![]() April 29, 2024
April 29, 2024
![]() 4202
4202
![]() 0
0
They are strong low-pressure center’s that originate over oceans in tropical areas and move over to the coastal areas bringing about large-scale destruction due to violent winds, heavy rainfall (torrential rainfall) and storm surges. They originate in tropical regions and move towards coastlines, causing widespread damage and posing significant threats to communities in their path. With characteristics like a calm eye surrounded by a wall of strong winds, they are known by different names in different regions, such as cyclones, hurricanes, typhoons, and willy-willies.
Below are the characteristics of Tropical Cyclone:
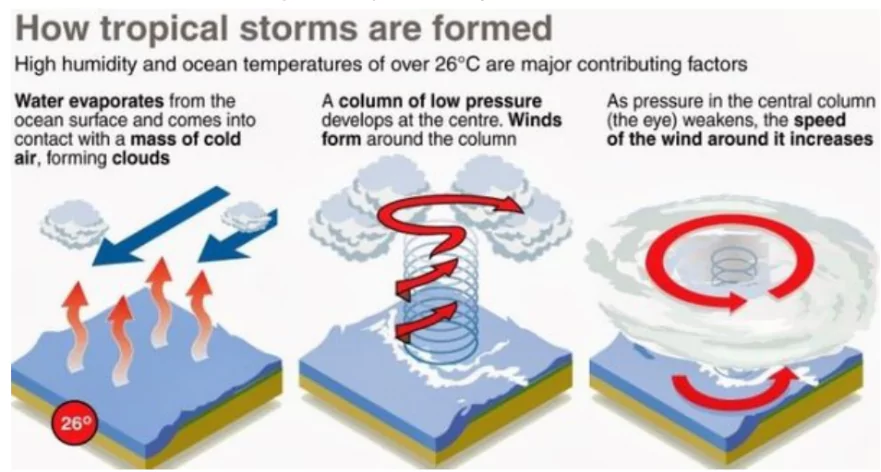
 A roughly circular calm area of comparatively light winds and fair weather at the centre.
A roughly circular calm area of comparatively light winds and fair weather at the centre.
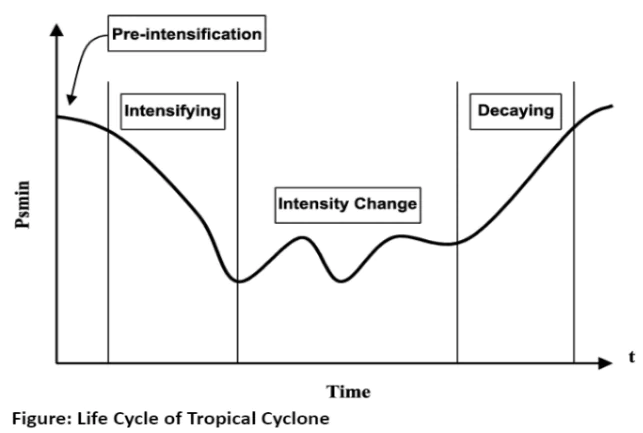 Intensification Stage: During this phase, the central pressure of the cyclone drops, and the maximum surface wind speed increases.
Intensification Stage: During this phase, the central pressure of the cyclone drops, and the maximum surface wind speed increases. 
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments