![]() May 1, 2024
May 1, 2024
![]() 12169
12169
![]() 0
0
The Warm Temperate Eastern Margin, also known as the China Type climate, is found on the eastern edges of continents in warm temperate latitudes. It is characterized by warm, moist summers and cool, dry winters; these regions experience significant rainfall throughout the year supporting diverse economic activities such as rice cultivation, sugarcane farming, and lush vegetation.
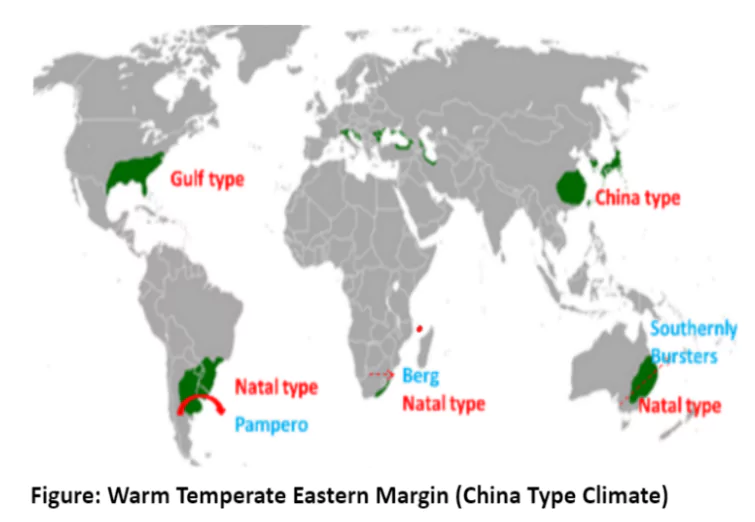 Northern Hemisphere:
Northern Hemisphere:
 Gulf Type (South Eastern USA): slight monsoonal; no distinct dry period; occurrence of hurricanes and tornadoes.
Gulf Type (South Eastern USA): slight monsoonal; no distinct dry period; occurrence of hurricanes and tornadoes.
 Tornadoes: resulting from intense local heating, can cause significant damage, especiall in the central plain.
Tornadoes: resulting from intense local heating, can cause significant damage, especiall in the central plain.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
| Related Articles | |
| TYPES OF CLIMATE | Characteristics Of Equatorial, Tropical Monsoon Regions |
| Forest In India | Hydrological Cycle: Clouds, Precipitation, and Rainfall Patterns |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments