![]() June 11, 2024
June 11, 2024
![]() 1719
1719
![]() 0
0
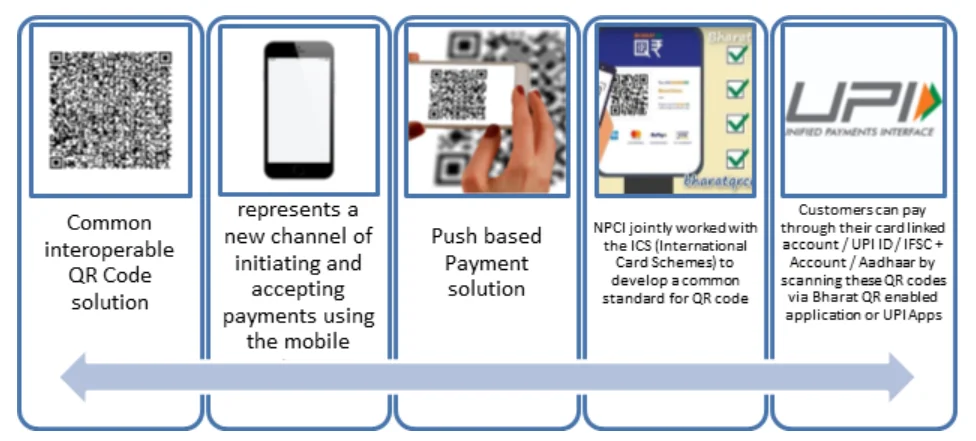
QR technology, known as Quick Response Code, revolutionizes data storage and retrieval through its two-dimensional barcode system, offering vast applications from product tracking to marketing. Its capacity to store diverse information and ease of scanning with digital devices like smartphones make it an indispensable tool in various fields.
BHARAT QR facilitates seamless transactions across banks for all cardholders and UPI users by allowing them to pay for purchases at merchant outlets through their bank’s application.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
| Related Articles | |
| BANKS IN INDIA | CRYPTOCURRENCY |
| General Insurance Council Launches Cashless Everywhere Initiative | Electron Orbits: Distribution Patterns and Valency in Atomic Structures |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments