![]() May 28, 2024
May 28, 2024
![]() 2282
2282
![]() 0
0
The animal kingdom classification systems categorize animals into groups (phyla) based on shared characteristics. This section explores three key phyla: Porifera (sponges), Cnidaria (jellyfish, sea anemones), and Platyhelminthes (flatworms).
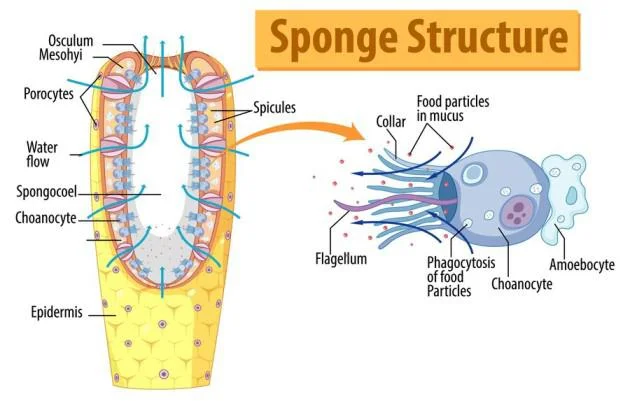
About: Members of this phylum are commonly known as sponges.
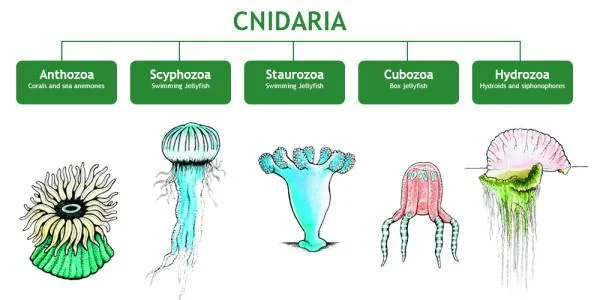
Phylum- Coelenterata (Cnidaria)
About: They are aquatic, mostly marine, sessile or free-swimming.
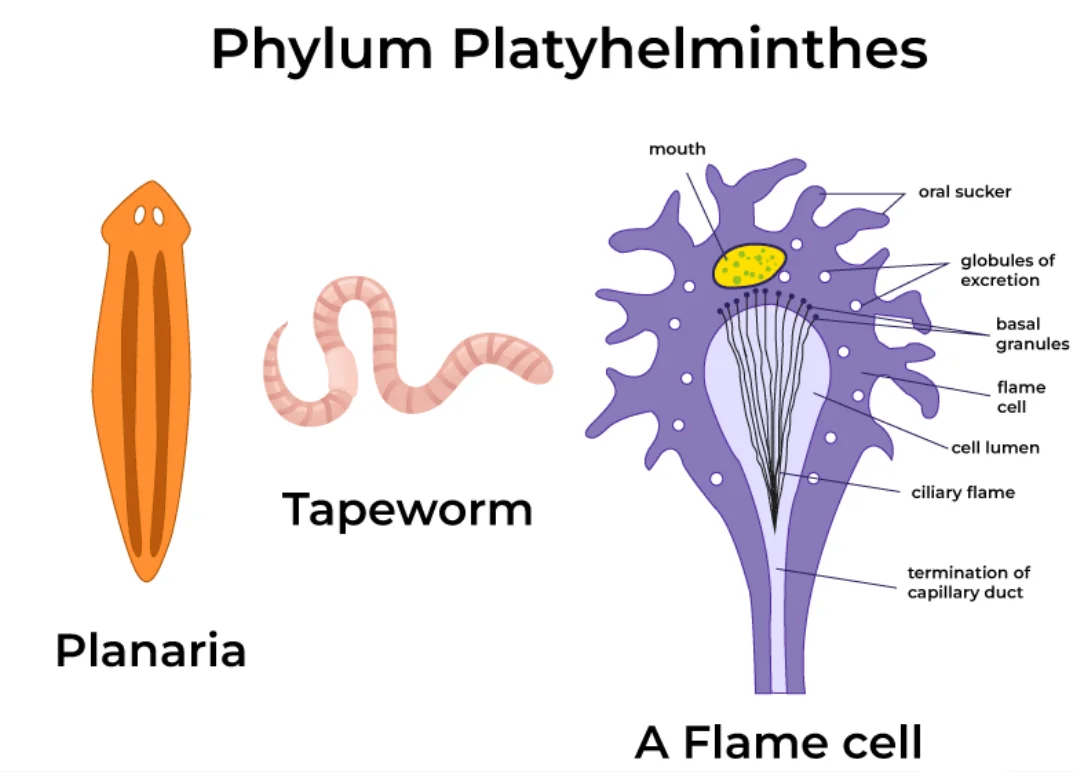
About: These are commonly known as Flatworms.
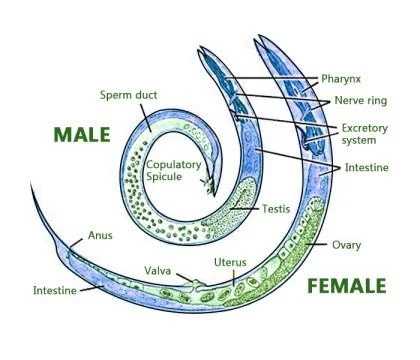
About: Phylum- Aschelminthes commonly called Roundworms.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
These few phyla showcase the incredible diversity within animals. Porifera’s simplicity contrasts with Cnidaria’s stinging defense and Platyhelminthes’ parasitic adaptations. Each phylum reflects a unique evolutionary path, enriching Earth’s animal diversity.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments