![]() May 28, 2024
May 28, 2024
![]() 1906
1906
![]() 0
0
Cells, the building blocks of life, come in all shapes and sizes. Scientists use cell classification to group them based on key features. This helps us understand why some cells contract our muscles, while others capture sunlight in plants.
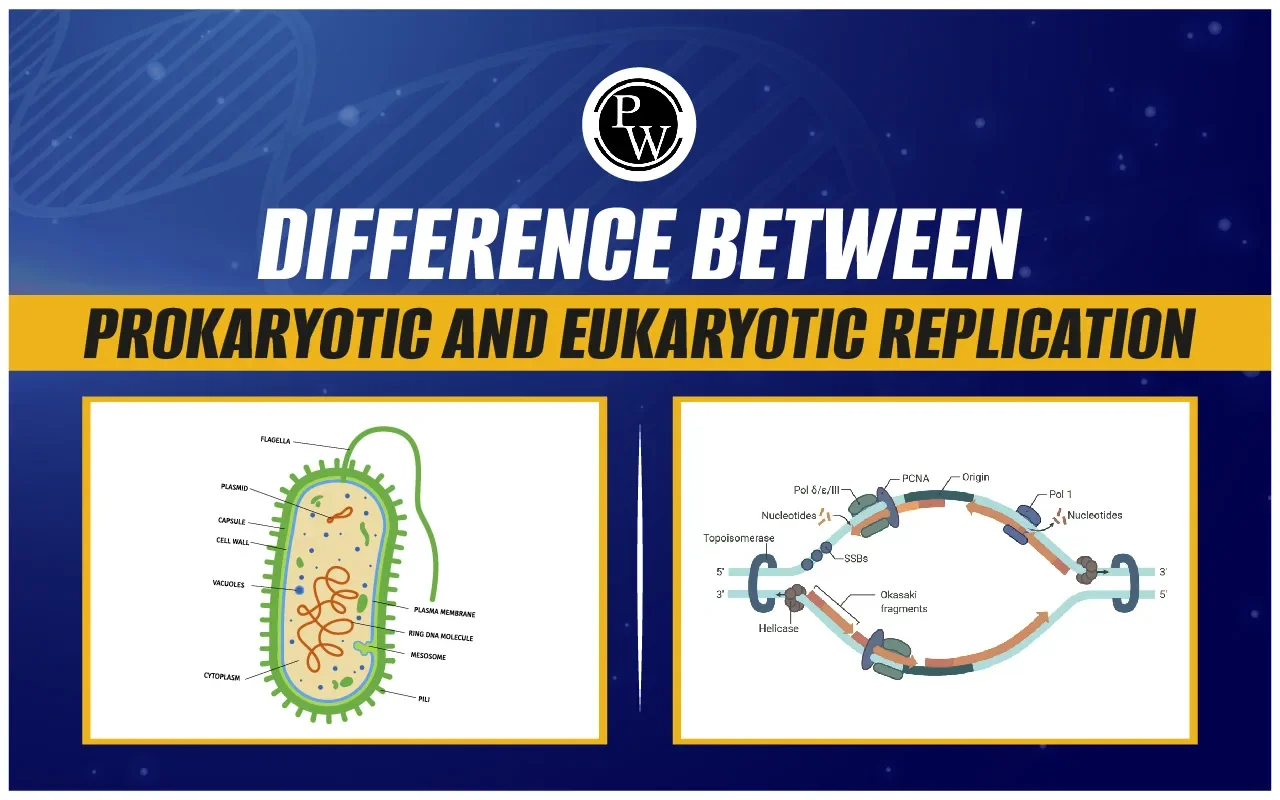
| Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells | ||
| Characteristic | Prokaryotic cell | Eukaryotic cell |
| Size of cell |
|
|
| Example |
|
|
| Nucleus |
|
|
| Membrane-enclosed
organelles |
|
|
| Flagella |
|
|
| Cell wall |
|
|
| Plasma membrane
with steroid |
|
|
| Cytoplasm |
|
|
| Ribosomes |
|
|
| Cell division |
|
|
| Number of
chromosomes |
|
|
| Sexual reproduction |
|
|
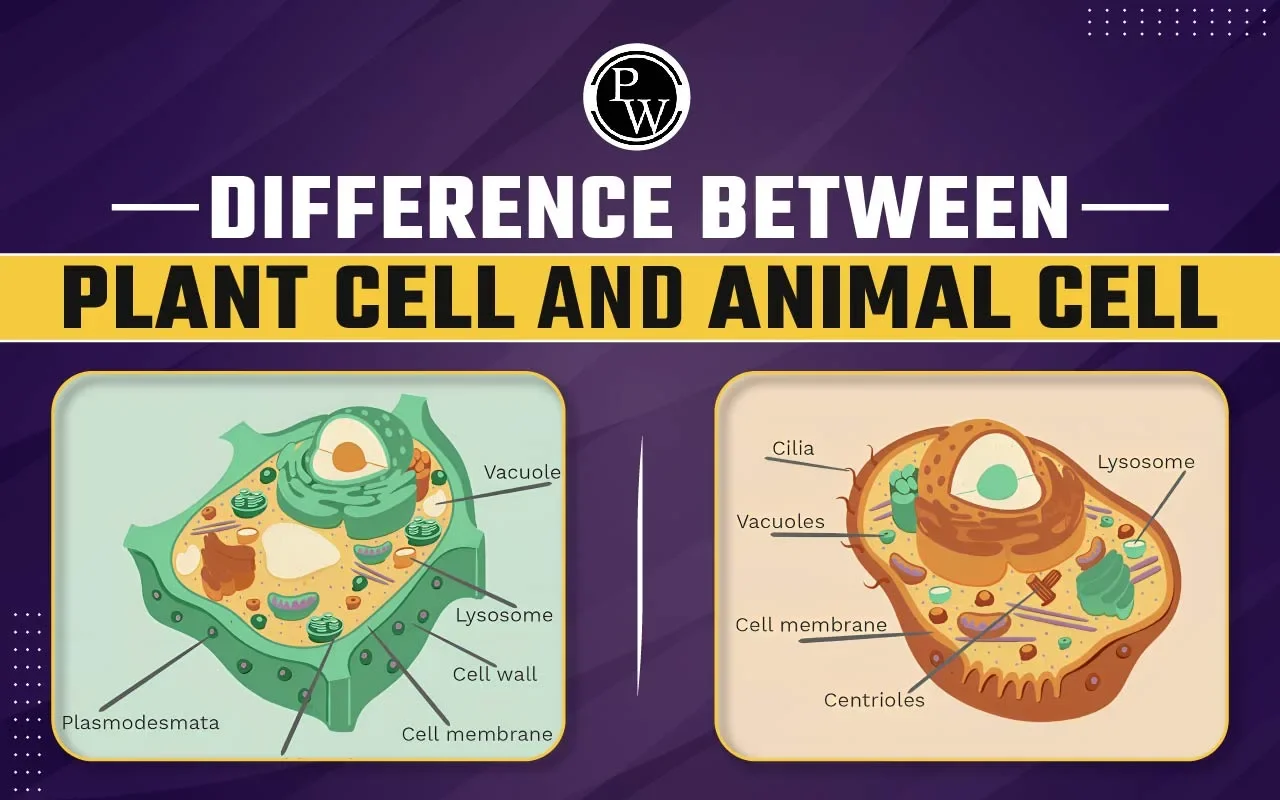
| Difference between Plant and Animal Cells | |
| Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Grouping cells by their structure (like having a nucleus or not) helps scientists understand what they can do. Muscle cells look different from nerve cells because they have different jobs! Cell classification is a way to organize this information, making it easier to learn about the amazing variety of life on Earth.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments