![]() March 26, 2024
March 26, 2024
![]() 15703
15703
![]() 0
0
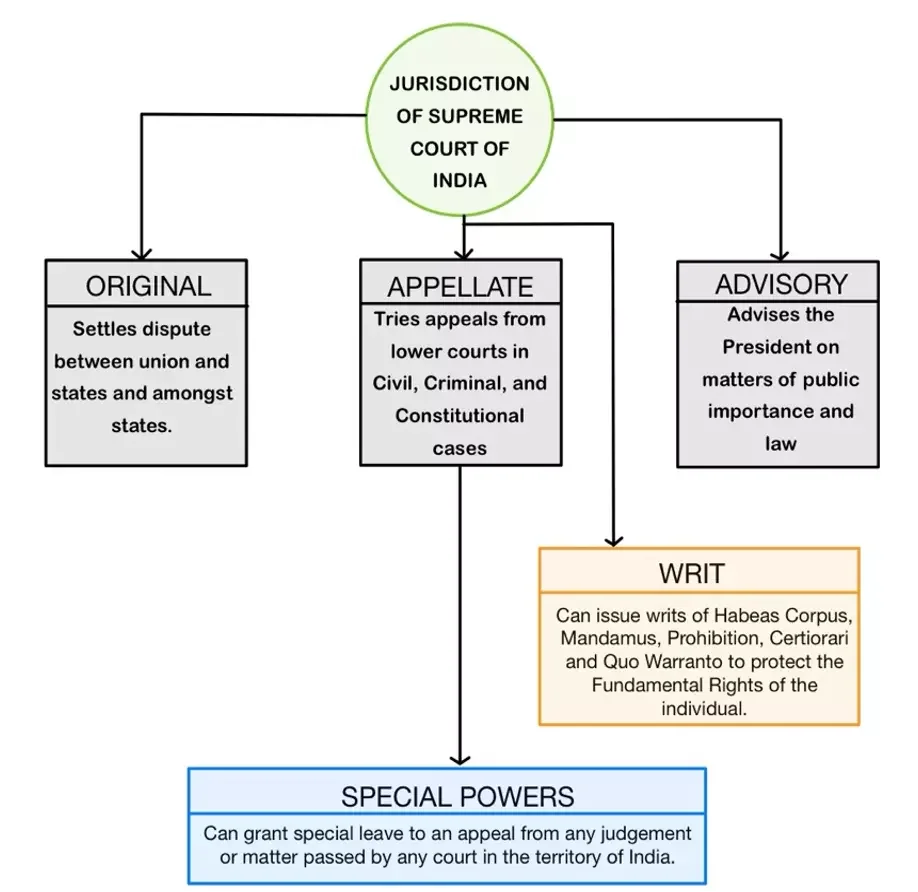
The jurisdiction and powers of the Supreme Court of India enshrined in the Constitution, outline the types of cases the Supreme Court can hear, the decisions it can render, and the extent of its authority over lower courts and government entities.
Understanding the jurisdiction and powers of the Supreme Court is fundamental to comprehending its role as the highest judicial body in India and its impact on the administration of justice and protection of constitutional rights.

Supreme Court Appeal by Special Leave: Article 136
Advisory Jurisdiction of Supreme Court: Article 143
Supreme Court as a Court of Record: Article 129
The Supreme Court possesses two powers as a court of record,
Court of Record:
Contempt of Court
Judicial Review
Interpretation of Constitution (Article 147)
Other Powers of SC
Other Important Articles
Conclusion
The jurisdiction and powers vested in the Supreme Court of India under the Constitution establish its authority as the highest judicial body in the country. With the ability to interpret and enforce fundamental rights, adjudicate disputes between states and the Centre, and issue writs for the protection of citizens’ rights, the Supreme Court plays a pivotal role in upholding the rule of law and safeguarding the principles of justice and equality in India.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments