![]() April 26, 2024
April 26, 2024
![]() 8823
8823
![]() 0
0
In 1912, Alfred Wegener introduced the “continental drift theory,” which revolutionized our understanding of Earth’s geography. His theory illuminated how oceans and continents have shifted over time. Wegener’s groundbreaking idea sparked a new era in geology, transforming our perception of the planet’s history and evolution.
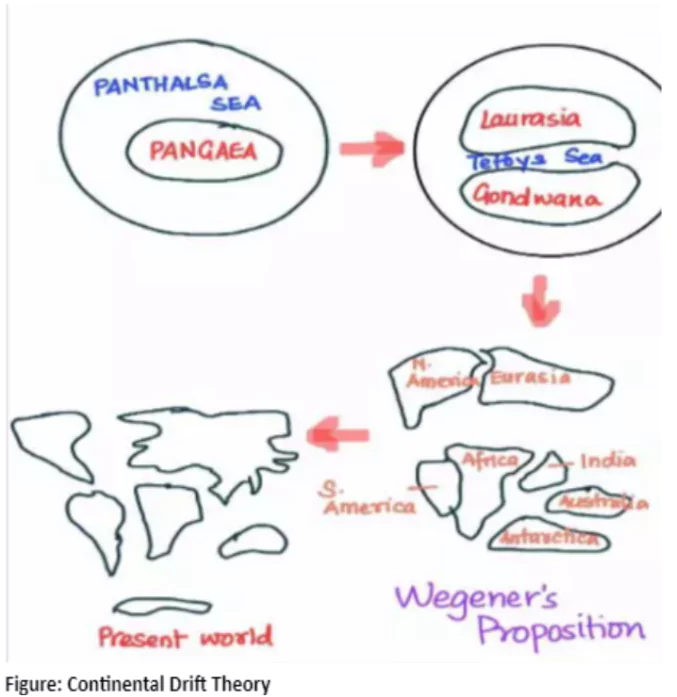
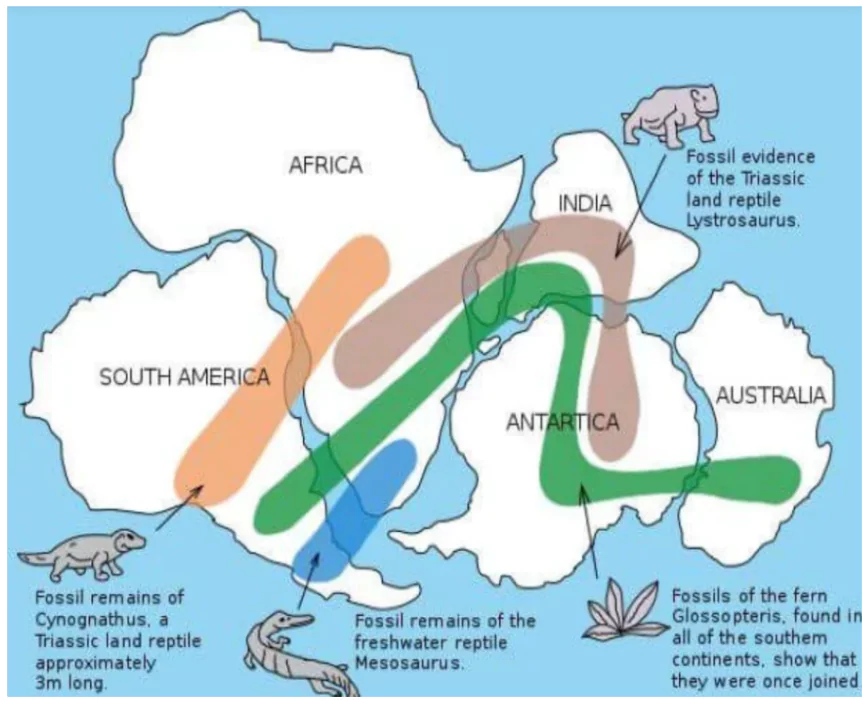 Bullard’s 1964 Computer-Generated Map: A computer-generated map aligning the Atlantic margin, proving remarkably accurate when matched at the 1,000 fathom line instead of the shoreline.
Bullard’s 1964 Computer-Generated Map: A computer-generated map aligning the Atlantic margin, proving remarkably accurate when matched at the 1,000 fathom line instead of the shoreline.| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
| Related Articles | |
| Continental Drift Theory | THE FORMATION OF EARTH: GEOLOGICAL HISTORY |
| Plate Tectonics: Definition, Feature and Evolution of Indian Plate | 7 Continents and 5 Oceans in Order of the World |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments