Exogenic forces, also known as external forces or land-wearing forces, are natural processes that shape the Earth’s surface from the outside. They work over long periods, like thousands or millions of years. These forces include things like erosion by water, wind, and ice, as well as movements of the Earth’s crust caused by things like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. They’re the things that wear down mountains, carve out valleys, and shape the landscape we see around us.
Understanding Exogenic Forces in Geomorphology
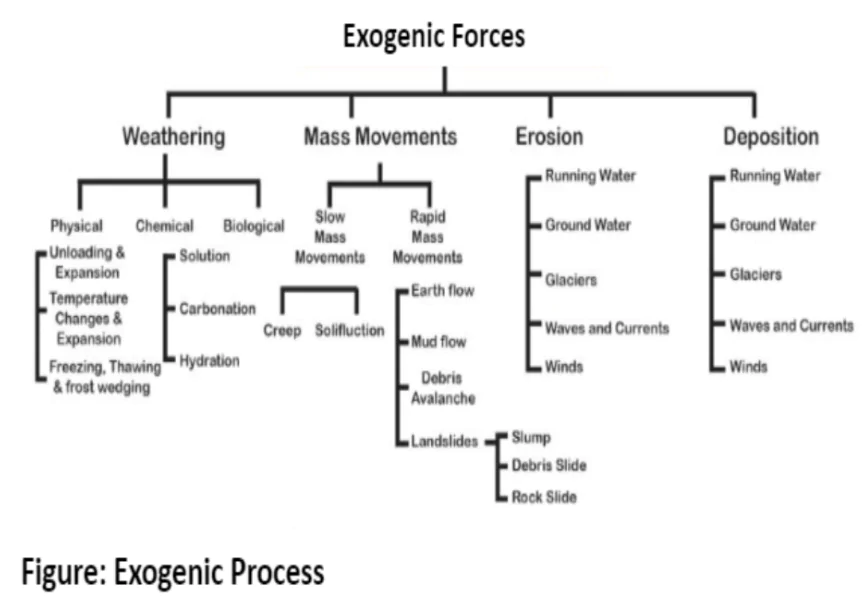
- External Forces: They originate at or near the Earth’s surface, are influenced by solar energy and tectonic gradient, and draw energy from the atmosphere.
- Characteristics: They are slow and gradual forces and are also known as denudational/ destructional/ exogenetic processes.
- Actions of exogenic forces result in wearing down (degradation) of relief/ elevations and filling up (aggradation) of basins.
- Rock type and structure significantly affect the intensity of exogenic processes.
- Climatic factors: Temperature, precipitation, insolation, wind patterns, etc. affect exogenic processes.
- Gradation: The phenomenon of wearing down of relief variations through erosion is known as gradation.
- Denudation: All the exogenic geomorphic processes are covered under a general term, denudation (weathering, mass wasting/movements, erosion, and transportation).
Weathering
- Definition: Weathering is defined as the mechanical disintegration and chemical decomposition of rocks through the actions of various elements of weather and climate. It is an In-Situ or Onsite process.
- Factors Influencing Weathering: Geology, weather and climate, topography, and vegetative factors.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Classification of Weathering processes
Chemical Weathering Processes
- It includes solution, carbonation, hydration, oxidation and reduction. Water, air and heat are vital for accelerating chemical reactions.
- Solution: Dissolution in water or acid. Minerals like calcium carbonate and calcium magnesium bicarbonate present in limestone are soluble in water containing carbonic acid.
- Carbonation: Process of atmospheric carbon dioxide causing solution weathering; common process helping in breaking down of felspar and carbonate minerals.
- Hydration: Minerals take up water and expand which increases the volume of the material (Calcium sulphate+water= Gypsum).
- Continued repetition leads to physical weathering through exfoliation and granular disintegration.
- Oxidation and Reduction: In oxidation, rock breakdown occurs due to the disturbance caused by addition of oxygen.
- When oxidized minerals are placed in an environment where oxygen is absent (eg: below water table/ waterlogged areas) reduction takes place.
Physical or Mechanical Weathering Processes
- Physical or mechanical weathering refers to a process that relies on applied forces. Most of the processes are caused by thermal expansion and pressure release. These forces could be gravitational forces, expansion forces, and water pressures.
- Unloading and Expansion: In areas of curved ground surface, arched fractures tend to produce massive sheets or exfoliation slabs of rock. Large smooth rounded domes called exfoliation domes are a result of this process.
- Temperature Changes and Expansion: Most effective in dry climates and high elevations where diurnal temperature changes are drastic.
- Freezing, Thawing and Frost Wedging: Most effective at high elevations in mid-latitudes where freezing and melting are often repeated.
- Freezing involves the transformation of water into ice.
- Thawing is the process of melting ice back into water, and
- Frost Wedging is the mechanical breakup of rocks caused by repeated freezing and thawing cycles.
- Salt weathering: Salts in rocks expand due to thermal action, hydration and crystallisation. Salt crystallisation is the most effective of all salt weathering processes.
- Exfoliation occurs when curved sheets of material peel away from rocks due to temperature-induced expansion and contraction.
- Exfoliation domes are large and smooth rounded domes formed due to unloading and expansion of rocks.
- Exfoliation tor is smooth surfaced and rounded small to big size boulders, formed due to temperature changes and expansion in rocks.
|
Biological Weathering
- It involves organisms and includes:
- Organism Growth: It involves burrowing and wedging activities by creatures like earthworms, termites, and rodents that expose fresh surfaces.
- Organic Matter Decay: Decomposing plant and animal matter generates humic, carbonic, and other acids, promoting the decay and solubility of certain elements.
- Root Pressure: mechanically breaking apart earth materials.
Erosion And Deposition
- Erosion: This involves the acquisition and transportation of rock debris by various geomorphic agents (running water, groundwater, glaciers, wind, and waves). Abrasion by rock debris carried by these geomorphic agents also aids greatly in erosion.
- Though weathering aids erosion, it is not a precondition for erosion to take place. Weathering, mass-wasting and erosion are degradational processes.
- Deposition: It is a consequence of erosion; and occurs in the reverse order of particle size, with coarser materials depositing first.
- Agents of Deposition: running water, glaciers, wind, waves, and groundwater.
Conclusion
Exogenic forces, covering weathering, erosion, and deposition processes, play a vital role in shaping Earth’s surface over long periods. Through chemical, physical, and biological actions, these forces gradually wear down and reshape landscapes, contributing to the dynamic evolution of the Earth’s topography.

