![]() June 14, 2024
June 14, 2024
![]() 5220
5220
![]() 0
0
Ocean energy, encompassing thermal gradients, tides, and waves, is a vast renewable resource with significant potential for coastal regions. Despite its promise, India has yet to fully realize its commercial capacity, though it holds an estimated potential of 54 GW. This emerging sector presents both opportunities and challenges for companies, given its undeveloped market structure.
Tide Generation: Caused by the gravitational pull of the sun and moon, and the Earth’s rotation.

Energy Generation: Captures energy from surface waves or pressure fluctuations below the surface.
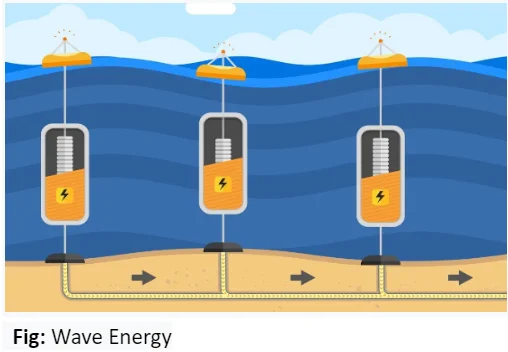
Variable energy supply dependent on wave conditions.
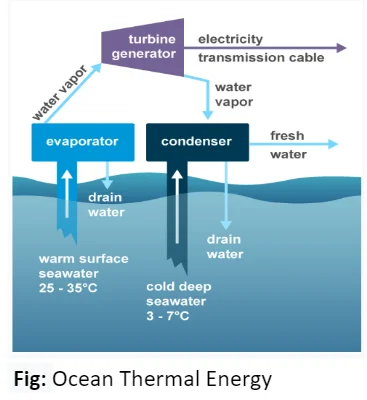
Energy Generation: Converts solar energy trapped by the ocean into usable energy.
| Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is derived from the natural heat of the Earth, typically from areas with volcanic or tectonic activity.
|
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Ocean energy offers a promising avenue for sustainable power generation, with various methods like tidal, wave, and thermal energy.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments