![]() June 14, 2024
June 14, 2024
![]() 2798
2798
![]() 0
0
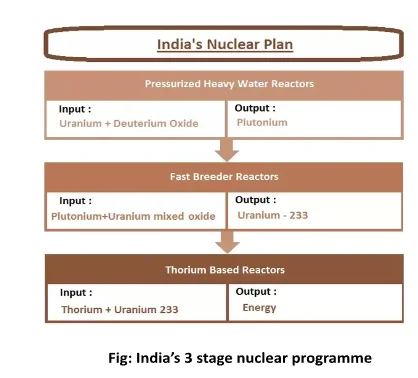
Nuclear energy, derived from nuclear reactions such as fission and fusion, plays a crucial role in India’s electricity generation. As the fifth-largest source of power, it significantly contributes to the nation’s energy mix. India’s ambitious Three-Stage Nuclear Power Program, proposed by Dr. Homi J. Bhabha, aims to create a self-sustaining nuclear industry. With multiple institutions involved in research and development, India is focused on harnessing nuclear energy for peaceful and innovative applications.
Establishment: Established in 1954, It is a premier multidisciplinary nuclear research facility located in Trombay, Mumbai, India.
It serves as a vital platform for international collaboration and innovation in the field of nuclear energy.
The Atomic Minerals Directorate for Exploration and Research (AMD) is an Indian government organisation responsible for exploring, assessing, and researching atomic minerals in the country.
India’s nuclear power and energy policy reflects a complex balancing act between diverse priorities and challenges.
Command and control of nuclear weapons is the authority and direction exercised by the President over nuclear weapon operations.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
India’s nuclear energy sector is poised for substantial growth, with plans to significantly increase its capacity by 2031.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments