![]() 30 Mar 2024
30 Mar 2024
Scientists are advocating for the adoption of Quantum Cryptography as a cutting-edge technology to safeguard sensitive communications.
 In this process, the sender transmits photons through a polarizer with four potential polarizations and bit designations: Vertical (One bit), Horizontal (Zero bit), 45 degrees right (One bit), or 45 degrees left (Zero bit).
In this process, the sender transmits photons through a polarizer with four potential polarizations and bit designations: Vertical (One bit), Horizontal (Zero bit), 45 degrees right (One bit), or 45 degrees left (Zero bit). 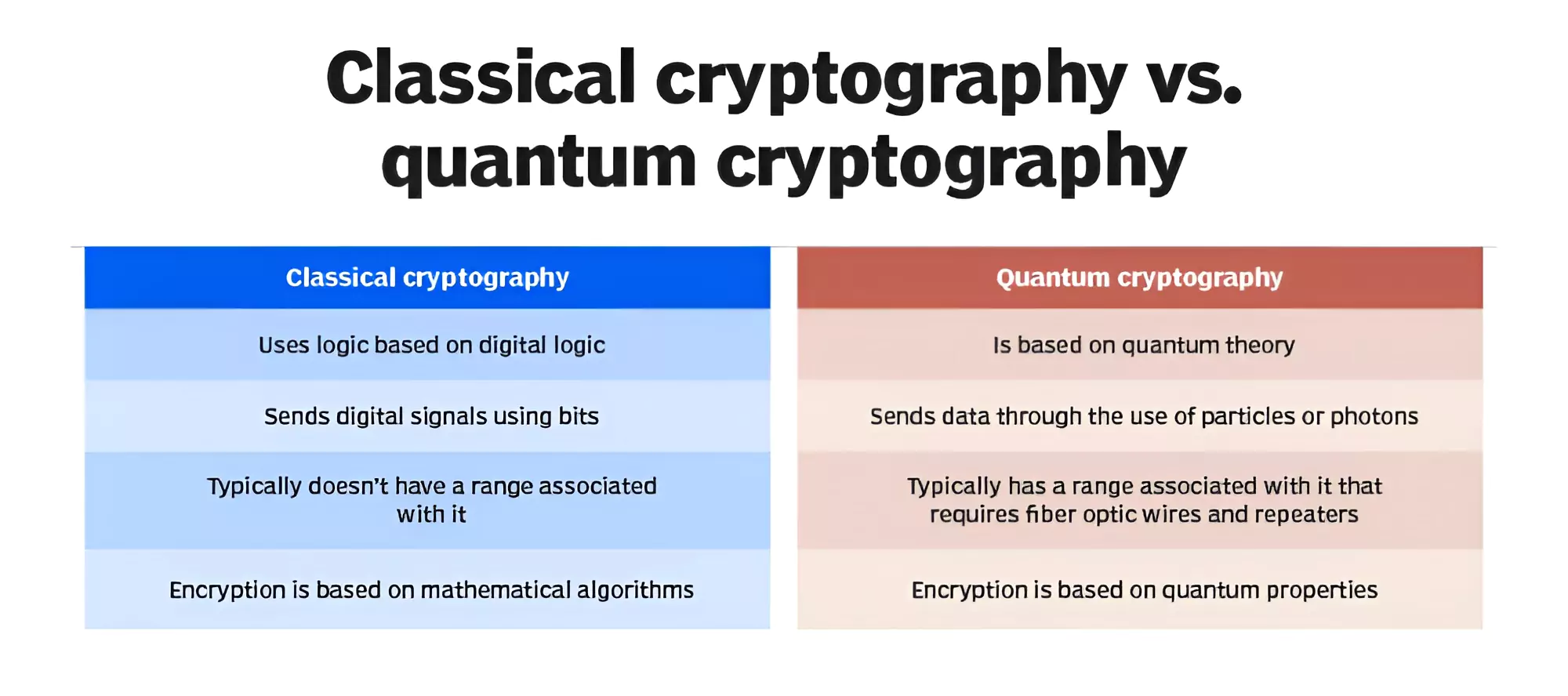
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>