![]() May 28, 2024
May 28, 2024
![]() 4784
4784
![]() 0
0
Living things are built from tiny building blocks called cells. These come in all shapes and sizes, but all have a control center (nucleus) and a special wall (membrane) that lets things in and out.
Biology is the study of living organisms and is divided into many specialised fields that cover their morphology, physiology, anatomy, behaviour, origin, and distribution.
The cell is the fundamental, structural and functional unit of all living organisms.
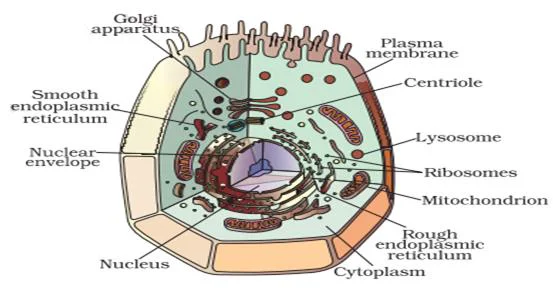
Components of a Cell
The general plan of cellular organisation varies between different organisms, but despite these
modifications, all cells resemble one another in certain fundamental ways. Features common to all cells are:
| Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) |
| It has ribosomes attached to its surface and is an active site for protein synthesis. | Due to the absence of ribosomes, they appear smooth and are major sites for the synthesis of lipids. In animal cells, lipid-like steroidal hormones are synthesised in SER. |
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Inside each cell, there are tiny machines (organelles) with specific jobs. Some make energy (mitochondria), some clean up waste (lysosomes), and plants even have special ones for color (plastids). These all work together to keep the cell alive.
| Related Articles | |
| Animal Organisms: Adaptations, Habitats, Diversity in the Animal Kingdom | Cell Organelles: Structures, Functions & Role |
| Energy Transition | Nuclear Bomb |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments