an international transaction with its Associated Enterprises (“AEs”), shall be computed after the application of an arm’s length principle.
Authority for Advance Rulings
- Emerged as an important adjudicatory body on tax matters.
- Responsibility of the AAR: provide the facility of ascertaining the income-tax liability of a non-resident as well as that of certain special categories of residents.
- Impact of Advance Rulings: Ruling given by AAR become policy guide to the company as well as to the tax authorities.
- Based on these the companies can plan their income-tax affairs well in advance and avoid long-drawn and expensive litigation.
- Establishment of the Advance Rulings Scheme in India: The scheme of Advance Rulings has been introduced under the Income-tax Act, 1961. It was reinforced by the Finance Act, of 1993.
- Under the scheme, the power of giving advance rulings has been entrusted to an independent adjudicatory body.
- Accordingly, a high-level body headed by a retired judge of the Supreme Court has been set-up.
- Criteria for Seeking Advance Rulings: Individuals, companies, firms, associations of persons, or other bodies of corporations can make an application for seeking an advance ruling regarding his/tax liability.
General Anti-Avoidance Rules (GAAR)
- Implementation in India: India has sought to address the issues relating to tax avoidance and evasion by bringing in General Anti-Avoidance Rules (GAAR)
- Effective in India from 1 April 2017, almost eight years after it was first introduced in the then-proposed Direct Taxes Code Bill (DTC), 2009.
- Measures to Combat Aggressive Tax Planning: These are regulatory measures enacted by governments to counter aggressive tax planning strategies that exploit the loopholes in tax laws to avoid taxes.
- Objective: While tax avoidance is legal, GAAR is designed to curb arrangements that, while legal, are primarily aimed at obtaining a tax benefit in a way that is not intended by the law.
- Empowering Revenue Authorities: These rules empower the Revenue Authority in a country to deny tax benefit of transactions or arrangements which do not have any commercial substance and the only purpose of such a transaction is achieving the tax benefit.
Conclusion
- Tax evasion and Tax avoidance undermine the fairness and effectiveness of tax systems, albeit through different means.
- Efforts to combat tax evasion and avoidance require a multi-faceted approach, including robust enforcement measures, legislative reforms, and international cooperation to ensure that taxpayers fulfill their obligations while maintaining a fair and equitable tax regime.
![]() March 27, 2024
March 27, 2024
![]() 3401
3401
![]() 0
0

