![]() May 28, 2024
May 28, 2024
![]() 2511
2511
![]() 0
0
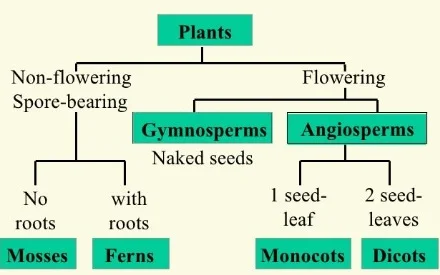
The plant kingdom, encompassing a staggering diversity of life forms, necessitates a structured approach for comprehension. Plant classification offers a hierarchical system, grouping plants based on shared characteristics like vascular systems, seed formation, and reproductive structures. This framework empowers botanists to delve into plant evolution, ecological roles, and their critical contributions to Earth’s biosphere.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
Plant classification provides a roadmap for navigating the remarkable diversity of the plant kingdom. By grouping plants based on shared features, scientists gain insights into evolutionary relationships, habitat preferences, and ecological functions. This vital framework underpins further exploration, enabling researchers to unlock the secrets of plant diversity and its profound influence on life on our planet.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments