![]() May 1, 2024
May 1, 2024
![]() 6313
6313
![]() 0
0
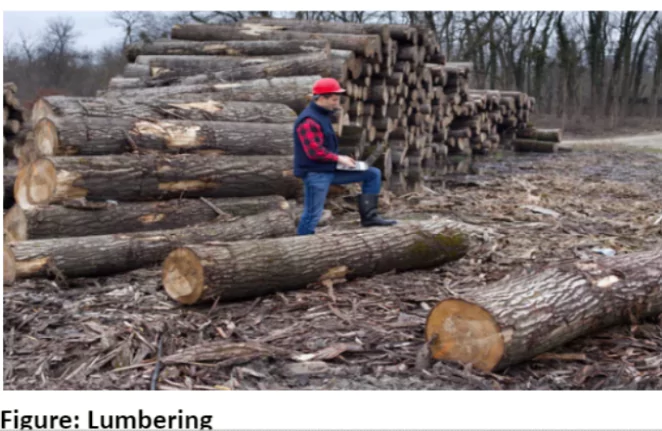
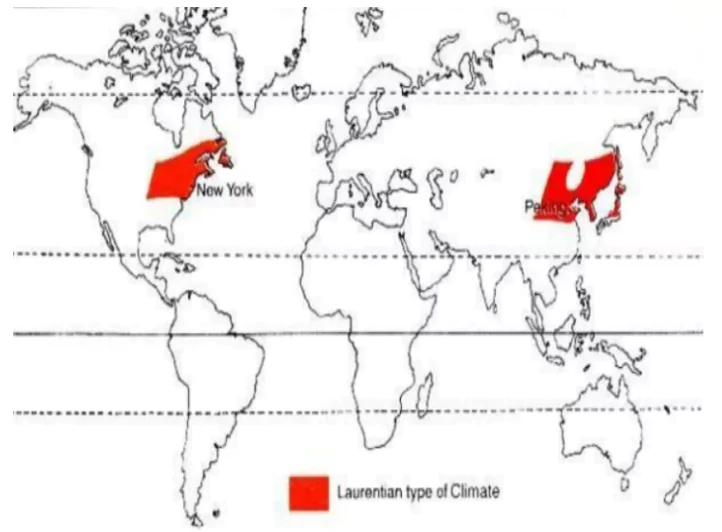
The Laurentian climate sits between British and Siberian types, blending maritime and continental features. It spans North America and Eastern Asia, shaping unique weather patterns and vegetation. Winters bring freezing temperatures and snow, while summers are warm and moist, thanks to off-shore currents. Rainfall is steady, with a summer peak due to easterly winds. The climate supports lush forests and vital economic activities like lumbering and fishing.

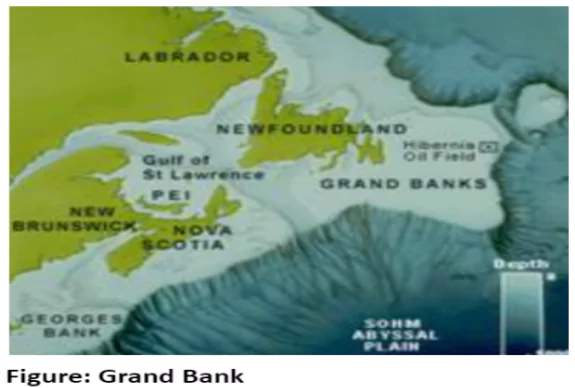 The fishing industry provides significant employment and export opportunities, with modern techniques ensuring efficient harvesting.
The fishing industry provides significant employment and export opportunities, with modern techniques ensuring efficient harvesting.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments