![]() May 15, 2024
May 15, 2024
![]() 21681
21681
![]() 0
0
The Peshwas, meaning “Foremost Ministers,” played a crucial role in shaping the Maratha Empire’s power and influence from 1713 to 1818. With their strategic leadership and military prowess, they expanded Maratha territory and consolidated their rule across the Indian subcontinent.

| Confederacy: Under this system, each Maratha chief was assigned a territory that could be administered autonomously. | |
| Confederacy | Area |
| GAEKWADS | Baroda |
| BHONSLES | Nagpur |
| HOLKARS | Indore |
| SCINDIAS | Gwalior |
| PESHWAS | Poona |
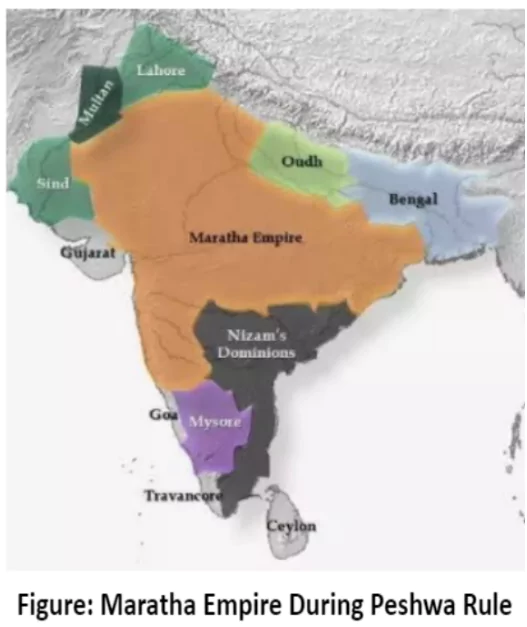 Expanded the Maratha rule from Cuttack (Krishna) to Attock.
Expanded the Maratha rule from Cuttack (Krishna) to Attock.
|
Battle of Udgir (1760)
|
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
The era of the Peshwas marked a significant chapter in Indian history, characterized by territorial expansion, diplomatic maneuvers, and military campaigns. Despite facing challenges such as the Third Battle of Panipat, their legacy endured, influencing subsequent developments in the region for years to come.
| Related Articles | |
| THE RISE OF MARATHAS (1674-1818) | MUGHAL PERIOD (1526-40 AND 1555-1857) |
| third battle of Panipat | PORTUGUESE IN INDIA (1505-1961) |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments