![]() April 26, 2024
April 26, 2024
![]() 12967
12967
![]() 0
0
There are diverse geological features created by volcanic activity, these are collectively known as volcanic landforms. They include volcanoes, lava flows, ash deposits, volcanic cones, and calderas. These features result from the eruption of magma onto the Earth’s surface or its intrusion beneath the surface. Volcanic landforms can vary widely in size, shape, and composition, and they play a significant role in shaping the Earth’s surface and influencing local ecosystems.
Common Types of Volcanic Landforms are mentioned below:
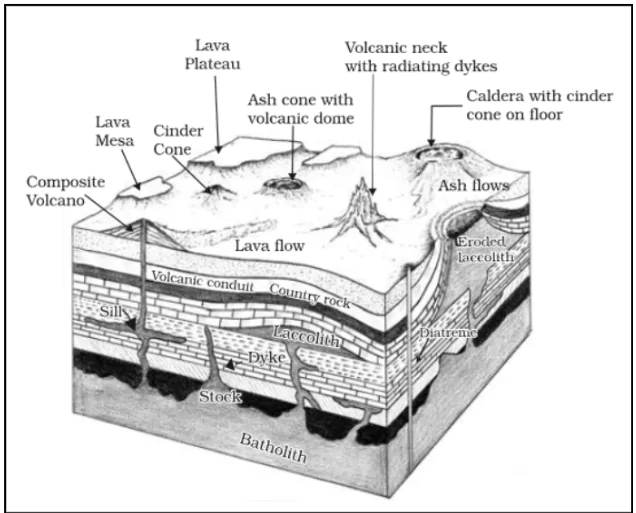 Plutonic Rocks: These rocks cool within the crust.
Plutonic Rocks: These rocks cool within the crust.
| 1. StratoVolcano |
|
| 2. Parasite Cones |
|
| 3. Shield Volcano
/BASIC LAVA DOME |
|
| 4. Lava Dome |
|
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
| Related Articles | |
| Volcanic Landforms: Geological Formation, Types, and Impact | INTERIOR OF THE EARTH: FROM CRUST TO CORE |
| Earth’s Interior | ECOSYSTEM: COMPONENTS, FUNCTIONS AND INTERACTIONS |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>

Latest Comments