Neighbouring Countries of India: Discover detailed insights on their geographical boundaries, relations, and key facts in this comprehensive article.
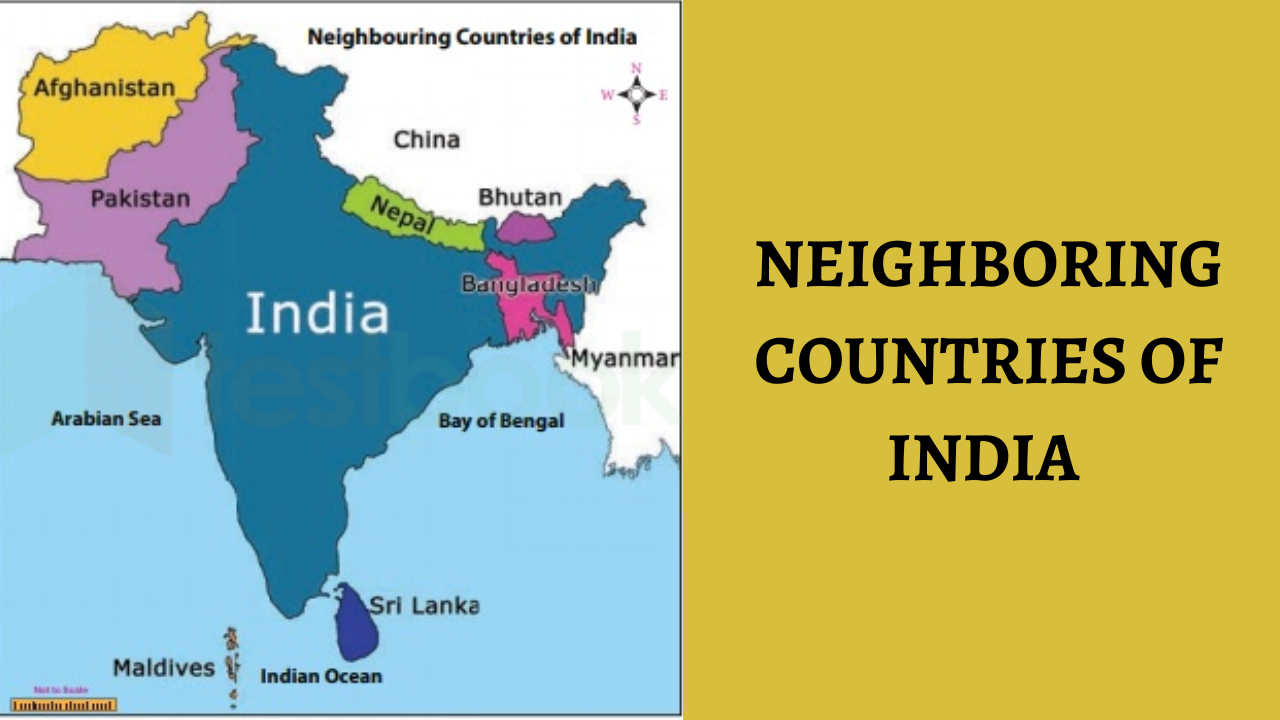
India’s neighboring countries play a crucial role in shaping the nation’s foreign relations and regional stability. With diverse cultures and geopolitical interests, these countries influence India’s economic partnerships and security strategies. Navigating these relationships is vital for anyone studying India’s position in global affairs.
Neighbouring Countries of India: The geographic location of a nation plays a pivotal role in shaping its diplomatic, economic, and strategic policies. For India, a nation boasting a rich tapestry of diverse cultures, languages, and landscapes, its neighbors hold a crucial significance in its international relations. Surrounded by a constellation of countries with unique histories and geopolitical interests, India’s neighborhood presents an intricate web of opportunities and challenges.
This article will discuss the Neighbouring Countries of India. Understanding and navigating these dynamics are of paramount importance for the UPSC aspirants, as it forms a vital component of the nation’s foreign policy and profoundly impact regional stability and global interactions.
India, situated in the southern part of Asia, boasts a unique geographic location that has significantly influenced its history, culture, and strategic importance. With a vast land border spanning 15,106.7 km and a diverse coastline stretching for 7,516.6 km, India shares its borders with nine neighbouring countries. Positioned in the Northern Hemisphere longitudinally and in the Eastern Hemisphere latitudinally, the country holds a pivotal position on the global map.
Beyond India’s geographic extent, India stands as one of the world’s most populous nations, a testament to its vibrant tapestry of languages, cultures, and traditions. Covering an extensive area, India ranks as the seventh-largest country globally. This immense size and population have contributed to India’s economic and political significance, making it a key player in regional and global affairs.
India’s geographic features, rich heritage, and forward-looking aspirations continue to shape its path on the global stage. As the nation navigates through the complexities of the 21st century, it seeks to foster harmonious ties with its neighbors while upholding its core values of peace, cooperation, and mutual development.
Nestled in the southern part of Asia, India is a nation of vast geographic expanse, and this geographical advantage fosters close relationships with nine neighbouring countries. Each neighbor uniquely shapes India’s foreign policy, regional cooperation, and economic engagements. From the towering peaks of the Himalayas to the azure waters of the Indian Ocean, India’s diverse borders serve as gateways to cultural exchange, trade, and diplomacy.
The table provided presents a comprehensive overview of the Neighbouring Countries of India, their capitals, and the Indian states and union territories (UTs) with which they share borders.
| List of Neighbouring Countries of India | ||
|---|---|---|
| Neighbouring Country | Capital | Indian State/UTs with Shared Border |
| Afghanistan | Kabul | Ladakh (PoK) |
| Bangladesh | Dhaka | West Bengal, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Tripura, and Assam |
| Bhutan | Thimphu | West Bengal, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, and Assam |
| China | Beijing | Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh |
| Myanmar | Yangon | Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Mizoram, and Manipur |
| Nepal | Kathmandu | Bihar, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Sikkim, and West Bengal |
| Pakistan | Islamabad | Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Punjab, Rajasthan, and Gujarat |
| Sri Lanka | Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte
Columbo (Executive Capital) |
Separated from India by the Gulf of Mannar |
| Maldives | Male | It lies in the south-west part of the Indian Ocean below the Lakshadweep Islands |
India shares its land borders with 7 Neighbouring countries that are Nepal, China, Myanmar, Bangladesh and Bhutan. Additionally, India shares its maritime borders with 2 Neighbouring countries, Sri Lanka and Maldives, thus making it a total of 9 countries India shares its borders with. Check the Neighbouring Countries of India on Map below to get the exact idea of the Neighbouring Countries of India.

India’s geographical location places it at the crossroads of South Asia, with nine neighbouring countries that share both land and maritime borders. Each country plays a crucial role in shaping India’s foreign policy, trade relations, and regional dynamics. Let’s explore the Neighbouring Countries of India and their significance.
India’s relationship with its neighbouring countries is essential for regional stability, economic growth, and cooperation in various fields. As India continues to strengthen its diplomatic ties, it seeks to foster peaceful coexistence and collaborative efforts to address mutual challenges and create opportunities for shared prosperity.
1. Neighbouring Countries of India: Afghanistan
– Border Length: 106 km
– Official Languages: Dari, Pashto
– Currency: Afghan Afghani
– States/Provinces: 34 Provinces
– Area: About 652,230 sq km
– Major Economy: Agriculture, Manufacturing of textiles, carpets, handicrafts, and woollens
– Religion: Islam
Afghanistan is situated to the northwest and shares its borders with Ladakh (PoK). Geopolitically, Afghanistan’s stability has been a matter of concern for India, and the two nations have collaborated on various developmental and infrastructure projects.
2. Neighbouring Countries of India: Bangladesh
– Border Length: 4,096.7 km
– Official Language: Bengali
– Currency: Bangladeshi Taka
– States/Provinces: 8 Provinces
– Area: 143,998 sq km
– Economy: Agriculture, Industry, and Services
– Religion: Islam
Located to the east, Bangladesh shares its borders with five Indian states: West Bengal, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Tripura, and Assam. India and Bangladesh share deep cultural, economic, and historical ties, and their relations have significantly improved in recent years.
3. Neighbouring Countries of India: Bhutan
– Border Length: 699 km
– Official Language: Dzongkha
– Currency: Bhutanese Ngultrum
– States/Provinces: 20 States
– Area: 38,394 sq km
– Economy: Hydropower, Agriculture, Forestry, and Tourism
– Religion: Buddhism, Hinduism
India and Bhutan enjoy a unique and strong bond. Bhutan shares its borders with four Indian states: West Bengal, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, and Assam. India has been a significant development partner for Bhutan.
4. Neighbouring Countries of India: China
– Border Length: 3,488 km
– Official Language: Mandarin
– Currency: Chinese Yuan
– States/Provinces: 26 Provinces
– Area: About 9,596,960 sq km
– Economy: Manufacturing, Agriculture, and Services
– Religion: Atheism, Buddhism, Taoism, Christianity, and Islam
India’s northern neighbor, China, shares its borders with five Indian states: Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh. The Sino-Indian border remains a subject of occasional tension, but both countries have also sought to enhance economic cooperation.
5. Neighbouring Countries of India: Myanmar
– Border Length: 1,643 km
– Official Language: Burmese
– Currency: Burmese Kyat
– Area: 676,578 sq km
– Economy: Agriculture, Industry, and Services
– Religion: Buddhism, Christianity, Islam, Hinduism
Located to the east, Myanmar shares its borders with four Indian states: Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Mizoram, and Manipur. India and Myanmar share cultural and economic ties and collaborate on regional connectivity and security issues.
6. Neighbouring Countries of India: Nepal
– Border Length: 1,751 km
– Official Language: Nepali
– Currency: Nepalese Rupee
– States/Provinces: 7 Provinces
– Area: 147,181 sq km
– Economy: Agriculture, Industry, and Tourism
– Religion: Hinduism, Buddhism
Sharing its borders with five Indian states—Bihar, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Sikkim, and West Bengal—Nepal enjoys close historical and cultural links with India. It is a landlocked country and relies on India for trade and transit.
7. Neighbouring Countries of India: Pakistan
– Border Length: 3,323 km
– Official Language: Urdu
– Currency: Pakistani Rupee
– States/Provinces: 4 Provinces
– Area: 796,095 sq km
– Economy: Agriculture, Industry, and Services
– Religion: Islam
India’s western neighbor, Pakistan, shares its borders with Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Punjab, Rajasthan, and Gujarat. The relationship between India and Pakistan has been complex, with historical disputes and occasional military conflicts.
8. Neighbouring Countries of India: Sri Lanka
– Border Line: Sea Border
– Official Languages: Sinhala, Tamil
– Currency: Sri Lankan Rupee
– States/Provinces: 9 States
– Area: 65,610 sq km
– Economy: Agriculture, Industry, and Services
– Religion: Buddhism, Hinduism, Islam, and Christianity
Separated from India by the Gulf of Mannar, Sri Lanka lies to the south of India. India and Sri Lanka share cultural and economic ties and collaborate on various regional issues.
9. Neighbouring Countries of India: Maldives
– Border Line: Sea Border
– Official Language: Dhivehi
– Currency: Maldivian Rufiyaa
– States/Provinces: 1 Only
– Area: 298 sq km
– Economy: Tourism, Fishing, and Agriculture
– Religion: Islam
Located in the south-west part of the Indian Ocean, the Maldives lies below the Lakshadweep Islands. India and the Maldives share close maritime ties and cooperate on security and developmental issues.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
India shares its borders with nine Neighbouring countries.
Ladakh (PoK) shares the border with Afghanistan.
The border between India and China is approximately 3,488 km long.
The border between India and Pakistan stretches over approximately 3,323 km.
Nepal is, the Neighbouring country of India, home to Mount Everest, the world's tallest peak.

<div class="new-fform">
</div>