Reserve Bank of India is India's central bank, managing monetary policy, banking regulations, and currency issuance. The Reserve Bank of India plays a vital role in financial stability and growth.

Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the central bank of the country, responsible for regulating and overseeing the financial and banking system. Established under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, it plays a significant role in maintaining monetary stability and economic growth. This blog explores the history, structure, functions, and responsibilities of the Reserve Bank of India.
The Reserve Bank of India is the apex financial institution in India, which controls the monetary policy of the country. It manages currency issuance, regulates the banking sector, and ensures financial stability. Acting as the Central Bank of India, the RBI also formulates and implements monetary policies to maintain inflation and promote economic development.
| Reserve Bank of India (RBI) | |
| Aspect | Details |
| Full Form | Reserve Bank of India |
| Established On | April 1, 1935 |
| Established Under | Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 |
| Headquarters | Mumbai, Maharashtra |
| Initial Headquarters | Kolkata, West Bengal |
| Nationalization Year | 1949 |
| Current Governor | Shri Sanjay Malhotra |
| Logo | Royal Bengal Tiger under a Palm Tree |
| Role | Central Bank of India, Regulator of Financial System |
| Key Functions | Monetary Policy Formulation, Currency Issuance, Financial Regulation, Foreign Exchange Management, Government’s Banker |
| Official Website | https://www.rbi.org.in |
The RBI full form is the Reserve Bank of India. It is often referred to as the country’s Central Bank and serves as the primary regulator of the Indian financial system. Established to ensure monetary stability, it has been instrumental in guiding the Indian economy since its inception.
The Reserve Bank of India History dates back to 1926 when the Royal Commission on Indian Currency and Finance recommended the establishment of a central bank. After years of discussions and legislative processes, the RBI was established under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. It began operations on April 1, 1935, as a privately owned bank, but was later nationalized in 1949 to strengthen the financial system.
| Key Historical Events of RBI | |
| Year | Event |
| 1926 | Hilton-Young Commission recommends the creation of a central bank. |
| 1934 | Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 was passed. |
| 1935 | RBI started operations as a private bank. |
| 1949 | RBI was nationalized and became India’s Central Bank. |
| 1991 | Economic reforms led to the liberalization of the banking sector. |
The Reserve Bank of India was established in the year 1935. Specifically, it commenced its operations on April 1, 1935. The idea for its formation arose from the necessity to manage the currency system and regulate credit in the country. Over the decades, it has evolved into a robust institution managing India’s financial framework.
This act provided the legal foundation for the bank’s establishment, empowering it to regulate the issuance of currency, maintain reserves, and control credit. The act outlines the roles and responsibilities of the RBI, ensuring financial stability and growth.
The RBI logo features a majestic Royal Bengal Tiger standing beneath a palm tree. It symbolizes strength, authority, and the country’s economic resilience. The design was inspired by the East India Company’s seal and represents the central bank’s commitment to safeguarding the financial interests of the nation.

The RBI headquarters is located in Mumbai, Maharashtra. Initially, the Central Office was established in Kolkata, but it was moved to Mumbai in 1937. The headquarters serves as the administrative center where the RBI Governor and other top officials formulate monetary policies and oversee the country’s financial system.
The RBI Governor is the chief executive officer of the Reserve Bank of India, responsible for executing its policies and decisions. Appointed by the Government of India, the Governor holds significant authority in shaping the nation’s financial and economic policies. The Governor also represents India in various international financial forums.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) operates as an autonomous institution with a well-defined governance structure. It is managed by a central board of directors, which includes the Governor, Deputy Governors, and other appointed members. The RBI follows a structured decision-making process to ensure effective financial regulation and monetary stability.
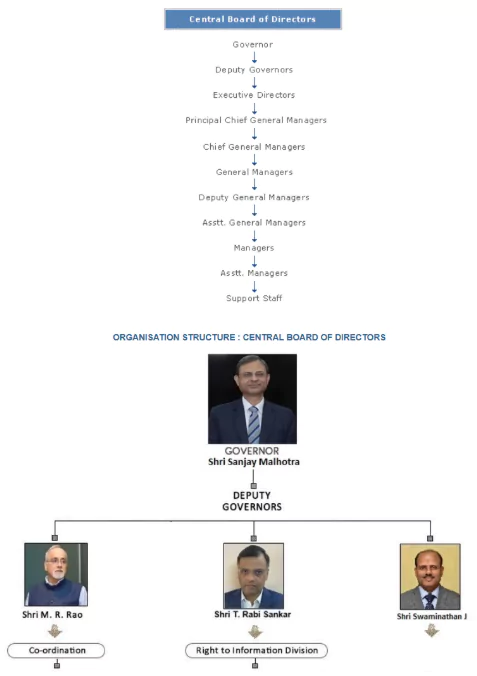
The Reserve Bank of India is governed by a Central Board of Directors, which is responsible for policy formulation. The Board consists of:
The RBI Governor is the chief executive of the Reserve Bank of India. As of 2025, the current RBI Governor is Sanjay Malhotra.
The Reserve Bank of India plays a pivotal role in managing the Indian economy. Below are its primary functions:
The RBI formulates and implements monetary policy to control inflation and promote economic growth. It does this through:
The Reserve Bank of India has extensive powers under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, and the Banking Regulation Act, 1949. These laws grant it authority over monetary policy, banking supervision, and financial regulation.
These powers enable the Reserve Bank of India to maintain economic stability and ensure the smooth functioning of the financial system.
The Reserve Bank of India plays a vital role in maintaining economic stability. Some key impacts include:
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
The Reserve Bank of India is the backbone of India’s financial system. Since its establishment in 1935, it has played a crucial role in monetary policy, banking regulation, and economic development. As India’s central bank, it ensures financial stability while supporting growth and development. Through its various powers and functions, the RBI continues to shape India’s financial landscape, making it a key institution in the nation’s progress.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is India's central bank, responsible for monetary policy, banking regulation, and currency issuance.
The Reserve Bank of India was established on April 1, 1935, under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
The RBI headquarters is in Mumbai, Maharashtra. It was initially in Kolkata but shifted to Mumbai in 1937.
As of 2025, the RBI Governor is Sanjay Malhotra, responsible for managing India's monetary policy and banking regulations.
The RBI logo features a tiger and a palm tree, symbolizing India's financial strength and economic stability.
The Reserve Bank of India was established under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, which defines its powers, functions, and responsibilities.

<div class="new-fform">
</div>