![]() June 17, 2024
June 17, 2024
![]() 1393
1393
![]() 0
0
The Sun, a massive ball of electrically charged gas, plays a crucial role in various celestial phenomena through its strong magnetic field and dynamic solar cycle. Understanding the solar cycle, sunspots, and their impact on Earth helps us grasp the intricacies of solar activity. Additionally, phenomena like the Geotail, pulsars, and solar eclipses provide fascinating insights into the interactions between celestial bodies and the Sun.
Sun Cycle: The Sun’s magnetic field turns every 11 years.
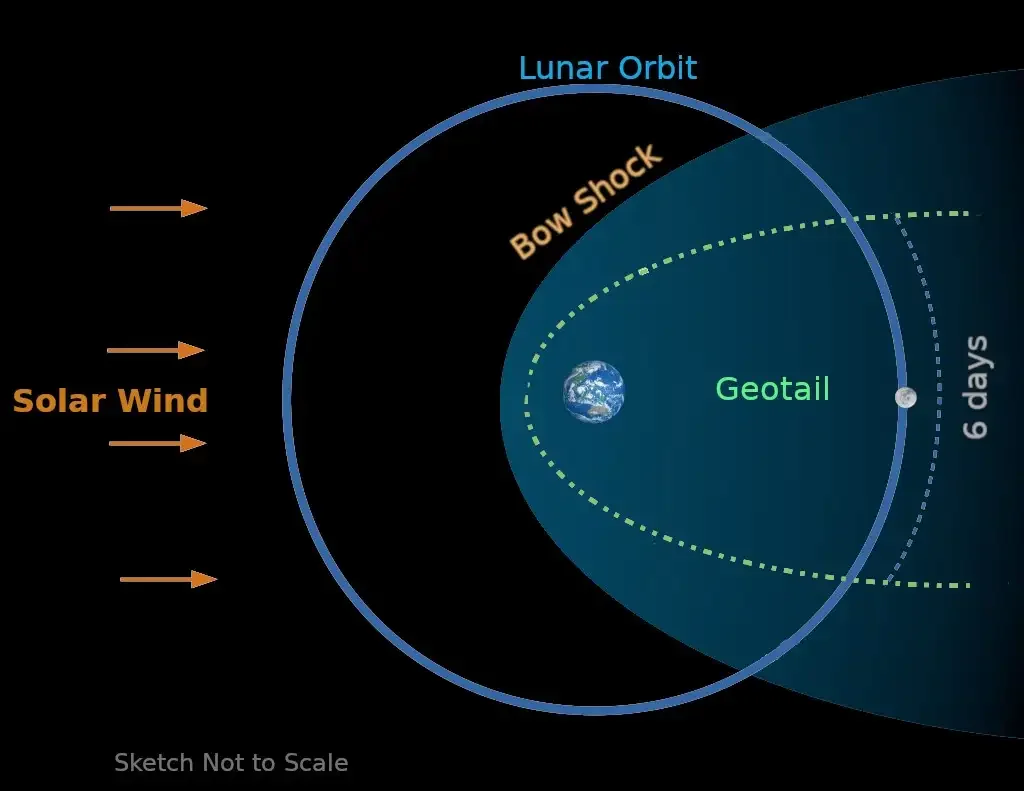
GEOTAIL
Meaning: A location in space where the finest observations may be made. The zone exists as a result of the Sun’s and Earth’s interactions.
PULSARS [UPSC 2023]
|

| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Solar phenomena and celestial events, from the solar cycle and sunspots to Geotails and solar eclipses, reveal the complex and dynamic nature of our universe.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments