India’s climate, characterized by distinct seasonal patterns, is influenced by various factors. These include the Coriolis force, latitude, altitude, the Himalayas, land-water distribution, and proximity to the sea. Understanding these factors helps comprehend India’s diverse weather conditions and climatic variations.
Understanding Key Factors Affecting India’s Climate
- Climate: refers to the sum total of weather conditions and variations over a large area for a long period of time.
 The Climate of India is “monsoon” type (characterized by a distinct seasonal pattern) which is found mainly in South Asia and South-East Asia.
The Climate of India is “monsoon” type (characterized by a distinct seasonal pattern) which is found mainly in South Asia and South-East Asia.
- Weather: refers to the state of the atmosphere over an area at any point of time. India’s climate is controlled by a number of factors
- Coriolis Force: An apparent force caused by the earth’s rotation. The Coriolis force is responsible for deflecting winds towards the right in the northern hemisphere and towards the left in the southern hemisphere. This is also known as ‘Ferrel’s Law’.
- Factors Affecting India’s Climate: India’s climate is controlled by a number of factors which can be divided into two groups
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
A. Factors Related to Location and Relief
- Latitude: The Tropic of Cancer divides India, placing the northern part in the sub-tropical and temperate zones, and the southern part in the tropical zone.
- Altitude: Elevated regions are cooler due to the decline in temperature with height.
- The Himalayas: It shields India from cold northern winds originating near the Arctic. They also help trap the monsoon winds.
- Distribution of Land and Water: Differential heating of land and sea (water heats up or cools down slowly) creates different air pressure zones in different seasons in the Indian subcontinent that cause reversal in the direction of monsoon winds.
- Proximity to the Sea: The coastal areas have a balanced climate and distant locations from the sea, experience more pronounced seasonal contrasts.
- Relief: India’s topography influences temperature, rainfall, and wind patterns.
- Example: The windward side of the Western Ghats receives high rainfall, while the leeward side remains relatively dry.
B. Factor Related to Air Pressure and Wind
- Surface Pressure and Wind:
- Winter: High-pressure area north of the Himalayas leads to cold dry winds blowing southward towards low-pressure areas over southern oceans
- Summer: Low-pressure areas develop over interior Asia and northwestern India, causing a reversal of wind direction
- Southwest Monsoon Winds: Emerge moving from high-pressure areas over the southern Indian Ocean to low-pressure regions over the Indian subcontinent
- These winds gather moisture over warm oceans and bring widespread rainfall over mainland India
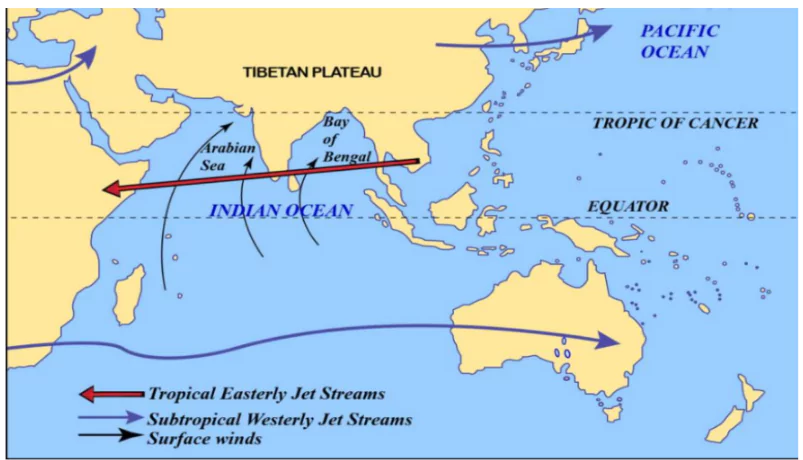
- Jet Stream and Upper Air Circulation:
-
- Jet streams exhibit peaks (ridges) and troughs.
- Ridges: Occur when warm air collides with cold air, inducing high pressure below.
- Thus, ridges produce anticyclonic conditions
- Troughs: Occur where cold air descends into warm air, generating low pressure below.
- It results in cyclonic conditions at the surface.
- Weakening Jet Streams: It is caused due to temperature contrasts between subtropical and temperate regions that drive these phenomena.
- Western Cyclonic Disturbances: originate from the Mediterranean region and affect the northwestern parts of India, bringing rain and sometimes causing floods.
- Tropical Cyclones: form over warm ocean waters and can affect India’s coastal regions, causing heavy rainfall, strong winds, and storm surges
Conclusion
India’s climate is shaped by various factors, including its geographical location, relief features like the Himalayas, and atmospheric conditions such as jet streams and monsoon winds. These elements interact to create the unique climate patterns experienced across the Indian subcontinent, affecting temperature, rainfall, and wind patterns.
 The Climate of India is “monsoon” type (characterized by a distinct seasonal pattern) which is found mainly in South Asia and South-East Asia.
The Climate of India is “monsoon” type (characterized by a distinct seasonal pattern) which is found mainly in South Asia and South-East Asia. 