![]() 14 Feb 2024
14 Feb 2024

This article is based on the news “Old-fashioned trust and credibility bind India-UAE ties” which was published in the Hindu. The visit of the Indian Prime Minister to the United Arab Emirates, reflects the growing importance of their bilateral relations and significance of UAE in India’s engagement in the Gulf region.
| Relevancy for Prelims: INDIA-UAE Relations, First Hindu Temple In Abu Dhabi, and Joint Military Exercise Desert Cyclone, and India-Middle East-Europe Corridor.
Relevancy for Mains: India UAE Relations: Background, Economic, Trade, Defence, Cultural Relations, and Way Forward. |
|---|
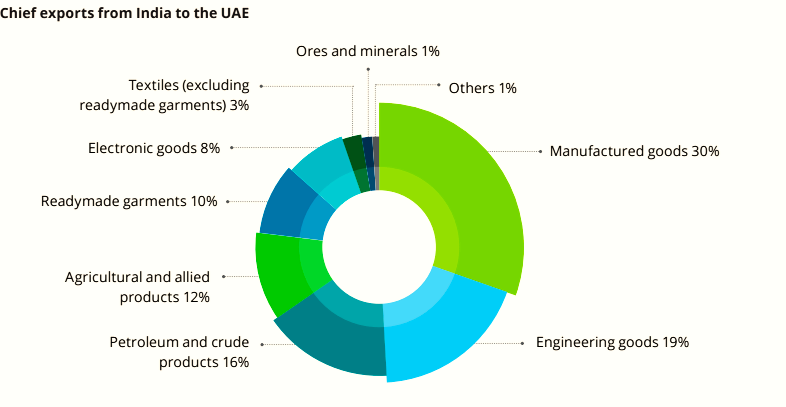
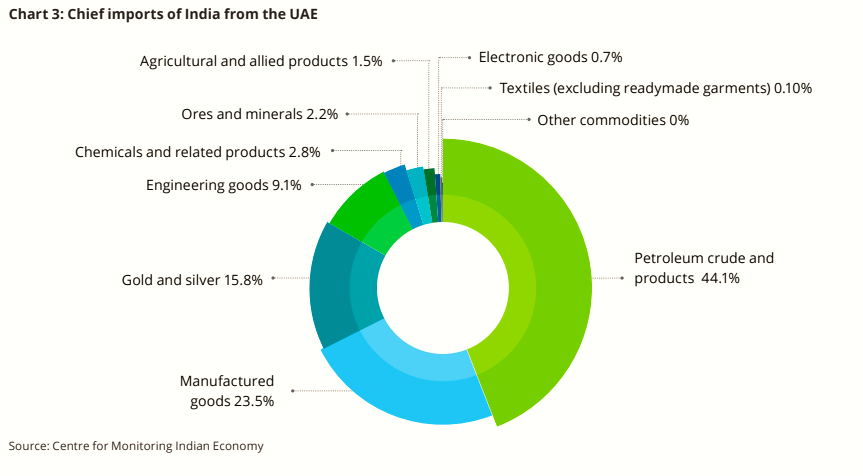 Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA): India and UAE signed CEPA in February 2022 which acted as a catalyst in reducing tariff barriers and increasing trade and investment flows between the nations.
Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA): India and UAE signed CEPA in February 2022 which acted as a catalyst in reducing tariff barriers and increasing trade and investment flows between the nations.
Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA)
Other Types of Trade Agreements
|
| Mains Question: How will I2U2(India, Israel, UAE and USA) grouping transform India’s position in global politics? |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>