![]() May 4, 2024
May 4, 2024
![]() 3638
3638
![]() 0
0
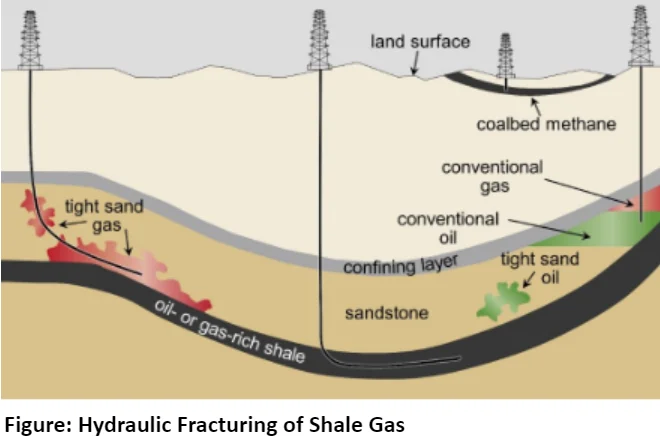
With conventional hydrocarbons facing depletion, unconventional sources have gained prominence, necessitating advanced extraction technologies. These unconventional hydrocarbons, like shale gas and coalbed methane, are trapped in low-permeability formations, demanding specialized recovery methods. India, endowed with substantial reserves, particularly in shale gas and coal bed methane, stands poised to harness these resources to meet its energy needs.
| Shale gas is the natural gas that is trapped within shale formations; Distribution: Cambay Basin, Cauvery Basin, Krishna-Godavari Basin, Assam – Arakan; Gondwana basin (including Damodar). [UPSC 2016] |
| Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) (MMDR) Act, 1957, State Governments have the power to frame rules to grant mining leases of minor minerals. State government also has the power to frame rules to prevent illegal mining of minor minerals. [UPSC 2019] |
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
Unconventional hydrocarbons like shale gas and coalbed methane are vital energy sources as conventional hydrocarbons deplete. India has significant potential in these resources, particularly in shale gas and coalbed methane, found across various basins. Shale gas extraction requires hydraulic fracturing, while coalbed methane is extracted through specialized recovery methods. Gas hydrates, though in the research phase, also hold potential as future energy sources.
| Related Articles | |
| Conventional Sources of Energy in India | Hydrocarbons: Formation, Forms, Uses, and Exploration |
| NITI AAYOG | Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments