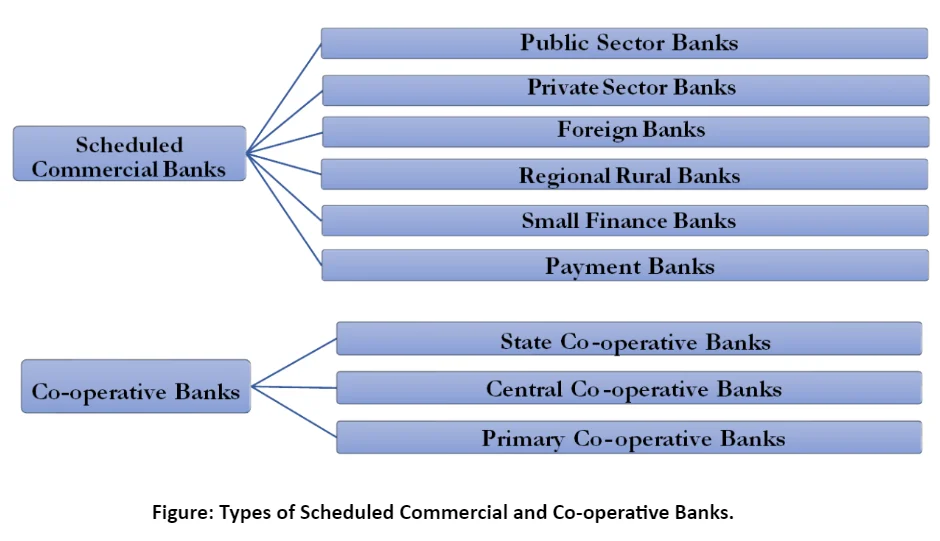
-
- Assets of the Bank: Investments, money at call and short notice, loans and advances and bills discounted and purchased. [UPSC 2019]
- Reserves are deposits which commercial banks keep with the Central bank (RBI) and its cash.
- These reserves are kept partly as cash and partly in the form of financial instruments (bonds and treasury bills) issued by the RBI.
- Liabilities of the Bank = Deposits
- Net Worth of the Bank = Assets – Liabilities.
- Money Multiplier: The ratio of total money supply to the stock of high-powered money in an economy.
- Fractional Reserve Banking: Banks only need to keep a specific amount of cash on hand and can create loans from the money you deposit.
- Reserve Bank of India regulates the commercial banks in matters of Liquidity of assets (through tools like SLR and CRR), Branch expansion, Merger of banks, Winding-up of banks etc. [UPSC 2013]
- Demand Liabilities of a Bank (CASA)
-
- Current Account, Savings Account, Demand Draft
- Overdue balance in Fixed Deposits
- Unclaimed deposits
- Currency Deposit Ratio (CDR): Proportion of funds held by the public in the form of currency compared to their holdings in bank deposits (CDR = Currency in Circulation / Demand Deposits).
- It reflects individuals’ preferences for liquidity.
- Reserve Deposit Ratio (RDR): Percentage of total deposits that commercial banks retain as reserves.
- Reserve money comprises vault cash in banks and deposits of commercial banks with the Reserve Bank of India.
- Provision Coverage Ratio: Percentage of funds that a bank sets aside for losses due to bad debts.
- A high PCR can be beneficial to banks to buffer themselves against losses if the NPAs start increasing faster.
| Net Non-Performing Assets = Gross NPAs – Provisions |
-
- Liquidity coverage ratio (LCR): is a clause of Basel III norms. Under it, banks are supposed to maintain enough short-term liquidity (their needs for the next 30 days) so that they can survive acute financial stress if such situations arise in the economy.
- Inter Creditor Agreement: The agreement is part of the proposed Project Sashakt.
- The Sashakt plan is approved by the government to address the problem of resolving bad loans.
- The objective is to use this ICA for faster facilitation of resolution of stressed assets.
- Aim: It is aimed at the resolution of loan accounts with a size of ₹. 50 crore and above that are under the control of a group of lenders
- Letter of Undertaking/Letter of Comfort: It is a form of bank guarantee under which a bank can allow its customer to raise money from another Indian bank’s foreign branch in the form of a short term credit.
- Nostro Account: Maintained by Indian banks in foreign countries where they have operations for facilitating easy clearing of their transactions.
- Vostro Account: The account maintained by foreign banks in India with their corresponding banks is called vostro accounts.
- SWIFT System: Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication.
- It is a messaging network used by banks to securely send and receive information, such as money transfer instructions.
- Banking Regulation (Amendment) Act, 2020
| Type of Bank |
Regulator |
| Commercial (SBI, Axis, etc) |
|
| Cooperative (Single State: Rural) |
- RBI + State Govt’s Registrar for Coop
|
| Cooperative (Single State: Urban) |
|
| Cooperative (Multi State) |
|
| Cooperative (PACS) |
- State Govt’s Registrar for Coop
|
-
- Formal Sector loans: Loans from banks and cooperatives.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) oversees the functioning of formal loan sources, ensuring banks maintain a minimum cash balance from their received deposits.
- Informal Sector loans: Mainly from moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives and friends, etc.
- Terms of Credit: Interest rate, collateral and documentation requirement, and the mode of repayment together comprise what is called the Terms of Credit.
- Collateral: It is an asset that the borrower owns (such as land, building, vehicle, livestock, and deposits with banks) and uses this as a guarantee to a lender until the loan is repaid.
- Teaser Loan: It is any loan that offers a lower interest rate for a fixed amount of time as a purchase incentive;
- Considered an aspect of subprime lending; Generally offered/provided to entrepreneurs and new homeowners, experience is not a criterion. [UPSC 2011]
- Shadow Banking: It is a set of activities or institutions that operate partially outside the traditional commercial banks.
- They are not fully regulated by the RBI.
- They are not under Banking Regulations Act, 1950.
- Core Investment Company: Specialized Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs). A Core Investment Company registered with the RBI has an asset size of above ₹ 100 crore.
- Their main business is acquisition of shares and securities with certain conditions.
- Self Help Group: SHGs are organized groups of rural poor, particularly women, who themselves manage these groups by pooling their resources; no collateral is required for the loan from the group.
- After a year or two, if the group is regular in savings, it becomes eligible for availing loan from the bank;
- Loan is sanctioned in the name of the group;
- It is the group which is responsible for the repayment of the loan.
- The origin of the self-help group can be traced from Grameen bank of Bangladesh, which was founded by Mohamed Yunus. In India NABARD initiated this in 1986-1987.
- The Regional Rural Banks and Scheduled Commercial banks support SHGs. [UPSC 2023]
- Credit Rating Agencies: In India, credit rating agencies are regulated by Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI);
- The rating agency popularly known as ICRA is a public limited company;
- Indian Rating Agencies: In India there are six credit rating agencies registered under Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) namely, CRISIL, ICRA, CARE, SMERA, Fitch India and Brickwork Ratings;
- International Credit Rating Agencies: Fitch Ratings, Moody’s Investors Service and Standard & Poor’s (S&P) are controlling approximately 95% of global ratings business. [UPSC 2022]
- Banks Board Bureau (BBB): Chairman is selected by the central government and the RBI governor does not head it;
- Recommends for the selection of head for Public Sector Banks and other key personnel if required;
- The Ministry of Finance takes the final decision on the appointments in consultation with the Prime Minister’s Office. ;
- Develops strategies for raising capital and improving performance of PSBs. [UPSC 2019, 2022]
- Core Banking Solution (CBS) is a network of bank branches, which allows customers to manage their accounts, and use various banking facilities from any part of the world. [UPSC 2016]
- Business Correspondent (BC) Model: Launched in 2006;
- Enables the beneficiaries to draw their subsidies and social security benefits in their villages;
- Enables the beneficiaries in the rural areas to make deposits and withdrawals. [UPSC 2014]
- Regional Rural Banks, Land Development Banks /grant direct credit assistance to rural households; NABARD provides refinance facilities to Commercial banks, State Cooperative Banks, Central Cooperative Banks, Regional Rural Banks, and Land Development Banks. [UPSC 2013]
- Serious Fraud Investigation Office (SFIO)
-
- Based on the recommendation of Naresh Chandra Committee on corporate governance
- SFIO is a fraud investigating agency in India under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs
- Investigates white – collar crimes
- Bail In: It is the bank’s own deposits that are used to rescue the bank or reduce its liabilities.
- Bail Out: Involves the rescue of a financial institution by external parties, typically governments using taxpayer’s money.
- Willful Defaulters: A wilful defaulter is an entity or a person that has not paid the loan back despite the ability to repay it.
- Core Banking Solutions (CBS): eKuber: It is the process which is completed in a centralized environment i.e. under which the information relating to the customer’s account (i.e. financial dealings, profession, income, family members etc.) is stored in the Central Server of the bank instead of the branch server.
- Selective Credit Control: It refers to a qualitative method of credit control by the central bank.
- It aims at encouraging good credit, i.e., development credit while at the same time discouraging bad credit, i.e., speculative credit.
- Ratan Watal Committee on Digital Payments.
|
![]() March 29, 2024
March 29, 2024
![]() 4902
4902
![]() 0
0