![]() April 29, 2024
April 29, 2024
![]() 67
67
![]() 0
0
The Tropical Monsoon climate, predominant in regions like the Indian subcontinent and parts of Southeast Asia, showcases a unique seasonal reversal of winds, impacting temperature variations and precipitation patterns. Characterized by distinct seasons and heavy rainfall during the monsoon period, it supports diverse vegetation and sustains agricultural practices crucial for local economies.
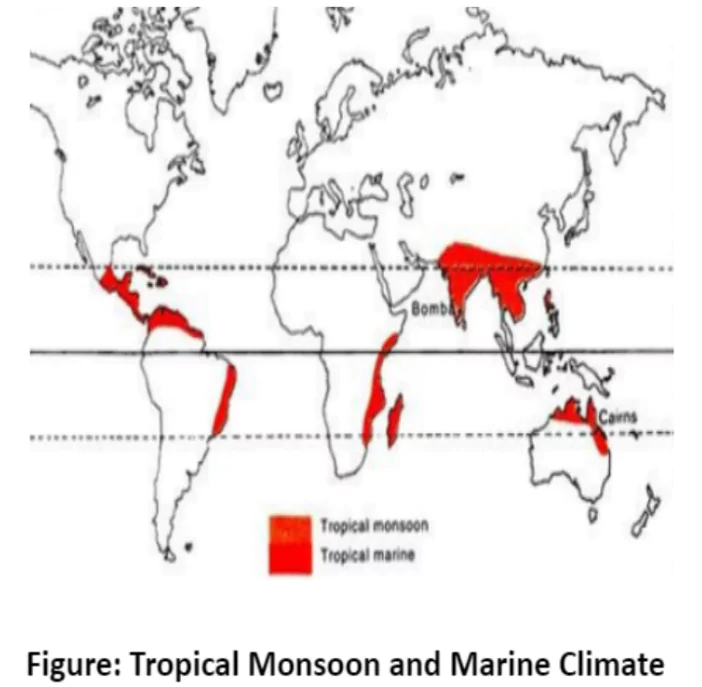 The Monsoon Phenomenon: The region witnesses complete seasonal reversal of winds.
The Monsoon Phenomenon: The region witnesses complete seasonal reversal of winds.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
The Tropical Monsoon climate, found in regions like the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, is characterized by seasonal winds, heavy rainfall, and distinct temperature changes. This climate sustains diverse vegetation, from lush forests to dry scrublands, supporting livelihoods through farming and grazing. Similarly, the Tropical Marine climate along eastern coasts experiences year-round influence from trade winds, fostering rich rainforests and coastal vegetation despite the threat of tropical cyclones.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>

Latest Comments