The scientific categorize the immense variety of living organisms boasts a rich history. Early efforts, like Aristotle’s classification based on basic morphological features, paved the way for more sophisticated systems. Modern taxonomy employs a hierarchical structure with seven ranks, from the all-encompassing kingdom to the highly specific species. This framework serves as a critical tool for organizing life and elucidating the intricate relationships between organisms.
Aristotle Classification
- Aristotle was the earliest to attempt a scientific classification, using simple morphological characteristics to classify plants into trees, shrubs and herbs.
- He also divided animals into two groups, those which had red blood and those that did not.
|
Taxonomy is the branch of science concerned with classification, especially of organisms.
|
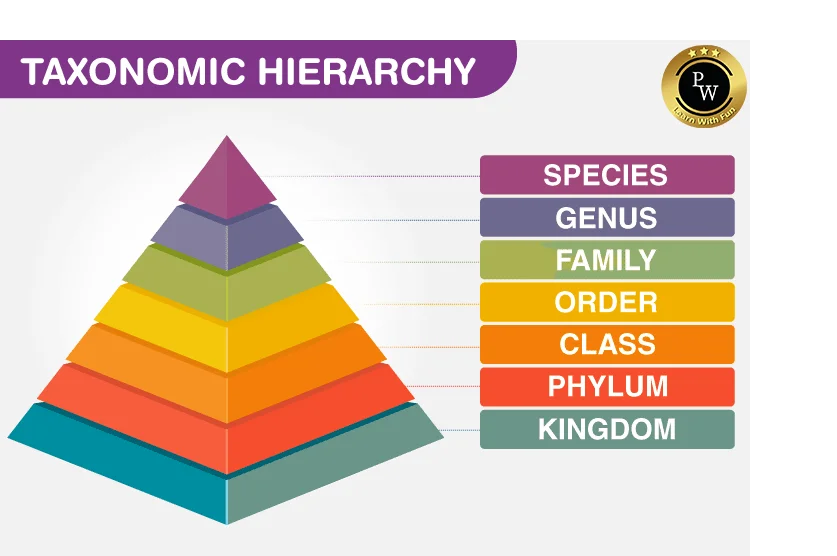
Taxonomic Category
There are seven main taxonomic ranks: kingdom, phylum or division, class, order, family, genus,
and species.
- Kingdom: The kingdom is the highest level of classification, with subcategories at other levels.
- Phylum: Phylum is the classification of living organisms to find some kind of physical similarities among organisms within the Kingdom. E.g., Phylum Arthropoda Under Kingdom Animalia.
- Class: A class is a rank used in the biological taxonomy of all organisms and is split into orders.
- Order: It is a group of organisms above the taxa family, sharing a similar set of characters. E.g., order primates contain humans and other apes.
- Family: It is a taxonomic group containing one or more genera sharing a common set of characteristics.
- Genus: Condensed group of related species having similar characters in common.
- Species: Its basic unit of classification. For example: Homo Sapiens.
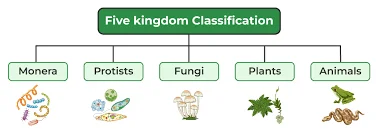
Five Kingdom Classification
R.H. Whittaker proposed a Five Kingdom Classification in 1969. The kingdoms classified by him were named Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia.
Kingdom Monera
- Bacteria are the sole members of the Kingdom Monera.
- Types: Some of the bacteria are autotrophic, i.e., they synthesise their own food from inorganic substrates.
- Features: They may be photosynthetic autotrophic or chemosynthetic autotrophic.
- Classification:
- Heterotrops: The vast majority of bacteria are heterotrophs, i.e. they depend on other organisms or on dead organic matter for food.
- E.g., Methanogens present in the gut of several ruminant animals, such as cows and buffaloes, and responsible for the production of methane (biogas) from the dung of these animals.
- Mycoplasma: They are organisms that completely lack a cell wall.
- They are the smallest living cells known and can survive without oxygen.
- Many mycoplasma induced diseases in animals and plants.
Kingdom Protista
- About: All single-celled eukaryotes are placed under Protista.
- Members of Protista are primarily aquatic.
- The protist cell body contains a well-defined nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
Algae
- These are members of a group of predominantly aquatic photosynthetic organisms of the kingdom Protista.
- Algae have many types of life cycles, and they range in size from microscopic Micromonas species to giant kelps that reach 60 metres (200 feet) in length.
- Their photosynthetic pigments are more varied than those of plants, and their cells have features not found among plants and animals.
- At least half of the total carbon dioxide fixation on earth is carried out by algae through photosynthesis.
- In addition to their ecological roles as oxygen producers and as the food base for almost all aquatic life, algae are economically important as a source of crude oil and as sources of food and a number of pharmaceutical and industrial products for humans.
- The taxonomy of algae is contentious and subject to rapid change as new molecular information is discovered.
- The study of algae is called phycology, and a person who studies algae is a phycologist.
|
Kingdom Fungi
- About: Fungi are multicellular, with a cell wall (made up of Chitin), organelles including a nucleus, but no chloroplasts.
- They have no mechanisms for locomotion.
- Example: Mushroom Belongs to this Phylum.
- They are saprophytic, decomposers, parasitic or coprophilous (growing on dung). [UPSC 2023]
-
- Mucormycosis (also called zygomycosis) is a serious but rare fungal infection caused by a group of moulds called mucormycetes.
- People get mucormycosis by coming in contact with the fungal spores in the environment.
- It is also termed as black fungus due to the necrosis of affected tissue of the patient’s skin which turns it into black.
- Mycorrhizal fungi play a crucial role in plant nutrient uptake, water relations, ecosystem establishment, plant diversity, and productivity of plants.
- They also protect plants against root pathogens and toxic stresses.
- The fundamental importance of mycorrhizal biotechnology in the restoration and to improve revegetation of disturbed mined lands is well recognised. [UPSC 2013]
|
Kingdom Plantae
- It includes all eukaryotic chlorophyll-containing organisms commonly called plants.
- A few members are partially heterotrophic such as the insectivorous plants or parasites.
- Bladderwort and Venus fly trap are examples of insectivorous plants and Cuscuta is a parasite.
- The plant cells have an eukaryotic structure with prominent chloroplasts and cell walls mainly made of cellulose.
Conclusion
The Five Kingdom Classification, proposed by R.H. Whittaker, categorizes life into distinct groups based on cellular complexity, nutritional mode, and locomotion. These kingdoms include Monera (bacteria), Protista (single-celled eukaryotes), Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. While this system provides a valuable foundation for understanding life’s diversity, ongoing research and discoveries using advanced techniques may necessitate further refinements in our approach to organism classification.


