India’s natural vegetation is rich and varied, influenced by climate and soil diversity. From lush tropical forests to arid thorn forests, each biome supports unique flora and fauna. Understanding these ecosystems is essential for environmental conservation and sustainable development.
India’s Natural Vegetation: Forest Diversity and Conservation Efforts
India boasts diverse natural vegetation due to variations in climate and soil. Indian forests can be categorized into distinct groups:
- Tropical Evergreen and Semi-Evergreen Forests
- Tropical Deciduous Forests
- Tropical Thorn Forests
- Montane Forests
- Littoral and Swamp Forests
A. Tropical Wet Evergreen
- Found in: Warm and humid areas with precipitation of over 200 cm and mean annual temperature above 22℃.
- Location: Western slope of Western Ghat, Lakshadweep, Andaman & Nicobar Island & Tamil Nadu Coast, Purvanchal hills [UPSC 2015]
- Characteristics: Well-stratified forest, featuring layers near the ground covered in shrubs and creepers, followed by short and tall trees, creating a multi-layered forest; Leaf litter decomposes faster than in any other biome and as a result the soil surface is often almost bare. [UPSC 2013, 2021]
- Flora: Ebony, Mahogany, Rosewood, rubber, Aini, Jackfruit [UPSC 2023] & Epiphytes.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
B. Tropical Semi Evergreen Forests
- Location: Western coast, Assam, Lower slopes of the Eastern Himalayas, Odisha, Andamans
- Characteristics:
-
- Located in regions with lower rainfall.
- Mixture of evergreen and moist deciduous trees with the presence of under growing climbers.
- Transitional forests between tropical evergreen and tropical deciduous forests and are less dense;
- Dry season is not short like a tropical evergreen forest.
- Flora: White Cedar, Hollock, and Kail.
C. Tropical Deciduous Forests
- These are the most widespread forests in India and are also called monsoon forests which receive rainfall between 70-200 cm.
|
Classification on the basis of the availability of water: |
| Moist Deciduous Forests |
Dry Deciduous Forests |
| Rainfall |
100-200 cm |
70-100 cm |
| Location |
Northeast States along foothills of Himalayas, eastern slopes of Western Ghats & Odisha, Chota Nagpur Plateau, Manipur & Mizoram. |
Rainier areas of Peninsula & Plains: Uttar Pradesh & Bihar. (Transitions to moist deciduous on the wetter margins, while on the drier margins to thorn forests.) |
| Flora |
Teak, sal, shisham, hurra,
mahua, amla, semul, kusum, and sandalwood etc. [UPSC 2015, 2023] |
Tendu, palas, amaltas, bel, khair, axlewood etc. |
D. Tropical Thorn Forests
- Rainfall: less than 50 cm.
- Location: Semi-arid areas of southwest Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
- Characteristics:
-
- Adaptations to drier regions to conserve water – Succulent Stems; Thick and small leaves; Long roots penetrating deep into the soil [UPSC 2013].
- Plants remain leafless for the most part of the year and give an expression of scrub vegetation.
- Flora: babool, ber, wild date palm, khair, neem, khejri, palas, acacias, palms, euphorbias and cacti etc.; Tussocky grass as the undergrowth.
E. Montane Forests [UPSC 2014]
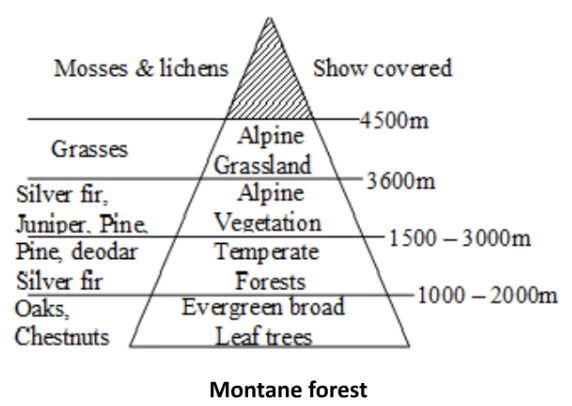
1. Northern Mountain Forests:
- Succession of vegetation with the altitude from the tropical to the tundra.
- Deciduous Forests: in the foothills of the Himalayas;
- Succeeded by the wet temperate type of forests between an altitude of 1,000-2,000 m.
- Evergreen Broadleaf Trees: such as oak and chestnut are predominant in the higher northeastern hill ranges, hilly areas of West Bengal and Uttarakhand.
- Pine Forests: between 1,500-1,750m in this zone, with Chir Pine as a very useful commercial tree. Deodar (used in construction) is found mainly in the western part of the Himalayas. Chinar and walnut (support Kashmir handicrafts) belong to this zone.
- Blue Pine and Spruce: found at altitudes of 2,225-3,048 m. Temperate grasslands are also found in many places in this zone. There is a transition to Alpine forests and pastures in the higher reaches.
- Silver firs, junipers, pines, birch, rhododendrons, etc. occur between 3,000-4,000 m.
- Transhumance: Tribes like the Gujjars, Bakarwals, Bhotiyas and Gaddis use pastures for transhumance.
- Tundra: At higher altitudes surpassing 4,000 meters, mosses and lichens as part of the tundra landscape are present.
- Himalayas have a thicker vegetation cover on southern slopes because of relatively higher precipitation than drier north-facing slopes.
2. Southern Mountain Forests
- Found In: three distinct areas of Peninsular India: Western Ghats, Vindhyas and Nilgiris.
- Temperate Vegetation: At higher regions and subtropical (lower regions ) in Western Ghats, especially in Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Karnataka as they are closer to the tropics, and only 1,500 m above sea level,
- Shola Forests: The temperate forests are called Sholas also known as rolling grassland in the Nilgiris, Anaimalai and Palani hills.
- Example: Trees of economic significance in these forests: Magnolia, laurel, Cinchona and Wattle.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
F. Mangroves
- They grow along the coasts in salt marshes, tidal creeks, mud flats and estuaries and consist of salt-tolerant species of plants.
- Areas: Deltas of Ganga, Mahanadi, Krishna, Godavari and Kaveri; In the Ganga-Brahmaputra delta, Sundari trees are found, which provide durable hard timber.
Medicinal Plants
- Sarpagandha: used to treat blood pressure; found only in India.
- Jamun: Powder of the seed is used to control diabetes; juice is used to prepare vinegar, which is carminative and diuretic and has digestive properties.
- Arjun: Fresh juice of leaves is a cure for earaches; also used to regulate blood pressure.
- Babool: Leaves are used as a cure for eye sores; Its gum is used as a tonic.
- Neem: Antibiotic and antibacterial properties.
- Tulsi: Cures cough and cold.
- Kachnar: Cures asthma; Buds and roots are good for digestive problems.
|
Sacred Groves
- Definition: Sacred groves refer to natural vegetation that is protected by a certain community due to religious reasons. It is usually dedicated to a local deity.
- Found In: These sacred groves are found in Himachal Pradesh, Kerala, Rajasthan, Bihar, Meghalaya and Maharashtra;
- Shipin: in Himachal Pradesh is believed to be the largest deodar grove;
- Devrais: The groves in Maharashtra;
- Umang Lai: (sacred grove) is found in Manipur.
- The Festival of Lai Haraoba is celebrated especially in regard to these holy sacred groves.
| National Forest Policy 1952: Bring 33 percent of the geographical areas under forest cover. |
Social Forestry
- Management and protection of forests and afforestation on barren lands with the purpose of helping in environmental, social and rural development. The National Commission on Agriculture (1976) has classified social forestry into three categories:
- Urban Forestry: Raising and management of trees on public and privately owned lands in and around urban centers.
- Rural Forestry: Agroforestry – Raising trees and agriculture crops on the same land; Community Forestry – Raising of trees on public or community land.
- Farm Forestry: Farmers grow trees for commercial and non-commercial purposes on their farm lands, the margins of agricultural fields etc.
- Protected Forest : An area notified under the provisions of Indian Forest Act or the State Forest Acts having limited degree of protection. In Protected Forests, all activities are permitted unless prohibited.
- Reserved Forest : An area notified under the provisions of Indian Forest Act or the State Forest Acts having full degree of protection. In Reserved Forests, all activities are prohibited unless permitted.
- Unclassed Forest : An area recorded as forest but not included in reserved or protected forest category. Ownership status of such forests varies from state to state.
- Virgin Vegetation: Virgin vegetation refers to plant communities that have developed naturally without human interference and have remained untouched by human activities.
|
Conclusion
India’s natural vegetation, including tropical evergreen forests and mangroves, is crucial for biodiversity and ecosystem stability. Efforts like social forestry and protected area management aim to preserve these invaluable resources for future generations. By adopting sustainable practices, we can ensure the preservation of our diverse natural heritage.

