![]() 15 Mar 2024
15 Mar 2024
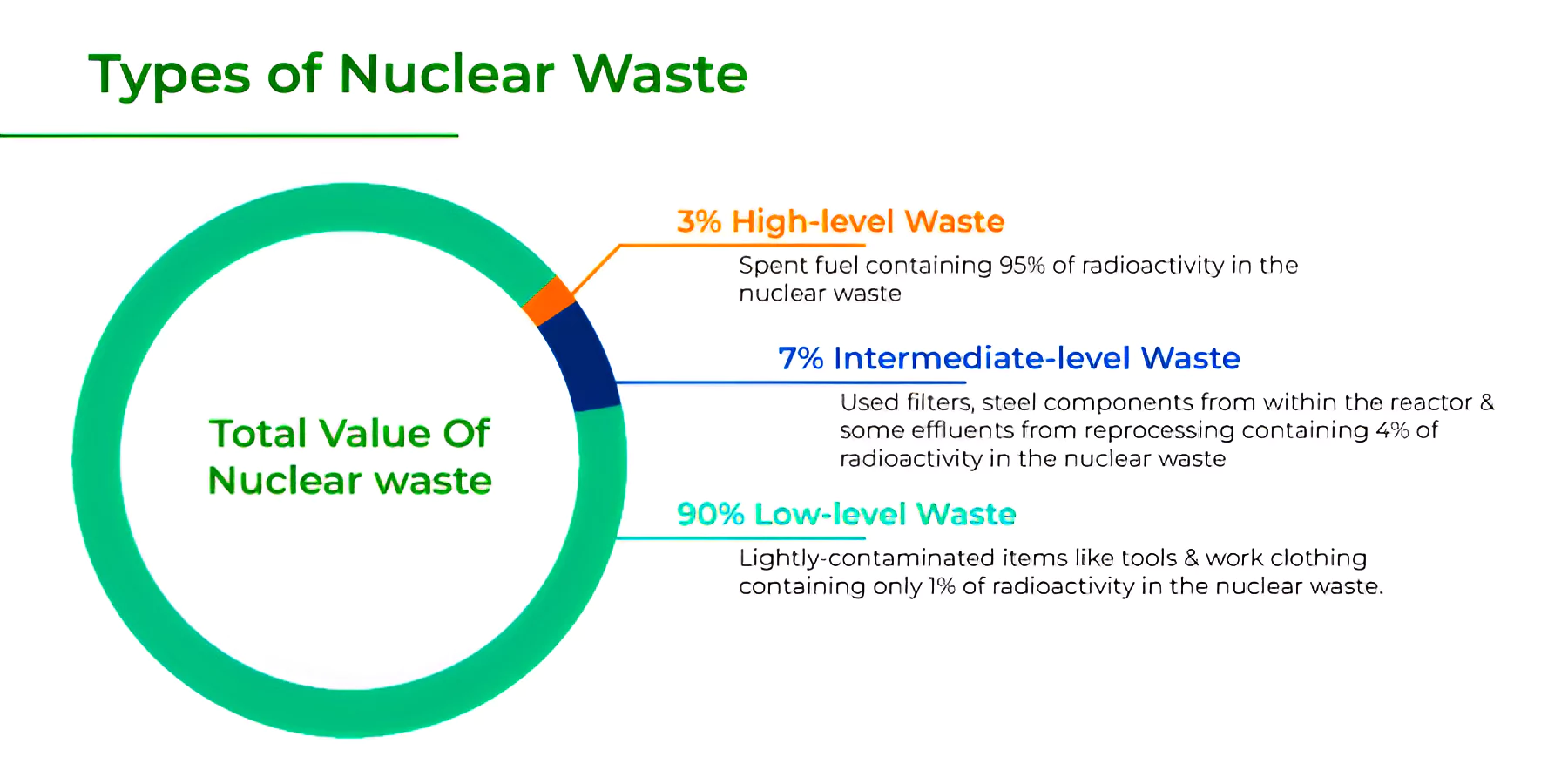
India recently started its Prototype fast breeder reactor (PFBR) into operation, progressing towards the second stage of its nuclear program.
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>