Types of forests in India include moist tropical, dry tropical, montane, alpine, and littoral/swamp forests. These forests vary by rainfall, altitude, and climate, supporting rich biodiversity across regions—from Western Ghats' evergreen forests to Himalayan alpine zones. Understanding forest types aids in conservation and sustainable resource management.

Types of Forests in India: India has a diverse range of forests in the entire world. These types of forests in India reflect the variations in the rainfall, temperature, soil, and altitude. From tropical evergreen rainforests in the Western Ghats to alpine vegetation in the Himalayas, each forest type plays an important role in ecology and human life. Knowing these forests helps in understanding biodiversity, conservation, and sustainable resource use.
Here, we cover the different types of forests in India in complete detail. One can refer to the section covered here for the information. Knowing these 5 types of forests in India can also prove useful for UPSC aspirants.
The different types of forests in India are based on the climate, temperature, and altitude. These variations divide the forest areas into 5 types of forests in India. All these types cover a different region, coasts to the mountains. Thereby, all highlight the country’s ecological diversity.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
The most dominant type of forest in India is the Moist tropical forest. Moist tropical forests grow in areas with high rainfall and humidity. These forests are dense, layered, and green, supporting diverse plants and animals. They thrive in warm and wet climates across multiple regions of India.
Also Read: Forest In India
Tropical Wet Evergreen Forests receive heavy rainfall throughout the year. They are evergreen, dense, and multi-layered, creating ideal conditions for unique plants and wildlife. Found mainly in the Western Ghats and Northeast India. The table below shows the other important aspects of these types of forest in India:
| Tropical Wet Evergreen Forests | |
| Feature | Details |
| Location | Western Ghats, Northeast India |
| Canopy | Dense, multi-layered, limited sunlight penetration |
| Tree Types | Mahogany, Rosewood, Ebony |
| Evergreen | Yes, trees remain green all year |
| Importance | Supports biodiversity, timber-rich |
Semi-evergreen forests combine evergreen and deciduous species. They occur in areas with slightly less rainfall, where both seasonal leaf-shedding and evergreen vegetation are visible, creating a mixed canopy with high ecological importance. Here’s a table that carries important details of these types of forest in India:
| Tropical Semi-Evergreen Forests | |
| Feature | Details |
| Location | Odisha, Assam, Himalayan foothills |
| Canopy | Mix of evergreen and deciduous trees |
| Vegetation | Tall trees with dense undergrowth |
| Importance | Timber, non-timber resources, wildlife habitat |
| Example Species | Teak, Sal, Bamboo |
The most dominant type of forest in India, these forests shed leaves during dry seasons. They cover wide regions and are critical for timber production, rural livelihood, and wildlife conservation. Mentioned below are some of the crucial aspects of these types of forest in India:
| Tropical Moist Deciduous Forests | |
| Feature | Details |
| Location | UP, MP, Odisha, Chhattisgarh |
| Seasonal Pattern | Sheds leaves in dry season |
| Dominant Trees | Sal, Teak, Bamboo |
| Significance | Most dominant forest type, timber, fodder, livelihoods |
| Adaptation | Survives wet and dry seasonal cycles |
These coastal forests grow in saline and swampy regions. They protect shorelines, reduce storm impact, and support marine biodiversity, making them vital for both ecology and human settlements. Check the table below to know more about these types of forests in India:
| Littoral and Swamp Forests (Mangroves) | |
| Feature | Details |
| Location | Sundarbans, Mahanadi, Krishna deltas |
| Vegetation | Mangrove palms, Sundari trees |
| Climate | Coastal saline and swampy regions |
| Wildlife | Fish, crocodiles, migratory birds |
| Importance | Protects shorelines, natural disaster barrier |
Dry tropical forests thrive in areas with low rainfall and long dry periods. The vegetation is drought-resistant, ranging from small deciduous trees to thorny shrubs, suited for the hot and arid conditions of central and western India.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
These forests are rare and found in rain-shadow areas. Trees are small but remain green most of the year, with thick undergrowth adjusted to dry spells and occasional rains. Here’s the table that carries the gist of these types of forest in India:
| Tropical Dry Evergreen Forests | |
| Feature | Details |
| Location | Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh |
| Vegetation | Small evergreen trees with dense undergrowth |
| Adaptation | Survive dry spells, occasional rainfall |
| Uses | Fodder, medicinal plants |
| Canopy | Low canopy height |
These forests shed leaves for extended periods due to a lack of rainfall. They dominate central India and are important for timber supply, providing resources for rural communities. Know more about these forests via referring to the tabel below:
| Tropical Dry Deciduous Forests | |
| Feature | Details |
| Location | Central India, Rajasthan, Gujarat |
| Seasonal Pattern | Leaves fall for long dry periods |
| Dominant Trees | Teak, Palash, Tendu |
| Importance | Timber, firewood, livelihood support |
| Adaptation | Drought-resistant species |
Located in hot deserts and semi-arid regions, thorn forests are sparse and dry. Vegetation is hardy, with adaptations like thorns and waxy leaves to conserve water. The table below highlights the other important aspects of this types of forest in India:
| Tropical Thorn Forests | |
| Feature | Details |
| Location | Rajasthan, Gujarat, Haryana |
| Vegetation | Cactus, Acacia, Capparis |
| Adaptation | Survives extreme heat and drought |
| Canopy | Sparse, small trees and shrubs |
| Wildlife | Camels, antelopes, desert foxes |
Montane forests cover India’s hills and mountain ranges. Their vegetation varies with altitude, ranging from subtropical broad-leaved trees to temperate conifers, providing critical habitats for wildlife in the Himalayan and northeastern regions.
These forests grow at lower altitudes of mountains. They include both broad-leaved species and pine forests, which are economically useful and ecologically significant for maintaining soil stability.
| Montane Sub-Tropical Forests | |
| Feature | Details |
| Location | Lower Himalayas, NE Hills |
| Vegetation | Pine, Oak, Rhododendron |
| Climate | Moderate altitude, seasonal variations |
| Uses | Timber, resin |
| Wildlife | Leopards, pheasants, bears |
These forests are found at higher altitudes with cooler climates. They include coniferous and mixed forests, providing valuable resources and supporting species adapted to temperate environments.
| Montane Temperate Forests | |
| Feature | Details |
| Location | Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, J&K |
| Vegetation | Deodar, Fir, Spruce |
| Climate | Cool temperate, wet zones |
| Wildlife | Snow leopards, red pandas |
| Importance | Timber, ecological balance |
Alpine forests lie above the tree line in the Himalayas. Vegetation is stunted due to snow and extreme cold, but shrubs and grasses here support unique high-altitude wildlife and grazing practices. Refer to the table below to know more about the Alpine types of forest in India:
| Alpine Forests | |
| Feature | Details |
| Location | Above 3,500 meters, Himalayas |
| Vegetation | Shrubs, mosses, lichens |
| Adaptation | Survives extreme cold and wind |
| Canopy | No trees due to harsh climate |
| Wildlife | Yak, ibex, blue sheep |
The types of forests in India map highlights the geographical spread of different forest zones. Each region displays specific forest types linked to its climate and landscape, showing the nation’s ecological variety.
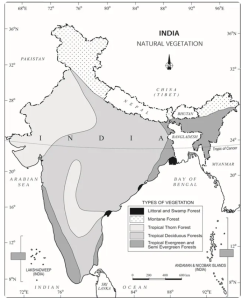
| Types of Forests in India Map | |||
| Forest Type | Major Regions | Climate | Key Species |
| Evergreen | Western Ghats, Northeast | Heavy rainfall | Rosewood, Ebony |
| Semi-Evergreen | Odisha, Assam | Moderate rainfall | Mixed hardwoods |
| Moist Deciduous | MP, UP, Odisha | Wet & dry season | Sal, Teak |
| Dry Deciduous | Rajasthan, Gujarat | Long dry periods | Palash, Tendu |
| Thorn | Rajasthan, Haryana | Arid climate | Acacia, Cactus |
| Montane | Himalayas | Subtropical & temperate | Pine, Oak, Deodar |
| Alpine | High Himalayas | Cold, snowy | Shrubs, Mosses |
Ready to boost your UPSC 2026 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
There are five main types of forest in India with several sub-categories.
The tropical moist deciduous forest is mostly found in India.
India has five primary types of forests: moist tropical, dry tropical, montane sub-tropical, montane temperate, and alpine.
India has moist tropical, dry tropical, montane sub-tropical, montane temperate, and alpine forests.
Tropical moist deciduous forest covers the maximum area of India’s forests.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>