![]() April 1, 2024
April 1, 2024
![]() 11756
11756
![]() 0
0
Municipalities also known as Urban local self-government refers to the system of governance at the local level within urban areas. It encompasses municipalities, municipal corporations, and other local bodies responsible for administering cities and towns. Urban local self-government bodies are typically headed by elected representatives, such as mayors or chairpersons, and function under the framework established by state governments. They play a vital role in addressing the needs and challenges of urban populations, promoting development, and enhancing the quality of life in urban areas across India.
The constitutionalizing of the urban government system was achieved through the 74th Constitutional Amendment Act of 1992.
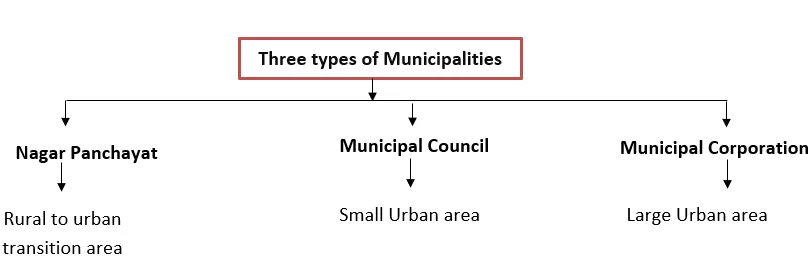
| The Governor is required to designate a transitional area, a smaller urban area, or a larger urban area, taking into consideration factors such as the extent of the area, population density, revenue generated for local administration, percentage of non-agricultural employment, economic significance, and any other factors deemed appropriate. |
Composition (Article 243 R)
Election to the Municipalities: Article 243 ZA
Reservation: Article 243 T
Bar to Interference by Courts in Electoral Matters: Article 243 ZG
Disqualification: Article 243 V
Duration: Article 243 U
Powers, Functions, and Finances Determined by State Legislature
|
Subjects under Twelve Schedule |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other provisions
Note:
|
Conclusion
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments