![]() May 2, 2024
May 2, 2024
![]() 23543
23543
![]() 0
0
The Census of India is a count of all the people living in the country that happens every ten years. The first census was conducted in 1872, with the first complete census taking place in 1881. Since then, the census has been done every ten years. This important process helps us understand how the population of India changes over time and provides essential information for planning and policymaking.

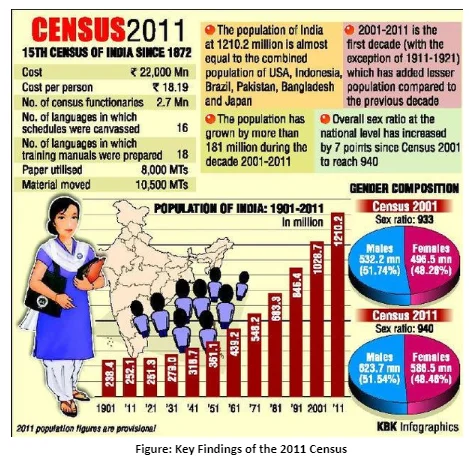
| Terms | Definition |
| Crude Birth Rate |
|
| General Fertility Rate |
|
| Crude Death Rate |
|
| Infant Mortality Rate |
|
| Life Expectancy |
|
| Total Fertility Rate |
|
| Gross Reproduction Rate |
|
| Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR) |
|
| Sex Ratio |
|
| Child Sex Ratio |
|
| Child Mortality Rate |
|
| Dependency Ratio |
|
| Demographic Window |
|
| Demographic Dividend |
|
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments