The Chalcolithic Period, also known as the Copper Age, marked a significant transitional phase in human prehistory, characterized by the emergence of metallurgy alongside the continued use of stone tools, laying the groundwork for the Bronze Age.
Development of Chalcolithic Cultures in Ancient India
- Towards the end of the Neolithic period, the use of metals began, with the first metal being copper. The Chalcolithic period witnessed the combined use of stone and copper tools.
- The Pre-Harappan cultures are the earliest Chalcolithic cultures of India which were found in the time before the beginning of the mature phase of the Harappan culture and continued to exist even after the decline of Harappan civilization.
- In the northwestern and western regions of India, the early farming cultures are associated with the Chalcolithic cultures rather than the Neolithic cultures. Their traces are found all over the country, except for the alluvial plains and thickly forested areas.
|
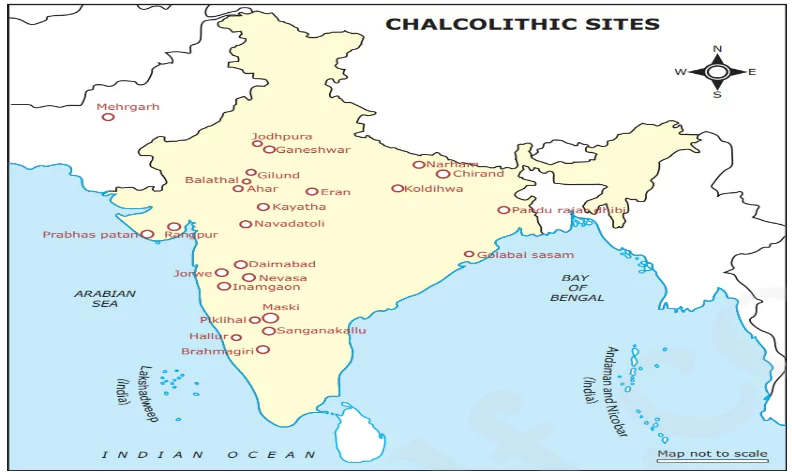
Early Chalcolithic Sites
|
- South-eastern Rajasthan (dry regions of Banas Valley).
- Important sites: Ahar (absence of stone axes or blades), Gilund (Stone-blade industry) and Ganeshwar.
- Ganeshwar principally supplied copper objects to Harappa [UPSC 2021].
- Their subsistence was based largely on hunting and agriculture.
|
- Western Madhya Pradesh: Important sites are Kayatha and Eran in Malwa and Navdatoli on Narmada.
|
- Uttar Pradesh: It had proximity to the Vindhyas and had multiple sites in the Allahabad region.
|
- Western Maharashtra: Important sites include Jorwe (evidence of flat and rectangular copper axes), Nevasa, and Daimabad (in the Ahmednagar district), Chandoli (evidence of Copper chisels), Songaon, Inamgaon (in the Pune district).
|
- Eastern India: Important sites are Chirand on the Ganga River; Pandu Rajar Dhibi and Mahishdal in West Bengal
|
- Andhra Pradesh: Some elements of Chalcolithic are present, but there is an absence of copper objects.
- Important sites are Kodekal, Utnur, Nagarjunakonda, and Palavoy.
|
Pottery
- Mainly black-and-red ware, that was wheel-based, and painted with white linear designs are found.
- People living in Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra produced channel-spouted pots, dishes-on-stand and bowls-on-stand.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Ochre Coloured Pottery Ware culture (2600-1200 BC)
It is found in northern India in the Indo-Gangetic plain dating to the Chalcolithic period.
- The sites produced copper figures and objects, and therefore it is also known as “copper hoard culture.”
- It is a rural culture and has evidence of agriculture and animal rearing.
- The villages had wattle-and-daub houses.
- They used copper and terracotta ornaments. Animal figurines have also been found.
|
Domestication of Animals and Food Grains
- Animals:
- The Chalcolithic people domesticated animals in addition to agriculture.
- Their acquaintance with horses is not clear.
- In eastern India, fish hooks have been found in Bihar and West Bengal.
- Food grains
- Wheat, rice, bajra, and pulses such as the lentil (masur), black gram, green gram, and glass pea were cultivated.
- Eastern India produced rice, Western India cultivated barley and wheat, Deccan India produced cotton in the black soil and lower Deccan produced ragi, bajra and several other millets.
Houses
- Their settlements were sedentary or semi-sedentary and their construction featured mud bricks (rarely burnt bricks), wattle and daub, and thatched houses. They were built on a stone foundation.
- Silos (well-prepared pits) meant for storage of grains have also been found.
- In an earlier Chalcolithic phase at Inamgaon, large mud houses and circular pit houses were discovered.
- The Jorwe culture (near the Pravara River, Maharashtra) had a cluster of houses of varying shapes, highlighting village settlements.
- Settlements like Inamgaon, Eran, and Kayatha had fortifications and moats, but urban civilization was absent.
Arts and crafts: The people were proficient coppersmiths with skill in stonework and produced numerous microliths (tiny stone tools). They had knowledge of spinning and weaving and expertise in cloth manufacturing.
Burial Practices (regional variation): In Maharashtra, burials occurred under house floors in north to south position, whereas in South India, the position was east to west.
- Almost complete or extended burial (lying flat with arms and legs straight, or with the arms folded upon the chest) was obtained in Maharashtra. Post-extraction or fractional burial prevailed in West Bengal.
Religious Worship: Terracotta figurines, such as female figurines (indicate reverence for the mother goddess), stylized bull terracottas in Malwa and Rajasthan, symbolised a religious cult.
Society: Emergence of social inequalities.
- Graves at Chandoli and Nevasa in western Maharashtra revealed differences in burial goods for children.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
| Importance of the Chalcolithic Phase |
Limitations of Chalcolithic Cultures |
- Proficiency in copper smelting
- First to use painted pottery for cooking, eating, and storage.
- Founded the first village in India and had surplus food production.
|
- High infant mortality observed in western Maharashtra, despite a food-producing economy.
- It was predominantly rural with limited copper supply and pliant copper tools;
- Bronze-tools were practically absent in the chalcolithic phase in the major part of India.
|
Conclusion
- The Chalcolithic Period stands as a pivotal chapter in human history, marking the dawn of metalworking and the gradual transition from the Stone Age to the Bronze Age.
- This era witnessed the early stages of urbanization, technological innovation, and social complexity, laying the foundation for future civilizations to flourish.

