Introduction
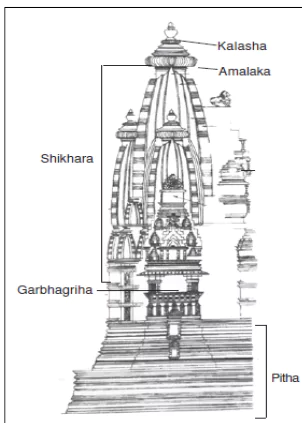
The Nagara style, prevalent in North Indian temple architecture, is characterized by its towering shikhara (spire), intricate carvings, and curved profile, reflecting Hindu cosmology and religious symbolism.
Key Features of Nagara style temples
- Platform: Northern temples are often constructed on a raised stone platform.
- Gateway: Unlike South India, there is typically an absence of elaborate boundary walls or gateways.
- Panchayatana Style: The temples generally followed the Panchayatana style of temple-making.
- Figures on Wall: Outside the garbhagriha, there were images of Ganga and Yamuna.
- Water Tank Absent: There were no water tanks or reservoirs on the temple premises.
- The vertical end of the shikhara ended in a horizontal fluted disc, known as amalak. On the top of that is a spherical shaped structure called Kalash.
Panchayatan style [UPSC 2014]
- Four subsidiary shrines, along with the temple of the principal deity.
- Square: The main temple is square in shape with an elongated mandap.
- Crucified Shape: The subsidiary shrines were placed opposite to each other on either side of the mandap, giving the ground plan a crucified shape.
- Example: Dashavatara temple at Deogarh (Uttar Pradesh), Durga temple at Aihole (Karnataka).
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Different Types of Temple Towers (Shikhara)
- Early temples had a single tower (shikhara), but later ones featured multiple towers.
- Garbhagriha (sanctum): Always situated directly under the tallest tower or shikhara.
Latina Type Shikhara
- This is a simple or basic form of shikhara, famously known as the ‘Latina’ or ‘rekha-prasada’ type.
- It has a square base and walls that curve or slope inward, culminating in a point at the top.
- Latina buildings evolved to support many smaller towers, clustered together like rising mountain peaks.
Phamsana Type Shikhara
- These are broader and shorter than the Latina ones.
- Their roofs consist of several slabs gently rising to a single point.
- In many North Indian temples, Phamsana design is applied to mandapas (halls), while the main garbhagriha is housed in a latina building.
Valabhi Type Building
- It is characterized by rectangular buildings with a roof rising into a vaulted chamber, often referred to as ‘wagon-vaulted buildings.’
- The edge of the vaulted chamber is rounded, resembling ancient bamboo or wooden wagons.
Conclusion
- The Nagara style exemplifies the rich cultural and architectural heritage of North India, serving as a visual representation of Hindu beliefs and traditions while inspiring awe and devotion among worshippers and admirers.
