Rocks are natural aggregates of minerals, formed through geological processes over millions of years. Unlike minerals, rocks do not have a definite chemical composition and can vary widely in color, hardness, and texture. Petrology, the science of rocks, focuses on studying their composition, texture, and formation processes.
Three Types of Rocks
Primary rocks are classified into three main types: Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic.
Igneous Rocks:
- solidified from magma and lava.
- Examples: Granite, gabbro, pegmatite, basalt, volcanic breccia and tuff.
- Very Large Grain: If molten material is cooled slowly at great depths (intrusive igneous rocks), mineral grains may be very large (Granite).
- Small Grain: Sudden Cooling at the surface (extrusive igneous rocks) results in small grains (Basalt).
- Intermediate Sizes of Grains: Intermediate conditions of cooling would result in intermediate sizes of grains.
- Features of Igneous Rocks:
- They are hard, granular and crystalline.
- Do not contain fossils.
- Do not allow water to percolate through them.
- Less affected by chemical weathering.
- No layers like sedimentary rocks.
Classification based on Location of Magma Solidification
- Intrusive Igneous Rocks: It is formed by the solidification of magma below the Earth’s surface. Examples:
- Granite: batholith generally; Felsic.
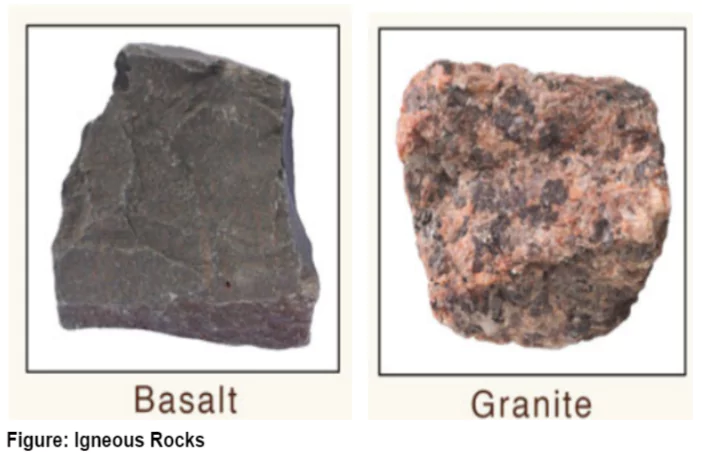 Gabbro: Mafic igneous rocks equivalent to extrusive basalt.
Gabbro: Mafic igneous rocks equivalent to extrusive basalt.- Pegmatite & Diorite
- Extrusive Igneous Rocks:
- If the magma reaches the surface and emerges as lava, it forms extrusive igneous rock.
- Examples: Basalt, Andesite, Rhyolite.
- Classification based on Chemical composition
- Those with a high proportion of silica are known as acidic rocks.
- Those with a high proportion of basic oxides are denser and darker in appearance are known as basic rocks.
- Felsic Rocks and Mafic Rocks:
- Felsic Rocks: These rocks are rich in silicon, oxygen, aluminium, sodium, and potassium.
- Mafic Rocks: rich in magnesium and iron.
- Ultramafic: Highly dominated by magnesium and Iron.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Sedimentary Rocks:
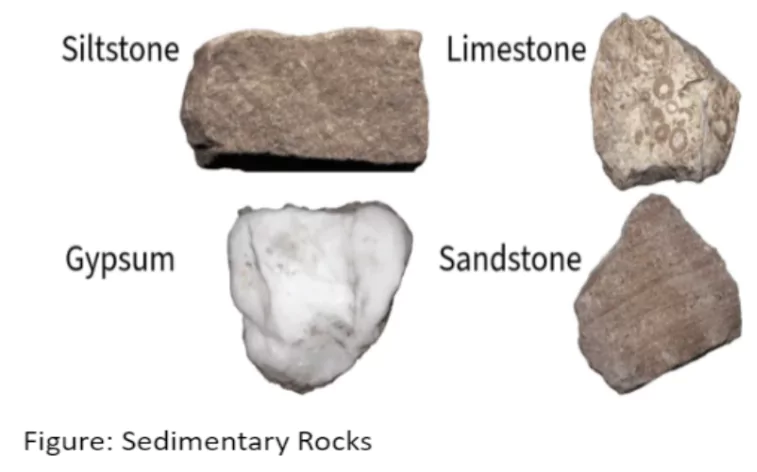

Result of deposition of fragments of rocks by exogenous processes. These deposits through compaction turn into rocks and this process is called Lithification.
- Mechanically Formed: Sandstone, conglomerate, shale, and, loess.
- Organically Formed: geyserite, chalk, limestone, and coal.
- Chemically Formed: dolomite, rock salt, chert, halite, and potash.
- Features of Sedimentary Rocks:
-
- Consist of layers and contain fossils
- Most of the sedimentary rocks are permeable and porous
Metamorphic Rocks
Formed out of existing rocks that undergo recrystallisation.

- Metamorphic rocks are classified into two major groups — foliated rocks and nonfoliated rocks.
- Example: Gneiss, slate, schist, marble, quartzite etc.
- Foliated Metamorphic Rocks: such as gneiss, phyllite, schist and slate which have a layered or banded appearance that is produced by exposure to heat and directed pressure.
- Non-foliated Metamorphic Rocks: such as marble and quartzite which do not have a layered or banded appearance.
Rock Cycle
- The rock cycle is a continuous process where old rocks transform into new ones over time.
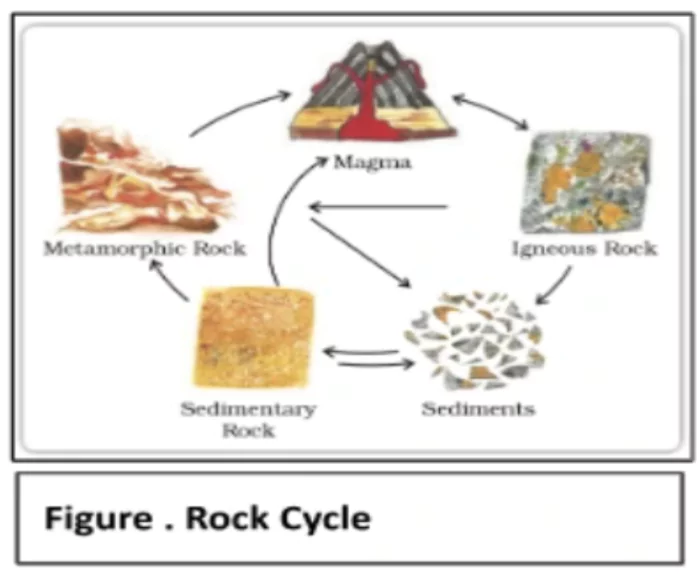 Igneous rocks are the starting point in the rock cycle, and other types of rocks are formed from them.
Igneous rocks are the starting point in the rock cycle, and other types of rocks are formed from them.- Igneous rocks can change into either sedimentary or metamorphic rocks.
- Formation of Sedimentary Rocks: Fragments from igneous and metamorphic rocks can come together to form sedimentary rocks.
- Formation of Metamorphic Rocks: Both sedimentary and igneous rocks have the potential to undergo metamorphism and become metamorphic rocks.
- Formation of Igneous Rocks: Crustal rocks, including igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary types, may be pulled down into the Earth’s mantle through a process called subduction.
- These rocks melt and transform into molten magma, which serves as the source for igneous rocks.
Conclusion
Rocks are natural formations shaped by geological processes over time, categorized into three main types: Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic. Each type has distinct characteristics and formation processes, providing insights into Earth’s history and landscapes. Understanding rocks is essential for various fields, from construction to archaeology, as it helps unravel Earth’s past and present conditions.
 Gabbro: Mafic igneous rocks equivalent to extrusive basalt.
Gabbro: Mafic igneous rocks equivalent to extrusive basalt.

 Igneous rocks are the starting point in the rock cycle, and other types of rocks are formed from them.
Igneous rocks are the starting point in the rock cycle, and other types of rocks are formed from them.