![]() May 1, 2024
May 1, 2024
![]() 10053
10053
![]() 0
0
Ocean water is in constant motion, both horizontally and vertically, shaping our marine environment. Horizontal movements, driven by ocean currents and waves, ripple across the surface, while vertical motions, like upwelling and tides, add depth to the aquatic dance. Understanding these movements is key to unlocking the secrets of our oceans and their impact on our planet.
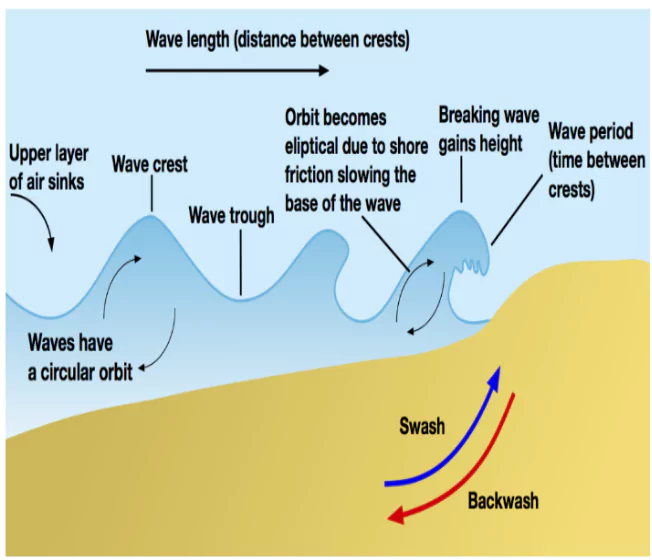 Frictional Force: Most of the waves are caused by the frictional force of the wind, which provides energy to the waves.
Frictional Force: Most of the waves are caused by the frictional force of the wind, which provides energy to the waves.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
| Related Articles | |
| ENVIRONMENT | Speed of Sound: Pitch, Amplitude, & Wavelength |
| ocean currents | IMD: Origin, Objectives, Functions, and Its Initiatives |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments