Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction:
- Begin by acknowledging the profound impact of Prof. Satyendra Nath Bose’s work on quantum mechanics.
Body
- Discuss the work of ‘Bose-Einstein Statistics’.
- Also, show how it revolutionized the field of Physics.
- Substantiate with appropriate examples.
Conclusion
- Conclude, emphasizing the enduring resonance of his work in quantum mechanics, inspiring ongoing research and technological advancements.
|
Introduction:
The realm of quantum mechanics underwent a profound transformation with the pioneering work of Prof. Satyendra Nath Bose, especially his revolutionary concept of ‘Bose-Einstein Statistics’. This fundamental shift in understanding underpins many modern physical theories and technologies.
Body:
Bose-Einstein Statistics:
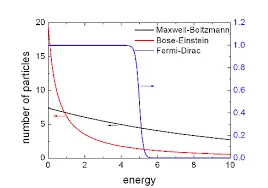
- Bose introduced a novel way to count states in the phase space, which allowed particles to occupy the same quantum state.
- This was contrary to the classical statistical methods used in physics, which required particles to occupy different states.
- Bose’s method of counting gave rise to Bose-Einstein statistics, named after Bose and Albert Einstein, who further extended Bose’s work.
Bose-Einstein statistics has triggered revolutionary advances in physics, leading to significant practical applications:
- Lasers and Superconductivity:
- Central to the operation of lasers (Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) is the Bose-Einstein statistics.
- These devices have become an integral part of technology and everyday life.
- Similarly, Bose-Einstein condensation principles applied to electron pairs form the basis of our understanding of superconductivity, a state allowing electric current to flow without resistance.
- Bose-Einstein Condensate (BEC):
- The theory also forecasted a unique state of matter, the Bose-Einstein condensate, characterized by a group of bosons condensing into the lowest quantum state.
- It was only in 1995 that scientists Eric Cornell, Carl Wieman, and Wolfgang Ketterle successfully demonstrated a BEC using cooling and trapping techniques with rubidium atoms, winning the 2001 Nobel Prize in Physics for their groundbreaking work.
- Bosons:
- Bose-Einstein statistics applies to particles known as bosons, named after Bose.
- This category includes particles such as photons, gluons, and W and Z particles.
- The concept of bosons has left a profound imprint on various domains, from particle physics to solid-state physics.
Conclusion:
In essence, Prof. Satyendra Nath Bose’s path-breaking contribution to Bose-Einstein statistics has profoundly reshaped physics, spurring the development of novel theories and technologies. His remarkable work continues to resonate in the corridors of quantum mechanics, inspiring innovative research and applications.
