![]() May 2, 2024
May 2, 2024
![]() 18176
18176
![]() 0
0
A human settlement is defined as a place inhabited more or less permanently. Whether rural or urban, are vital components of society. Human Settlement means a cluster of dwellings of any type or size where human beings live. While rural areas are often associated with villages and hamlets, defining them isn’t always straightforward due to their diverse characteristics. From clustered villages to dispersed hamlets, rural settlements vary widely and present unique challenges and opportunities for planners and policymakers.
Types of Rural Settlements
| Settlement Type | Characteristics | Examples/Locations |
| Clustered | Compact or closely built up area of houses with a recognisable pattern. | Found in fertile alluvial plains and northeastern states, Bundelkhand region, and areas in Rajasthan for water scarcity reasons. |
| Semi-Clustered | Results from fragmentation of a large compact village or clustering in a dispersed settlement. Dominant community occupies the central part. | Found in the Gujarat plain and parts of Rajasthan. |
| Hamleted | Settlement fragmented into several units bearing a common name (e.g., panna, para, palli, nagla, dhani). | Found in the middle and lower Ganga plains, Chhattisgarh, and lower valleys of the Himalayas. |
| Dispersed | Appears as isolated huts or hamlets in remote areas due to the terrain and fragmented land resource base. | Found in Meghalaya, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, and Kerala |
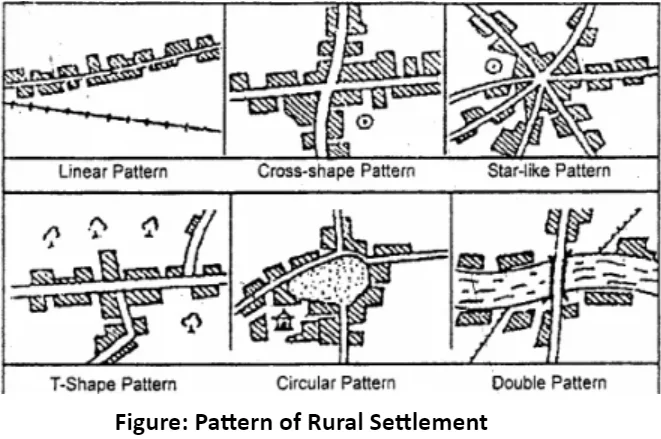
Patterns of Rural Human Settlement: Spatial Arrangements in Rural Human Settlements
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments