![]() 13 Feb 2024
13 Feb 2024
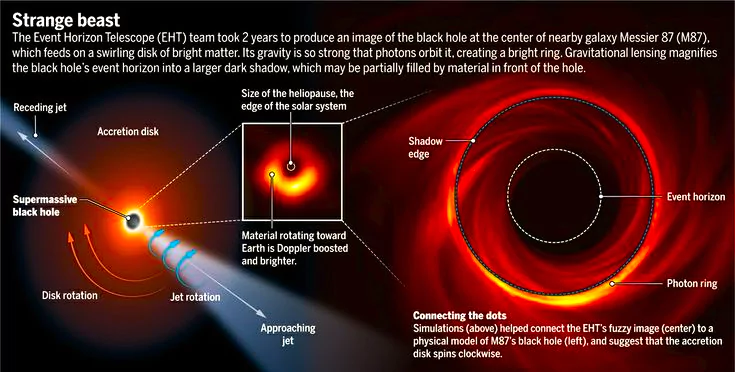
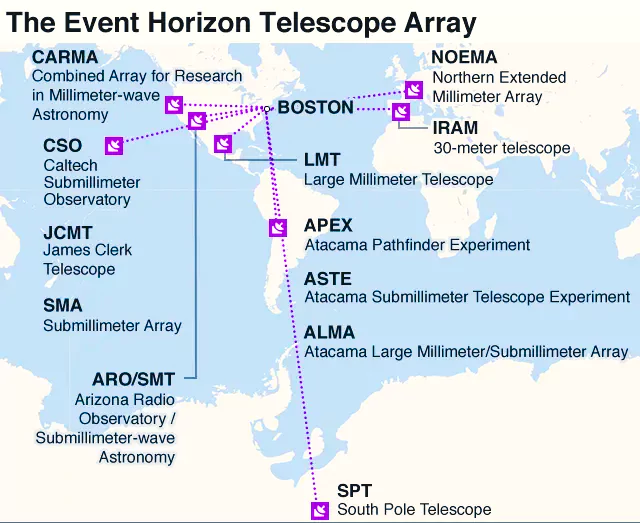
‘Event Horizon Telescope’ Confirms Black hole Shadow is ‘Real’.
|
|---|
News Source : The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>