![]() June 4, 2024
June 4, 2024
![]() 1041
1041
![]() 0
0
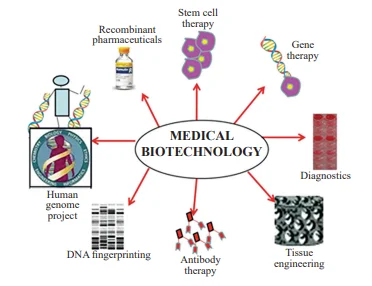
Emerging biological technologies are revolutionizing biology. Neuroinformatics unlocks nervous system mysteries, while neuroprosthetics offer hope for those with neurological conditions. Microbial fuel cells promote sustainability, and biotechnology drives innovation in healthcare and agriculture.
Emerging Technologies in Biology
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
These cutting-edge technologies promise to transform biology, medicine, and our environment. From brains to biofuels, the future holds immense potential. Responsible development and collaboration are key to unlocking the benefits for all.
| Related Articles | |
| Biotechnology Applications: Transforming Industries, Agriculture, and Healthcare | Biofuels |
| Genetic Engineering: Definition, Process, Tools & Mechanism | Soil Microbial Fuel Cell (SMFC) |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments