![]() June 4, 2024
June 4, 2024
![]() 1228
1228
![]() 0
0
The study of inheritance represents a cornerstone in biological sciences, delving into the mechanisms underlying the transmission of traits across generations. From the seminal work of Mendel to contemporary breakthroughs in molecular genetics, our comprehension of inheritance has undergone significant evolution.
In 1900, three Scientists (de Vries, Correns and von Tschermak) independently rediscovered Mendel’s results on the inheritance of characters.
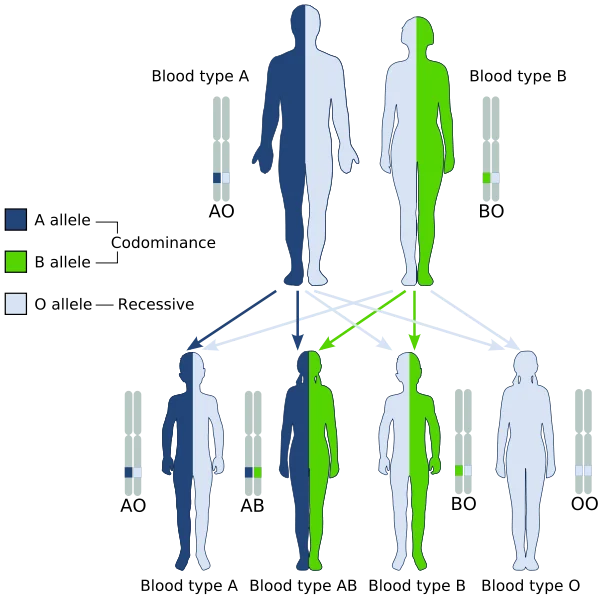
Role of DNA: DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the central information storage system of most animals and plants, and even some viruses.
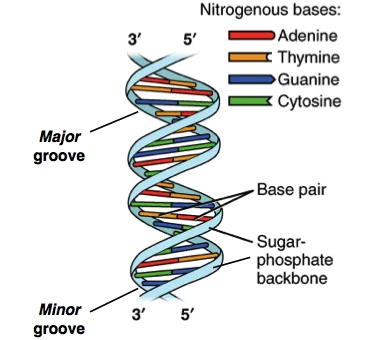
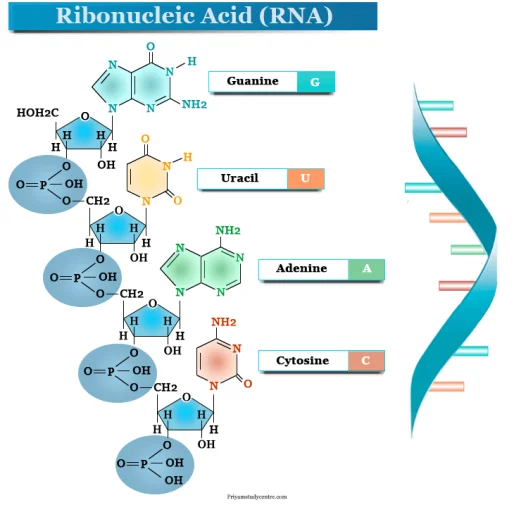
Why is DNA widely acceptable as a better Genetic material?
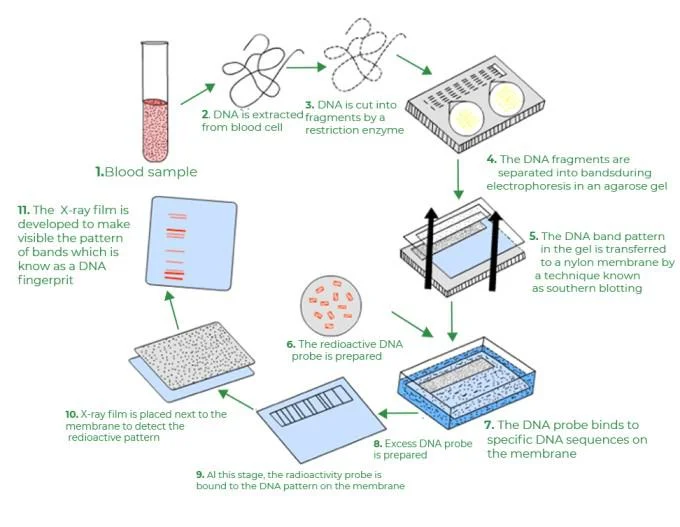
About: DNA profiling is the process where a specific DNA pattern, called a profile, is obtained from a person or sample of bodily tissue.
Short segment of DNA, usually one to six or more base pairs in length, that is repeated multiple times in succession at a particular genomic location.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
When traits are passed down through generations, researchers have uncovered a solid framework by studying chromosomes. The ongoing discoveries in molecular genetics have improved our understanding of Inheritance, highlighting DNA’s pivotal role as the keeper of genetic data, supported by RNA’s diverse functions.
| Related Articles | |
| Evolution Of Earth: Cosmic Origins and Geology | Recombinant DNA: Definition, Application, Tools & Process |
| Y Chromosome | Genetic Engineering: Definition, Process, Tools & Mechanism |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments