In the realm of biotechnology, breakthroughs like somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) and the cloning of Dolly the sheep have reshaped our understanding of genetic engineering. Recent advancements, such as three-parent babies and stem cell therapy, hold promise for regenerative medicine.
Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer
About: Somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT), technique in which the nucleus of a somatic (body) cell is transferred to the cytoplasm of an enucleated egg (an egg that has had its own nucleus removed).
- Once inside the egg, the somatic nucleus is reprogrammed by egg cytoplasmic factors to become a zygote (fertilized egg) nucleus.
- The egg is allowed to develop to the blastocyst stage, at which point a culture of embryonic stem cells (ESCs) can be created from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst. [UPSC 2017]
Cloning of Dolly Sheep
About: Dolly was cloned from a cell taken from the mammary gland of a six-year-old Finn Dorset sheep and an egg cell taken from a Scottish Blackface sheep.
- She was born to her Scottish Blackface surrogate mother on 5th July 1996.
- Dolly’s white face was one of the first signs that she was a clone because if she was genetically related to her surrogate mother, she would have had a black face.
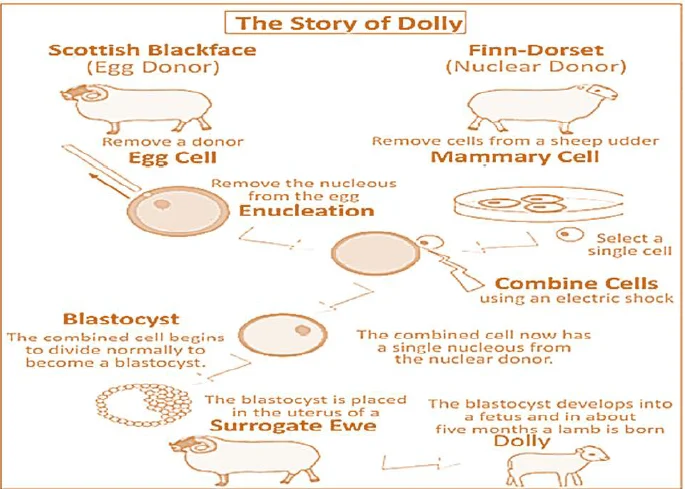
Fig: Cloning Of Dolly Sheep
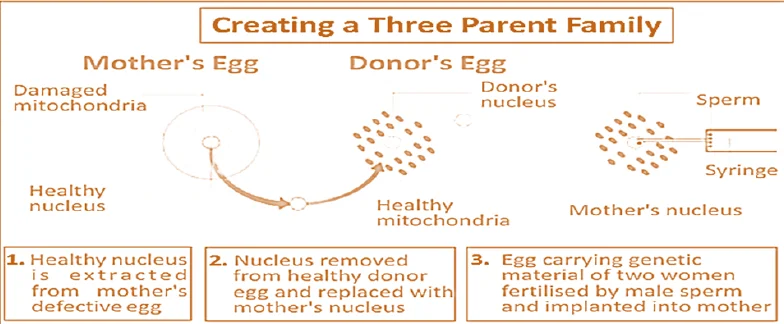
3-Parent Baby [UPSC 2021]
About: Techniques to create ‘three-parent babies’ seek to offer mothers a way to have a child without passing on metabolic diseases caused by faulty mitochondria.
- Researchers do this by exchanging the diseased mitochondria of a prospective mother with those of a healthy, unrelated donor: the third parent.
- Procedure: In addition to DNA in the nucleus, some DNA is also present in the mitochondria.
- During fertilisation, the nuclear DNA is formed with 46 chromosomes (i.e., 23 from the mother & 23 chromosomes from the father).
- The Mitochondrial DNA has only one chromosome, and it codes for only specific proteins responsible for metabolism.
- Mitochondrial DNA is inherited only from the mother & thus, it is more effective to trace human ancestry.
Stem Cell Therapy [UPSC 2012]
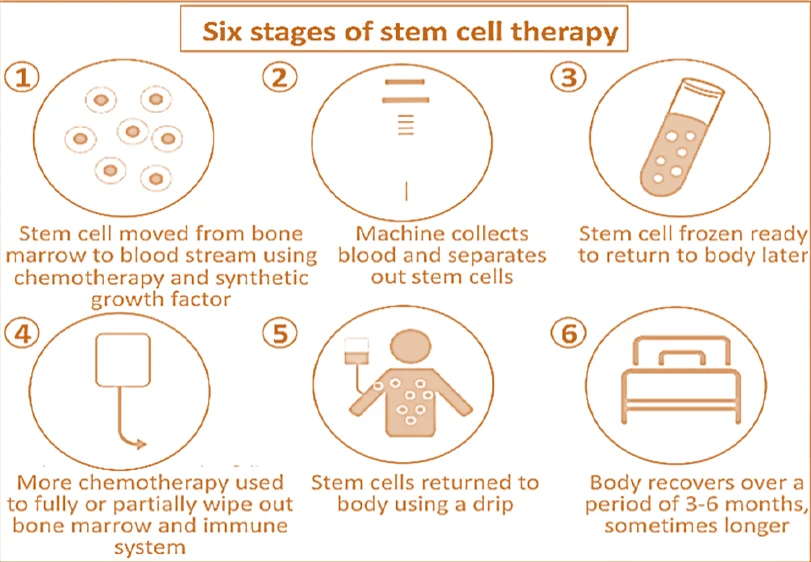
Fig: Stages of Stem Cell Therapy
- For purposes of tissue engineering and cell therapies, stem cells are usually obtained from four basic sources.
-
- Embryonic tissue,
- Fetal tissues, such as fetus, placenta (i.e., amnion and chorion), amniotic fluid and umbilical cord (wharton jelly, blood),
- Specific locations in the adult organism, Example: Fat, bone marrow, skeletal muscle, skin or blood.
- Differentiated somatic cells after they have been genetically reprogrammed.
-
Hierarchy of Cell Potency [UPSC 2020]
-
- Totipotent Stem Cells can give rise to any of 220 cell types found in embryos as well as extraembryonic cells(placenta).
- Pluripotent Stem Cells can give rise to all cell types of the body (but not the placenta).
- Multipotent Stem Cells can develop a limited number of cell types in a particular lineage.
- Unipotent Stem Cells give rise to cells of their own type along a single lineage.
Characteristics of Stem Cells
-
- Totipotency: generates all types of cells, including germ cells.
- Pluripotency: generate all types of cells except cells of the embryonic membrane.
- Multipotency: differentiate into more than one mature cell.
- Self-renewal: divide without differentiation and create everlasting supply.
- Plasticity: Multipotent stem cells have plasticity and can undergo differentiation.
- The trigger for plasticity is stress or tissue injury, which upregulates the stem cells and releases chemoattractants and growth factors.
- Stem cell therapy, also known as regenerative medicine, promotes the repair response of diseased, dysfunctional or injured tissue using stem cells or their derivatives.
- Researchers grow stem cells in a lab.
- These stem cells are manipulated to specialise into specific types of cells, such as heart muscle cells, blood cells or nerve cells.
- The specialised cells can then be implanted into a person.
-
- Example: if the person has heart disease, the cells could be injected into the heart muscle.
- The healthy transplanted heart muscle cells could then contribute to repairing defective heart muscle.
Conclusion
These advancements in biotechnology and medical research offer hope for addressing complex health challenges. Through ongoing innovation, we are unlocking the potential of regenerative medicine to improve human health and well-being.



