Animals in the subphylum Vertebrata have a true vertebral column and internal skeleton, enabling diverse muscle attachment points for movement.
Key Characteristics of Vertebrates
-
- Notochord: Present during the embryonic stage, replaced by a cartilaginous or bony vertebral column in adults.
- Chordates vs. Vertebrates: All vertebrates are chordates, but not all chordates are vertebrates.
-
- Ventral muscular heart with two, three, or four chambers.
- Kidneys for excretion and osmoregulation.
- Paired appendages (fins or limbs).
- Body Structure: Bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomic, and segmented with complex tissue and organ differentiation.
Classification of Vertebrata
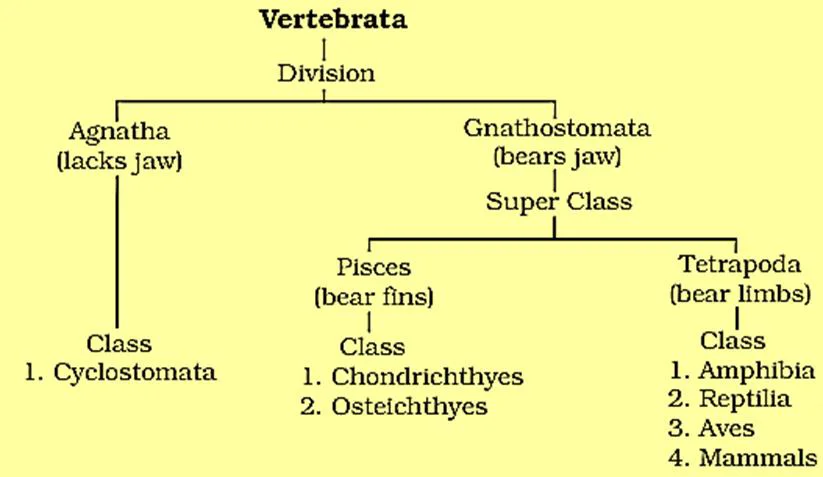
Class- Cyclostomata
- About: Members of the class Cyclostomata are known to be ectoparasites on some fishes.
- Features: Cyclostomes have a sucking and circular mouth without jaws.
- Their body is devoid of scales and paired fins.
- Cranium and vertebral columns are cartilaginous.
- Example: Petromyzon (Lamprey) and Myxine (Hagfish).
Class- Chondrichthyes
- About: They are marine animals with streamlined bodies and have cartilaginous endoskeleton.
- Features: Notochord is persistent throughout life.
- The skin is tough, containing minute placoid scales.
- Heart is two-chambered (one auricle and one ventricle).
- Example: Scoliodon (Dogfish), Pristis (Sawfish).
Class- Osteichthyes
-
- About: It includes both marine and freshwater fishes with bony endoskeleton.
- Heart is two-chambered (one auricle and one ventricle).
- They are cold-blooded animals.
-
- Marine– Exocoetus (Flying fish), Hippocampus (Sea horse).
- Freshwater– Labeo (Rohu), Catla (Katla).
Class- Amphibia
- About: Amphibians can live in aquatic as well as terrestrial habitats.
- Features: Most of them have two pairs of limbs.
- The body is divisible into the head and trunk.
- The eyes have eyelids.
- Respiration is by gills, lungs and through the skin.
- The heart is three-chambered (two auricles and one ventricle).
- These are cold-blooded animals.
- Example: Bufo (Toad), Rana (Frog), Hyla (Tree frog)
Class- Reptilia
- About: The class name refers to their creeping or crawling mode of locomotion (Latin- repere or reptum– to creep or crawl).
- Features:They are mostly terrestrial animals, and their body is covered by dry and cornified skin, epidermal scales or scutes.
- They do not have external ear openings.
- The tympanum represents the ear.
- Heart is usually three-chambered but four-chambered in crocodiles.
- Example: Chelone (Turtle), Testudo (Tortoise), Chameleon (Tree lizard).
- Poisonous snakes- Naja (Cobra), Bungarus (Krait).
Class- Aves
- The characteristic features of Aves (birds) are the presence of feathers and most of them can fly except flightless birds (e.g., Ostrich).
- They possess beaks.
- The forelimbs are modified into wings.
- The hind limbs generally have scales and are modified for walking, swimming or clasping the tree branches.
- Skin is dry without glands except the oil gland at the base of the tail.
- Endoskeleton is fully ossified (bony), and the long bones are hollow with air cavities (pneumatic).
- Heart is completely four-chambered.
- They are warm-blooded (homeothermic) animals, i.e., they are able to maintain a constant body temperature.
- Example: Corvus (Crow), Columba (Pigeon), Psittacula (Parakeet), Struthio (Ostrich)
Class- Mammalia
- About: They are found in a variety of habitats – polar ice caps, deserts, mountains, forests, grasslands and dark caves.
- Features: Some of them have adapted to fly or live in water.
- The most unique mammalian characteristic is the presence of milk-producing glands (mammary glands) by which the young ones are nourished.
- External ears or pinnae are present. Different types of teeth are present in the jaw.
- Heart is four-chambered.
- Example: Oviparous–Ornithorhynchus (Platypus); Viviparous– Macropus (Kangaroo), Pteropus (Flying fox Balaenoptera (Blue whale), Panthera tigris (Tiger), Panthera leo (Lion).
| Biorock Technology: Biorock is the name given to the substance formed by the electro-accumulation of minerals dissolved in seawater on steel structures that are lowered onto the sea bed and are connected to a power source, e.g., solar panels that float on the surface. It has been used for coral restoration. [UPSC 2022] |
Conclusion
The Vertebrata subphylum showcases a remarkable array of life forms. From jawless Cyclostomata to warm-blooded, feathered Aves, each class exhibits unique adaptations for locomotion, respiration, and reproduction. This intricate classification system reflects the evolutionary journey that has resulted in the extraordinary diversity of vertebrates on Earth.

